Related Research Articles

In physical geography, tundra is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sámi word тӯндар meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". There are three regions and associated types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra.

An endolith or endolithic is an organism that is able to acquire the necessary resources for growth in the inner part of a rock, mineral, coral, animal shells, or in the pores between mineral grains of a rock. Many are extremophiles, living in places long considered inhospitable to life. The distribution, biomass, and diversity of endolith microorganisms are determined by the physical and chemical properties of the rock substrate, including the mineral composition, permeability, the presence of organic compounds, the structure and distribution of pores, water retention capacity, and the pH. Normally, the endoliths colonize the areas within lithic substrates to withstand intense solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, wind, and desiccation. They are of particular interest to astrobiologists, who theorize that endolithic environments on Mars and other planets constitute potential refugia for extraterrestrial microbial communities.

The Balleny Islands are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about 160 km (99 mi) in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes into the sea. The islands were formed by the so-called Balleny hotspot.

Devon Island is an island in Canada and the largest uninhabited island in the world. It is located in Baffin Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the largest members of the Arctic Archipelago, the second-largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canada's sixth-largest island, and the 27th-largest island in the world. It has an area of 55,247 km2 (21,331 sq mi). The bedrock is Precambrian gneiss and Paleozoic siltstones and shales. The highest point is the Devon Ice Cap at 1,920 m (6,300 ft) which is part of the Arctic Cordillera. Devon Island contains several small mountain ranges, such as the Treuter Mountains, Haddington Range and the Cunningham Mountains. The notable similarity of its surface to that of Mars has attracted interest from scientists.

Somerset Island is a large, uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago, that is part of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The island is separated from Cornwallis Island and Devon Island to the north by the Parry Channel, from Baffin Island to the east by Prince Regent Inlet, from the Boothia Peninsula to the south by Bellot Strait, and from Prince of Wales Island to the west by Peel Sound. It has an area of 24,786 km2 (9,570 sq mi), making it the 46th largest island in the world and Canada's twelfth largest island.

The Queen Elizabeth Islands are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northern Canada. The Queen Elizabeth Islands contain approximately 14% of the global glacier and ice cap area.
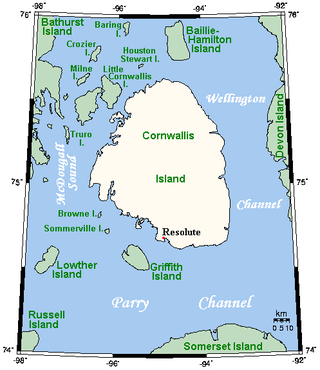
Cornwallis Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut in the Canadian Arctic. It lies to the west of Devon Island, the largest uninhabited island in the world, and at its greatest length is about 113 km (70 mi). At 6,995 km2 (2,701 sq mi) in size, it is the 96th largest island in the world, and Canada's 21st largest island. Cornwallis Island is separated by the Wellington Channel from Devon Island, and by the Parry Channel from Somerset Island to the south. Northwest of Cornwallis Island lies Little Cornwallis Island, the biggest of a group of small islands at the north end of McDougall Sound, which separates Cornwallis Island from nearby Bathurst Island.

Axel Heiberg Island is an uninhabited island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 32nd largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. According to Statistics Canada, it has an area of 43,178 km2 (16,671 sq mi). It is named after Axel Heiberg.
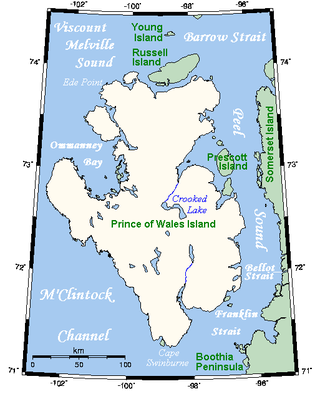
Prince of Wales Island is an Arctic island in Nunavut, Canada. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, it lies between Victoria Island and Somerset Island and is south of the Queen Elizabeth Islands.

Bathurst Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in Nunavut, Canada. It is a member of the Arctic Archipelago. The area of the island is estimated at 16,042 km2 (6,194 sq mi), 115 to 117 mi long and from 63 mi (101 km) to 72 mi (116 km) to 92.9 mi (149.5 km) wide, making it Canada's 13th largest island. It is located between Devon Island and Cornwallis Island in the east, and Melville Island in the west. Four small islands of Cameron, Vanier, Massey and Alexander lie in its northwest.
Polar ecology is the relationship between plants and animals in a polar environment. Polar environments are in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Arctic regions are in the Northern Hemisphere, and it contains land and the islands that surrounds it. Antarctica is in the Southern Hemisphere and it also contains the land mass, surrounding islands and the ocean. Polar regions also contain the subantarctic and subarctic zone which separate the polar regions from the temperate regions. Antarctica and the Arctic lie in the polar circles. The polar circles are imaginary lines shown on maps to be the areas that receives less sunlight due to less radiation. These areas either receive sunlight or shade 24 hours a day because of the earth's tilt. Plants and animals in the polar regions are able to withstand living in harsh weather conditions but are facing environmental threats that limit their survival.

The Flashline Mars Arctic Research Station (FMARS) is the first of two simulated Mars habitats located on Devon Island, Nunavut, Canada, which is owned and operated by the Mars Society. The station is a member of the European Union-INTERACT circumarctic network of currently 89 terrestrial field bases located in northern Europe, Russia, US, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, and Scotland as well as stations in northern alpine areas.

Pascal Lee is co-founder and chairman of the Mars Institute, a planetary scientist at the SETI Institute, and the Principal Investigator of the Haughton-Mars Project (HMP) at NASA Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California. He holds an ME in geology and geophysics from the University of Paris, and a PhD in astronomy and space sciences from Cornell University.
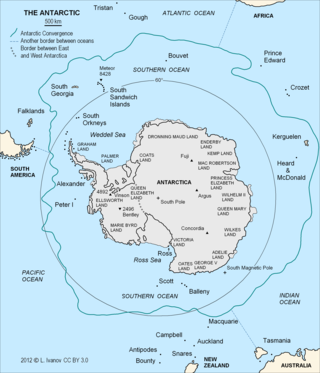
The Antarctic Convergence or Antarctic Polar Front is a marine belt encircling Antarctica, varying in latitude seasonally, where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the sub-Antarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath the warmer subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone very high in marine productivity, especially for Antarctic krill.

The sub-Antarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands in the southern parts of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans, especially those situated north of the Antarctic Convergence. Sub-Antarctic glaciers are, by definition, located on islands within the sub-Antarctic region. All glaciers located on the continent of Antarctica are by definition considered to be Antarctic glaciers.

Rhizocarpon geographicum is a species of lichen, which grows on rocks in mountainous areas of low air pollution. Each lichen is a flat patch bordered by a black line of fungal hyphae. These patches grow adjacent to each other, leading to the appearance of a map or a patchwork field.
Charles Cockell is a British astrobiologist who is professor of astrobiology in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Edinburgh and co-director of the UK Centre for Astrobiology.

Limacina helicina is a species of small swimming planktonic sea snail in the family Limacinidae, which belong to the group commonly known as sea butterflies (Thecosomata).

The wildlife of Antarctica are extremophiles, having adapted to the dryness, low temperatures, and high exposure common in Antarctica. The extreme weather of the interior contrasts to the relatively mild conditions on the Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands, which have warmer temperatures and more liquid water. Much of the ocean around the mainland is covered by sea ice. The oceans themselves are a more stable environment for life, both in the water column and on the seabed.

Loretta Hidalgo Whitesides is an American public speaker, co-creator of Yuri's Night, and an author on space exploration. She accumulated over five hours of weightless time as a Flight Director for Zero-G Corporation, and plans to travel to space as a "Founder Astronaut" on Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo with her husband George T. Whitesides.
References
- ↑ Charles S. Cockell; M. Dale Stokes (23 September 2004). "Widespread colonization by polar hypoliths". Nature. 431 (7007): 414. Bibcode:2004Natur.431..414C. doi: 10.1038/431414a . PMID 15386002.
- ↑ Charles S. Cockell; M. Dale Stokes (August 2006). "Hypolithic Colonization of Opaque Rocks in the Arctic and Antarctic Polar Desert". Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research. 38 (3): 335–342. doi:10.1657/1523-0430(2006)38[335:HCOORI]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 140167789.