
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a group of vascular plants that include the clubmosses. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldest lineages of extant (living) vascular plants; the group contains extinct plants that have been dated from the Silurian. Lycophytes were some of the dominating plant species of the Carboniferous period, and included the tree-like Lepidodendrales, some of which grew over 40 metres (130 ft) in height, although extant lycophytes are relatively small plants.

The La Brea Tar Pits is an active paleontological research site in urban Los Angeles. Hancock Park was formed around a group of tar pits where natural asphalt has seeped up from the ground for tens of thousands of years. Over many centuries, the bones of trapped animals have been preserved. The George C. Page Museum is dedicated to researching the tar pits and displaying specimens from the animals that died there. La Brea Tar Pits is a registered National Natural Landmark.

Paleobotany, also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeography), and the evolutionary history of plants, with a bearing upon the evolution of life in general. A synonym is paleophytology. It is a component of paleontology and paleobiology. The prefix palaeo- or paleo- means "ancient, old", and is derived from the Greek adjective παλαιός, palaios. Paleobotany includes the study of terrestrial plant fossils, as well as the study of prehistoric marine photoautotrophs, such as photosynthetic algae, seaweeds or kelp. A closely related field is palynology, which is the study of fossilized and extant spores and pollen.

The New Zealand merganser, also known as Auckland merganser or Auckland Islands merganser, was a typical merganser which is now extinct.

The Stenopodidea or boxer shrimps are a small group of decapod crustaceans. Often confused with Caridea shrimp or Dendrobranchiata prawns, they are neither, belonging to their own group.

Dryosaurus is a genus of an ornithopod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period. It was an iguanodont. Fossils have been found in the western United States and were first discovered in the late 19th century. Valdosaurus canaliculatus and Dysalotosaurus lettowvorbecki were both formerly considered to represent species of Dryosaurus.

Pteridospermatophyta, also called "pteridosperms" or "seed ferns" are a polyphyletic grouping of extinct seed-producing plants. The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type are the lyginopterids of late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though Komlopteris seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania.
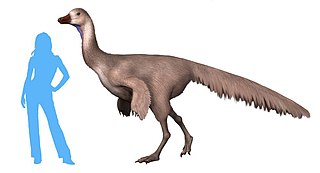
Arkansaurus is an extinct genus of ornithomimosaurian theropod dinosaur. It lived during the Albian and Aptian stages of the Early Cretaceous. The type and only species is Arkansaurus fridayi.

A compression fossil is a fossil preserved in sedimentary rock that has undergone physical compression. While it is uncommon to find animals preserved as good compression fossils, it is very common to find plants preserved this way. The reason for this is that physical compression of the rock often leads to distortion of the fossil.

Fossil wood, also known as fossilized tree, is wood that is preserved in the fossil record. Over time the wood will usually be the part of a plant that is best preserved. Fossil wood may or may not be petrified, in which case it is known as petrified wood or petrified tree. The study of fossil wood is sometimes called palaeoxylology, with a "palaeoxylologist" somebody who studies fossil wood.

The cladoxylopsids are an extinct group of plants related to ferns and sphenopsids.

Polysporangiophytes, also called polysporangiates or formally Polysporangiophyta, are plants in which the spore-bearing generation (sporophyte) has branching stems (axes) that bear sporangia. The name literally means 'many sporangia plant'. The clade includes all land plants (embryophytes) except for the bryophytes whose sporophytes are normally unbranched, even if a few exceptional cases occur. While the definition is independent of the presence of vascular tissue, all living polysporangiophytes also have vascular tissue, i.e., are vascular plants or tracheophytes. Extinct polysporangiophytes are known that have no vascular tissue and so are not tracheophytes.

The Baltic region is home to the largest known deposit of amber, called Baltic amber or succinite. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that these forests created more than 100,000 tons of amber. Today, more than 90% of the world's amber comes from Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. It is a major source of income for the region; the local Kaliningrad Amber Combine extracted 250 tonnes of it in 2014 and 400 tonnes in 2015.

Ginkgo is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and Ginkgo is now the only living genus within the order. The rate of evolution within the genus has been slow, and almost all its species had become extinct by the end of the Pliocene. The sole surviving species, Ginkgo biloba, is found in the wild only in China, but is cultivated around the world. The relationships between ginkgos and other groups of plants are not fully resolved.

Fungi diverged from other life around 1.5 billion years ago, with the glomaleans branching from the "higher fungi" (dikaryans) at ~570 million years ago, according to DNA analysis. Fungi probably colonized the land during the Cambrian, over 500 million years ago,, and possibly 635 million years ago during the Ediacaran, but terrestrial fossils only become uncontroversial and common during the Devonian, 400 million years ago.

The Elisha Taylor House is a historic private house located at 59 Alfred Street in Midtown Detroit, Michigan, within the Brush Park district. The house was designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1973 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. Since 1981, it has served as a center for art and architectural study, known as the Art House.

A seed plant or spermatophyte, also known as a phanerogam or a phaenogam, is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte that includes most of the familiar land plants, including the flowering plants and the gymnosperms, but not ferns, mosses, or algae.

Pseudobornia is a genus of plants known only from fossils found from the Upper Devonian. It contains a single species Pseudobornia ursina, and is the earliest fossil assigned with certainty to the Equisetopsida.

Sphenophyllales is an extinct order of articulate land plants and a sister group to the present-day Equisetales (horsetails). They are fossils dating from the Devonian to the Triassic. They were common during the Late Pennsylvanian to Early Permian, with most of the fossils coming from the Carboniferous period.
Iridopteridales is an order of the extinct cladoxylopsids. It contains the genus Ibyka which is a possible ancestor of the horsetails.


















