Related Research Articles
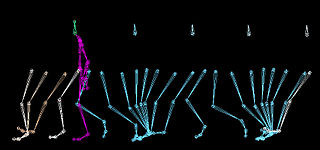
Walking is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an "inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step. This applies regardless of the usable number of limbs—even arthropods, with six, eight, or more limbs, walk. In humans, walking has health benefits including improved mental health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and death.

A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically. Pedestrians may also be wheelchair users or other disabled people who use mobility aids.

Bicycle-friendly policies and practices help some people feel more comfortable about traveling by bicycle with other traffic. The level of bicycle-friendliness of an environment can be influenced by many factors including town planning and cycling infrastructure decisions. A stigma towards people who ride bicycles and fear of cycling is a social construct that needs to be fully understood when promoting a bicycle friendly culture.
Street reclaiming is the process of converting, or otherwise returning streets to a stronger focus on non-car use — such as walking, cycling and active street life. It is advocated by many urban planners and urban economists, of widely varying political points of view. Its primary benefits are thought to be:

Utility cycling encompasses any cycling done simply as a means of transport rather than as a sport or leisure activity. It is the original and most common type of cycling in the world. Cycling mobility is one of the various types of private transport and a major part of individual mobility.

Pedestrian zones are areas of a city or town restricted to use by people on foot or human-powered transport such as bicycles, with non-emergency motor traffic not allowed. Converting a street or an area to pedestrian-only use is called pedestrianisation.

The car-free movement is a social movement centering the belief that large and/or high-speed motorized vehicles are too dominant in modern life, particularly in urban areas such as cities and suburbs. It is a broad, informal, emergent network of individuals and organizations, including social activists, urban planners, transportation engineers, environmentalists and others. The goal of the movement is to establish places where motorized vehicle use is greatly reduced or eliminated, by converting road and parking space to other public uses and rebuilding compact urban environments where most destinations are within easy reach by other means, including walking, cycling, public transport, personal transporters, and mobility as a service.

Sustainable transport refers to ways of transportation that are sustainable in terms of their social and environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used for road, water or air transport; the source of energy; and the infrastructure used to accommodate the transport. Transport operations and logistics as well as transit-oriented development are also involved in evaluation. Transportation sustainability is largely being measured by transportation system effectiveness and efficiency as well as the environmental and climate impacts of the system. Transport systems have significant impacts on the environment, accounting for between 20% and 25% of world energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. The majority of the emissions, almost 97%, came from direct burning of fossil fuels. In 2019, about 95% of the fuel came from fossil sources. The main source of greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union is transportation. In 2019 it contributes to about 31% of global emissions and 24% of emissions in the EU. In addition, up to the COVID-19 pandemic, emissions have only increased in this one sector. Greenhouse gas emissions from transport are increasing at a faster rate than any other energy using sector. Road transport is also a major contributor to local air pollution and smog.

A living street is a street designed with the interests of pedestrians and cyclists in mind by providing enriching and experiential spaces. Living streets also act as social spaces, allowing children to play and encouraging social interactions on a human scale, safely and legally. Living streets consider all pedestrians granting equal access to elders and those who are disabled. These roads are still available for use by motor vehicles; however, their design aims to reduce both the speed and dominance of motorized transport. The reduction of motor vehicle dominance creates more opportunities for public transportation.

Cycling advocacy consists of activities that call for, promote or enable increased adoption and support for cycling and improved safety and convenience for cyclists, usually within urbanized areas or semi-urban regions. Issues of concern typically include policy, administrative and legal changes ; advocating and establishing better cycling infrastructure ; public education regarding the health, transportational and environmental benefits of cycling for both individuals and communities, cycling and motoring skills; and increasing public and political support for bicycling.

A carfree city is an urban area absent of motor vehicles. Carfree cities rely on public transport, walking, and cycling for travel, as opposed to motor vehicles. Districts where motor vehicles are prohibited are referred to as carfree zones. Carfree city models have gained traction in the second half of the 20th century due to issues with congestion and infrastructure, and proposed environmental and quality of life benefits. Many cities in Asia, Europe, and Africa have carfree areas due to the cities being created before the invention of motor vehicles, while many developing cities in Asia are using the carfree model to modernize their infrastructure.

In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel.
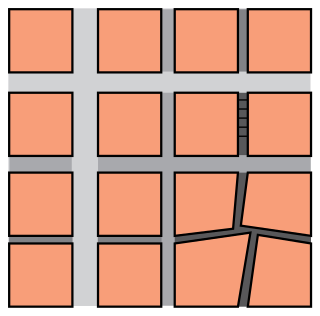
In urban design, permeability and connectivity are terms that describe the extent to which urban forms permit movement of people or vehicles in different directions. The terms are often used interchangeably, although differentiated definitions also exist. Permeability is generally considered a positive attribute of an urban design, as it permits ease of movement and avoids severing neighbourhoods. Urban forms which lack permeability, e.g. those severed by arterial roads, or with many long culs-de-sac, are considered to discourage movement on foot and encourage longer journeys by car. There is some empirical research evidence to support this view.

A pedestrian village is a compact, pedestrian-oriented neighborhood or town with a mixed-use village center. Shared-use lanes for pedestrians and those using bicycles, Segways, wheelchairs, and other small rolling conveyances that do not use internal combustion engines. Generally, these lanes are in front of the houses and businesses, and streets for motor vehicles are always at the rear. Some pedestrian villages might be nearly car-free with cars either hidden below the buildings, or on the boundary of the village. Venice, Italy is essentially a pedestrian village with canals. Other examples of a pedestrian village include Giethoorn village located in the Dutch province of Overijssel, Netherlands, Mont-Tremblant Pedestrian Village located beside Mont-Tremblant, Quebec, Canada, and Culdesac Tempe in Tempe, Arizona.
Montreal has a developed transport infrastructure network, which includes well-developed air, road, rail, and maritime links to the rest of Canada, as well as the United States and the rest of the world. Local public transport includes a metro system, buses, ferry services and cycling infrastructure.
Living Streets Aotearoa Inc. is the New Zealand organisation for people on foot, promoting walking-friendly communities. Living Streets Aotearoa is the national walking advocacy group with the vision of "more people choosing to walk more often."

Active mobility, soft mobility, active travel, active transport or active transportation is the transport of people or goods, through non-motorized means, based around human physical activity. The best-known forms of active mobility are walking and cycling, though other modes include running, rowing, skateboarding, kick scooters and roller skates. Due to its prevalence, cycling is sometimes considered separately from the other forms of active mobility.

A walking city or walkable city is a type of city that is created to avoid internal transportation, and therefore be small enough that a person can use walking to navigate the city. It is characterized by narrow, often winding streets. Its transport system is inherently egalitarian, with no one being disadvantaged by a lack of transport, unlike modern automotive cities. Walkability within areas positively impacts equity, sustainability, health, social benefits, less demand on other modes, economic development, and enjoyment.

The 15-minute city is an urban planning concept in which most daily necessities and services, such as work, shopping, education, healthcare, and leisure can be easily reached by a 15-minute walk, bike ride, or public transit ride from any point in the city. This approach aims to reduce car dependency, promote healthy and sustainable living, and improve wellbeing and quality of life for city dwellers.
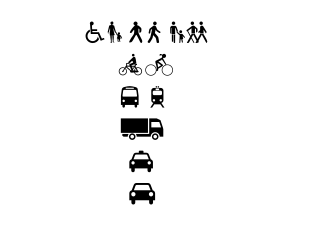
The green transport hierarchy (Canada), street user hierarchy (US), sustainable transport hierarchy (Wales), urban transport hierarchy or road user hierarchy is a hierarchy of modes of passenger transport prioritising green transport. It is a concept used in transport reform groups worldwide and in policy design. In 2020, the UK government consulted about adding to the Highway Code a road user hierarchy prioritising pedestrians. It is a key characteristic of Australian transport planning.
References
- ↑ "Home - International Federation of Pedestrians".
- ↑ Laker, Laura (2017-09-12). "Where is the world's most walkable city?". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2017-10-08.
- ↑ "Do Pedestrians Have Any Rights? Here's What Every Indian Must Know!". The Better India. 2017-05-12. Retrieved 2017-10-08.
- ↑ "United Nations Civil Society Participation – Advanced Search".