
Rambutan is a medium-sized tropical tree in the family Sapindaceae. The name also refers to the edible fruit produced by this tree. The rambutan is native to Southeast Asia. It is closely related to several other edible tropical fruits, including the lychee, longan, pulasan, and quenepa.

A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.

The Sapindaceae are a family of flowering plants in the order Sapindales known as the soapberry family. It contains 138 genera and 1,858 accepted species. Examples include horse chestnut, maples, ackee and lychee.

An aril, also called an arillus, is a specialized outgrowth from a seed that partly or completely covers the seed. An arillode or false aril is sometimes distinguished: whereas an aril grows from the attachment point of the seed to the ovary, an arillode forms from a different point on the seed coat. The term "aril" is sometimes applied to any fleshy appendage of the seed in flowering plants, such as the mace of the nutmeg seed. Arils and arillodes are often edible enticements that encourage animals to transport the seed, thereby assisting in seed dispersal. Pseudarils are aril-like structures commonly found on the pyrenes of Burseraceae species that develop from the mesocarp of the ovary. The fleshy, edible pericarp splits neatly in two halves, then falling away or being eaten to reveal a brightly coloured pseudaril around the black seed.

The cherimoya, also spelled chirimoya and called chirimuya by the Quechua people, is a species of edible fruit-bearing plant in the genus Annona, from the family Annonaceae, which includes the closely related sweetsop and soursop. The plant has long been believed to be native to Ecuador and Peru, with cultivation practised in the Andes and Central America, although a recent hypothesis postulates Central America as the origin instead, because many of the plant's wild relatives occur in this area.

Passiflora incarnata, commonly known as maypop, purple passionflower, true passionflower, wild apricot, and wild passion vine, is a fast-growing perennial vine with climbing or trailing stems. A member of the passionflower genus Passiflora, the maypop has large, intricate flowers with prominent styles and stamens. One of the hardiest species of passionflower, it is both found as a wildflower in the southern United States and in cultivation for its fruit and striking bluish purple blooms.

Passiflora tarminiana is a species of passionfruit. The yellow fruits are edible and their resemblance to small, straight bananas has given it the name banana passionfruit in some countries. It is native to the uplands of tropical South America and is now cultivated in many countries. In Hawaii and New Zealand it is now considered an invasive species. It was given the name banana passionfruit in New Zealand, where passionfruit are also prevalent. In Hawaii, it is called banana poka. In its Latin American homeland, it is known as curuba, curuba de Castilla, or curuba sabanera blanca (Colombia); taxo, tacso, tagso, tauso (Ecuador); parcha, taxo (Venezuela), tumbo or curuba (Bolivia); tacso, tumbo, tumbo del norte, trompos, tintin, porocsho or purpur (Peru).

Paeonia brownii is a low to medium height, herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Paeoniaceae. It has compound, steely-gray, somewhat fleshy leaves and small drooping maroon flowers. Its vernacular name is Brown's peony, native peony or western peony. It is native to the western United States and usually grows at altitude, often as undergrowth in part-shade. The fleshy roots store food to carry the plant through the dry summers and produce new leaves and flowers the following spring.

A flower, also known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants. Flowers consist of a combination of vegetative organs – sepals that enclose and protect the developing flower. Petals attract pollinators, and reproductive organs that produce gametophytes, which in flowering plants produce gametes. The male gametophytes, which produce sperm, are enclosed within pollen grains produced in the anthers. The female gametophytes are contained within the ovules produced in the ovary. In some plants, multiple flowers occur singly on a pedicel, and some are arranged in a group (inflorescence) on a peduncle.
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.

Chamaecrista fasciculata, the partridge pea, is a species of legume native to most of the eastern United States. It is an annual which grows to approximately 0.5 meters tall. It has bright yellow flowers from early summer until first frost, with flowers through the entire flowering season if rainfall is sufficient.

Cuttsia viburnea is a shrub or bushy tree which has toothed leaves and panicles of white flowers, and that is endemic to eastern Australia. It is sometimes called silver-leaved cuttsia, and confusingly also native elderberry, honey bush or native hydrangea. C. viburnea is the only species assigned to the genus Cuttsia.

Carpodetus serratus is an evergreen tree with small ovate or round, mottled leaves with a toothy margin, and young twigs grow zig-zag, and fragrant white flowers in 5 cm panicles and later black chewy berries. It is an endemic of New Zealand. Its most common name is putaputāwētā which means many wētā emerge - referring to the nocturnal Orthoptera that live in holes in the trunk of this tree made by Pūriri moth caterpillars. Regional variations on the name also refer to this insect that lives and feeds on it such as kaiwētā, and punawētā. The tree is also sometimes called marbleleaf. It is found in broadleaf forest in both North, South and Stewart Islands. It flowers between November and March, and fruits are ripe from January to February.

Strasburgeriaceae is a small family of flowering plants in the order Crossosomatales, only found in New Zealand and New Caledonia. It contains two genera, Strasburgeria and Ixerba. Both genera have simple, evergreen, alternated leaves, often in worl-like clusters, with gland-tipped serrations, hermaphroditic, pentamerous flowers with persistent sepals, clawed petals, flat and long filaments that extend beyond the petals and a persistent style with a punctiform stigma.
Borthwickia is genus of flowering plants, containing one species, Borthwickia trifoliata from Yunnan, China and Myanmar. The common name in Chinese is 节蒴木. It is a shrub or small tree with evergreen trifoliate leaves, whitish flowers clustered at the tip of the branches, with many stamens, and thin, knobbly, drooping fruits with many small red seeds.
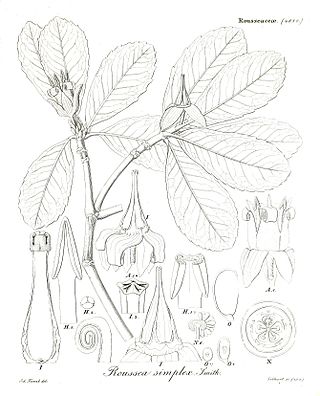
Roussea simplex is a woody climber of 4–6 m high, that is endemic to the mountain forest of Mauritius. It is the only species of the genus Roussea, which is assigned to the family Rousseaceae. It has opposing, entire, obovate, green leaves, with modest teeth towards the tip and mostly pentamerous, drooping flowers with yellowish recurved tepals, and a purse-shaped orange corolla with strongly recurved narrowly triangular lobes.

Brexia is a plant genus assigned to the Celastraceae. It is a dense evergreen shrub or small tree of usually around 5 m high, with alternately set, simple, leathery leaves with a short leaf stem and lanceolate to inverted egg-shaped leaf blades. The pentamerous flowers occur in cymes. The petals are greenish white, the stamens are alternating with wide, incised staminodes. The superior ovary develops in a long-ribbed fruit. Brexia naturally grows on the coast of East Africa, on Madagascar, the Comoros and Seychelles. Opinions differ about the number of species in Brexia. Sometimes the genus is regarded monotypic, B. madagascariensis being a species with a large variability, but other authors distinguish as many as twelve species. Common names for B. madagascariensis include jobiapototra, tsimiranjana, tsivavena, vahilava, voalava, voankatanana, voantalanina, voatalanina and votalanina, and mfukufuku (Swahili), mfurugudu and bwa kato (Seychelles).

Strasburgeria robusta is an evergreen tree with large toothed leaves and large but rather inconspicuous, single, pendulant flowers in a gloomy colorscheme of yellowish with brown markings, with about ten sepals, five petals, ten stamens, a very distinct circular nectar gland with radiating spikes and rather large globular fruits with a long persistent style, with a scent reminiscent of apples, which is endemic to New Caledonia. It is the only recognized species of the genus Strasburgeria.

Serruria fasciflora or common pin spiderhead is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae. It is a sprawling to upright shrublet of 40 cm to 1 m high and about 1⁄2 m wide. It has finely divided, upward curving leaves with thread-thin segments and clusters of sweetly scented heads, each consisting of five to seven silvery pink flowers, that may be found year-round, but mostly from May to December. It is a rather widespread and common species, that is restricted to the south of the Western Cape province of South Africa.

Leucospermum formosum is a large upright shrub of up to 3 m (9.8 ft) high, from the family Proteaceae. It grows from a single trunk and its branches are greyish felty. The softly felty leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic, 6+1⁄2–10 cm (2.6–3.9 in) long and 14–20 mm (0.55–0.79 in) wide. The flower heads are flattened and about 15 cm (5.9 in) across, and consist of bright yellow flowers from which long, styles emerge which are strongly clockwise bent just below the white, later pink thickened tip. From above, the heads look like turning wheels. It is called silver-leaf wheel-pincushion in English. It flowers during September and October. It is an endemic species of the Western Cape province of South Africa.



















