Related Research Articles
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication and the temporomandibular joints. The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life; this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.

Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of large blood vessels. Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth. Complications can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, as well as aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm. GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. It can be confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery in about 90% of people.

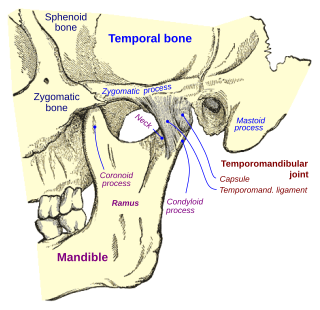
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the condylar process of mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. The joints are unique in their bilateral function, being connected via the mandible.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.

Trismus is a condition of restricted opening of the mouth. The term was initially used in the setting of tetanus. Trismus may be caused by spasm of the muscles of mastication or a variety of other causes. Temporary trismus occurs much more frequently than permanent trismus. It is known to interfere with eating, speaking, and maintaining proper oral hygiene. This interference, specifically with an inability to swallow properly, results in an increased risk of aspiration. In some instances, trismus presents with altered facial appearance. The condition may be distressing and painful. Examination and treatments requiring access to the oral cavity can be limited, or in some cases impossible, due to the nature of the condition itself.

Takayasu's arteritis (TA), also known as aortic arch syndrome, nonspecific aortoarteritis, and pulseless disease, is a form of large vessel granulomatous vasculitis with massive intimal fibrosis and vascular narrowing, most commonly affecting young or middle-aged women of Asian descent, though anyone can be affected. It mainly affects the aorta and its branches, as well as the pulmonary arteries. Females are about 8–9 times more likely to be affected than males.

Arteritis is a vascular disorder characterized by inflammation of the walls of arteries, usually as a result of infection or autoimmune responses. Arteritis, a complex disorder, is still not entirely understood. Arteritis may be distinguished by its different types, based on the organ systems affected by the disease. A complication of arteritis is thrombosis, which can be fatal. Arteritis and phlebitis are forms of vasculitis.
Claudication is a medical term usually referring to impairment in walking, or pain, discomfort, numbness, or tiredness in the legs that occurs during walking or standing and is relieved by rest. The perceived level of pain from claudication can be mild to extremely severe. Claudication is most common in the calves but it can also affect the feet, thighs, hips, buttocks, or arms. The word claudication comes from Latin claudicare 'to limp'.

Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a syndrome experienced as pain or stiffness, usually in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and hips, but which may occur all over the body. The pain can be sudden or can occur gradually over a period. Most people with PMR wake up in the morning with pain in their muscles; however, cases have occurred in which the person has developed the pain during the evenings or has pain and stiffness all day long.

Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt.

A giant cell is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells, often forming a granuloma.
Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy is the cause of vision loss that occurs in temporal arteritis. Temporal arteritis is an inflammatory disease of medium-sized blood vessels that happens especially with advancing age. AAION occurs in about 15-20 percent of patients with temporal arteritis. Damage to the blood vessels supplying the optic nerves leads to insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the nerve and subsequent optic nerve fiber death. Most cases of AAION result in nearly complete vision loss first to one eye. If the temporal arteritis is left untreated, the fellow eye will likely suffer vision loss as well within 1–2 weeks. Arteritic AION falls under the general category of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, which also includes non-arteritic AION. AION is considered an eye emergency, immediate treatment is essential to rescue remaining vision.
Aortitis is the inflammation of the aortic wall. The disorder is potentially life-threatening and rare. It is reported that there are only 1–3 new cases of aortitis per year per million people in the United States and Europe. Aortitis is most common in people 10 to 40 years of age.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.

Necrotizing vasculitis, also called systemic necrotizing vasculitis, is a general term for the inflammation of veins and arteries that develops into necrosis and narrows the vessels.

Dislocations occur when two bones that originally met at the joint detach. Dislocations should not be confused with subluxation. Subluxation is when the joint is still partially attached to the bone.

Condylar resorption, also called idiopathic condylar resorption, ICR, and condylysis, is a temporomandibular joint disorder in which one or both of the mandibular condyles are broken down in a bone resorption process. This disorder is nine times more likely to be present in females than males, and is more common among teenagers.
Dentomandibular sensorimotor dysfunction (DMSD) is a medical condition involving the mandible, upper three cervical (neck) vertebrae, and the surrounding muscle and nerve areas.

Orofacial pain (OFP) is a general term covering any pain which is felt in the mouth, jaws and the face. Orofacial pain is a common symptom, and there are many causes.
Acute visual loss is a rapid loss of the ability to see. It is caused by many ocular conditions like retinal detachment, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and giant cell arteritis, etc.
References
- ↑ Jaw claudication is the only clinical predictor of giant-cell arteritis. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology, 29 (3): 264-269. Hitoshi Sato, Mariko Inoue, Wataru Muraoka, Takaaki Kamatani, Seiji Asoda, Hiromasa Kawana, Taneaki Nakagawa, Koichi Wajima. (May 2017) doi : 10.1016/j.ajoms.2016.12.002
- ↑ Stone, John H. (2009). A Clinician's Pearls & Myths in Rheumatology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 287. ISBN 9781848009349 . Retrieved 11 November 2017.
- ↑ Goodman BW, Jr; Shepard, FA (February 1983). "Jaw claudication. Its value as a diagnostic clue". Postgraduate Medicine. 73 (2): 177–83. doi:10.1080/00325481.1983.11697764. PMID 6823455.