
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage.
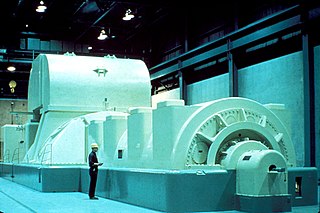
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power into electrical power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.

Kangaroo Island, also known as Karta, is Australia's third-largest island, after Tasmania and Melville Island. It lies in the state of South Australia 112 km (70 mi) southwest of Adelaide. Its closest point to the mainland is Snapper Point in Backstairs Passage, which is 13.5 km (8.4 mi) from the Fleurieu Peninsula.

A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity. As of 2014, the International Atomic Energy Agency reported there were 450 nuclear power reactors in operation in 31 countries.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.
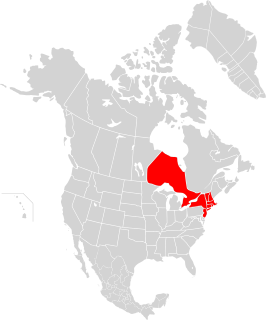
The northeast blackout of 1965 was a significant disruption in the supply of electricity on Tuesday, November 9, 1965, affecting parts of Ontario in Canada and Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, and Vermont in the United States. Over 30 million people and 80,000 square miles (207,000 km2) were left without electricity for up to 13 hours.

Lake Karapiro is an artificial reservoir lake on the Waikato River, 30 kilometres (19 mi) south-east of the city of Hamilton in New Zealand's North Island. The lake was formed in 1947 by damming the Waikato River to store water for the 96-megawatt Karapiro hydroelectric power station.

A thermal power station is a power station in which heat energy is converted to electric power. In most, a steam-driven turbine converts heat to mechanical power as an intermediate to electrical power. Water is heated, turns into steam and drives a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine the steam is condensed in a condenser and recycled to where it was heated. This is known as a Rankine cycle. The greatest variation in the design of thermal power stations is due to the different heat sources: fossil fuel, nuclear energy, solar energy, biofuels, and waste incineration are all used. Certain thermal power stations are also designed to produce heat for industrial purposes, for district heating, or desalination of water, in addition to generating electrical power.

A diesel generator (DG) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine-generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel, but some types are adapted for other liquid fuels or natural gas.
The Shoalhaven Scheme is a dual-purpose water supply and Pumped-storage Hydroelectricity scheme located on the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Murray Region Hydroelectric Power Stations refers to two of the original seven hydroelectric power stations, both located near the town of Khancoban in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The two power stations are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro. Although both power stations are physically located in New South Wales, since 1 July 2008 all power generated has been allocated to the Victorian region of the National Electricity Market. The stations are not located on the Murray River.

A black start is the process of restoring an electric power station or a part of an electric grid to operation without relying on the external electric power transmission network to recover from a total or partial shutdown.
The electricity sector in New Zealand uses mainly renewable energy sources such as hydropower, geothermal power and increasingly wind energy. 82% of energy for electricity generation is from renewable sources, making New Zealand one of the lowest carbon dioxide emitting countries in terms of electricity generation. Electricity demand has grown by an average of 2.1% per year from 1974 to 2010 but decreased by 1.2% from 2010 to 2013.

Power and Water Corporation is a Northern Territory Government owned corporation in the Northern Territory. Power and Water is the Northern Territory's premier provider of electricity, water and sewerage services. The Power and Water Corporation was formed on 1 July 2002, taking over from the former government utility Power and Water Authority. Power and Water became the first Government – owned corporation in the Northern Territory. The corporation has more than 142,120 customers.

The Karapiro Power Station is a hydroelectric power station on Waikato River, in the North Island of New Zealand. The power station lies on Lake Karapiro, a major rowing regatta venue. Karapiro is 30 kilometres (19 mi) upstream from the city of Hamilton and is the last of the eight hydroelectric power stations on the Waikato River.
The Jersey Electricity Company or Jersey Electricity is a public limited company, and the sole provider for electricity in Jersey. The JEC has two sites around the island, Queens Road, St Helier, the site of 2 Rolls Royce Olympus gas turbines and La Collette Power Station where there are 4 Sulzer Diesels, 1 Rolls Royce Olympus, and 3 Parsons steam turbines.
The South Australian blackout of 2016 was a widespread power outage in South Australia that occurred as a result of storm damage to electricity transmission infrastructure on 28 September 2016. The cascading failure of the electricity transmission network resulted in almost the entire state losing its electricity supply, affecting 850,000 SA customers. Kangaroo Island did not lose its supply, as the Kangaroo Island power station had been built to supply the island for the contingency of a failure in the power cable under the Backstairs Passage.

Zanzibar Electricity Corporation (ZECO) is a state owned utility firm that provides transmission and distribution service of electricity in the Zanzibar Archipelago. The firm was incorporated in 2006 as the successor of the State Fuel and Power Corporation and is wholly owned by the Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar.














