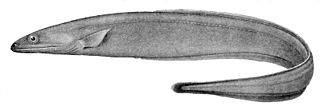
The grey cutthroat eel, Synaphobranchus affinis, is a cutthroat eel. It was originally described by Albert Günther in 1877. It lives a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope and global deep waters including near Portugal, Canary Islands, Morocco, Japan, Australia, and others. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which has been found at depths ranging from 300 to 2300 meters and at temperatures ranging from 3.3 - 11.3 °C. Males can grow to a length of up to 110 centimeters. It is primarily a scavenger, however it also actively hunts small fish and crustaceans.
Arrowtooth eel may refer to several species of cutthroat eels:

Synaphobranchus is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family, Synaphobranchidae. It currently contains the following species:
Gnathophis capensis, the Southern Atlantic conger or southern conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Leptocephalus. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including from False Bay to Plettenberg Bay, South Africa and also on Tristan da Cunha Island. It is known to dwell at a depth of 100 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 37 cm.
The Pacific worm eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1883. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, Colombia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, Guatemala, Panama, Nicaragua, and Peru. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 12 metres, and inhabits sand and mud sediments. Unlike many species of eel, it does not form burrows. Males can reach a maximum total length of 46 centimetres.
The snaggle-toothed snake-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and David Ross Robertson in 2001. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from a single specimen collected from Panama, in the eastern central Pacific Ocean. From the specimen it is known to dwell at a depth range of 5–10 metres, and reach a maximum total length of 104 centimetres. Based on other eel species it is estimated to inhabit burrows on a permanent or semi-permanent basis, and feed on small fish and crustaceans.
Apterichtus kendalli, the Western Atlantic finless eel or finless eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1891. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including North Carolina, USA; the western Bahamas, Venezuela, and St. Helena Island. It dwells at a depth range of 3 to 400 metres, and forms burrows in sandy sediments on the continental shelf. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres (24 in).
The smiling snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882, originally under the genus Apterichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Panama, Ecuador, and Mexico. It dwells at a maximum depth of 30 metres (98 ft), and inhabits sediments of sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 41 centimetres (16 in).
The Oriental worm-eel, also known as the Oriental snake eel, the Oriental sand-eel or the finny sand-eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John McClelland in 1844, originally under the genus Dalophis. It is a tropical, marine and freshwater-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific, including Somalia, South Africa, India, Papua New Guinea, Tahiti, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Oman, Palau, New Caledonia, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Seychelles, and Vanuatu. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 3 metres, and forms burrows in sand and mud sediments in estuaries, rivers, and inshore turbid waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36 centimetres (14 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 25 centimetres (9.8 in).
The Sailfin eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Raymond Carroll Osburn and John Treadwell Nichols in 1916, originally under the genus Letharchus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Mexico, and Panama. It is known to dwell at a depth of 35 metres (115 ft), and inhabits rock and sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 81 centimetres (32 in).

The highfin snake eel (Ophichthus altipennis, also known as the blackfin snake eel or the black-finned snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Microdonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the eastern Indian Ocean and northwestern and western central Pacific Ocean, including Australia, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Japan, the Marshall Islands, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 40 m, and forms burrows in soft inshore sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 103 cm.

The punctuated snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1837, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Nicaragua, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Peru, and Panama. It dwells at a depth range of 15 to 277 metres, and inhabits sand and mud sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 85 centimetres (33 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 60 centimetres (24 in).

The Pacific snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Muraenopsis. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, Peru, the Gulf of California, Mexico, the Galapagos Islands, Colombia, Ecuador, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Honduras, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Panama. It dwells at a maximum depth of 155 metres (509 ft), and forms burrows in mud and sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 115 centimetres (45 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 80 centimetres (31 in).

The Marble-toothed snake-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1898. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Colombia, Panama and Ecuador. It dwells in shallow waters at a maximum depth of 10 metres (33 ft), and inhabits sand and mud sediments and mangroves. Males can reach a maximum total length of 68 centimetres (27 in).
The smallfish snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, the Gulf of California and Costa Rica. It dwells in shallow waters at a maximum depth of 20 metres (66 ft), and inhabits sand and rock sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 70 centimetres (28 in).

The short-tooth sawpalate is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Johannes Schmidt in 1916 in its larval form, originally under the genus Leptocephalus, and later as a subspecies of Serrivomer sector by Roule & Bertin in 1929. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern central and western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Strait of Gibraltar, Cape Verde, the United States, the Bahamas and Bermuda, as well as the Strait of Gibraltar, Cape Verde, Canada and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 150 to 6,000 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 65 centimetres (26 in).
Atractodenchelys phrix, known under the common name "arrowtooth eel" is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1970. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from its type locality in the eastern Caribbean, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 385–425 metres.

Dysomma anguillare, the shortbelly eel, stout moray, mustard eel or arrowtooth eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Keppel Harcourt Barnard in 1923. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean and Indo-Western Pacific, including the United States, Venezuela, South Africa, Zanzibar, and Japan. It lives at a depth range of 30 to 270 metres, and inhabits muddy sediments in coastal waters and large rivermouths. Males can reach a maximum total length of 52 centimetres (20 in).
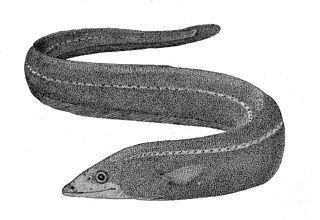
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).
Synaphobranchus oregoni is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Peter Henry John Castle in 1960. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Bahamas, Trinidad and Tobago, Mexico, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 512 to 1,900 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).









