
Wangdue Phodrang District is a dzongkhag (district) of central Bhutan. This is also the name of the dzong which dominates the district, and the name of the small market town outside the gates of the dzong. The name is said to have been given by the Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal who was searching for the best location for a dzong to prevent incursions from the south. The word "wangdue" means unification of Country, and "Phodrang" means Palace in Dzongkha.

Bhutan comprises twenty districts.

Lhuntse District is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. It consists of 2506 households. Located in the northeast, Lhuntse is one of the least developed dzhongkhags of Bhutan. There are few roads, the first gas station was opened in September 2005, electricity is not well distributed, and the difficult terrain makes distribution of social welfare problematic. Despite its favourable climate, farming is hindered by the lack of infrastructure.
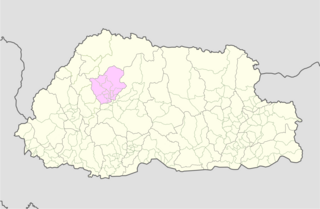
Punakha District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Thimphu, Gasa, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts. The dominant language in the district is Dzongkha, the national language.
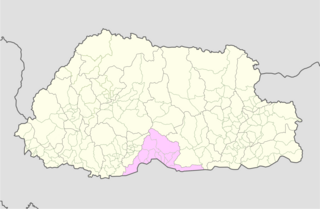
Sarpang District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan.

Trashiyangtse District is one of the twenty dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It was created in 1992 when Trashiyangtse district was split off from Trashigang District. Trashiyangtse covers an area of 1,437.9 square kilometres (555.2 sq mi). At an elevation of 1750-1880 m, Trashi yangtse dzongkhag is rich of culture filled with sacred places blessed by Guru Rimpoche and dwelled by Yangtseps, Tshanglas, Bramis from Tawang, Khengpas from Zhemgang and Kurtoeps from Lhuentse.
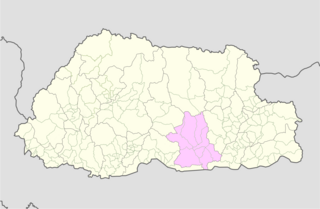
Zhemgang District, is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Sarpang, Trongsa, Bumthang, Mongar and Samdrup Jongkhar Districts, and borders Assam in India to the south. Administrative center of the district is Zhemgang.

A dzongkhag is an administrative and judicial district of Bhutan. The twenty dzongkhags of Bhutan are further divided into 205 gewogs. Some larger dzongkhags have one or more of an intermediate judicial division, known as dungkhags (sub-districts), which themselves comprise two or more gewogs. The Parliament of Bhutan passed legislation in 2002 and 2007 on the status, structure, and leadership of local governments, including dzongkhags. Its most recent legislation regarding dzongkhags is the Local Government Act of 2009. A dzongkhag is headed by a dzongdag, who is an elected official.

A gewog, in the past also spelled as geog, refers to a group of villages in Bhutan. The head of a gewog is called a gup. Gewogs form a geographic administrative unit below dzongkhag districts, and above Dzongkhag Thromde class B and Yenlag Thromde municipalities. Dzongkhag Thromde class A municipalities have their own independent local government body.

Chiwogs of Bhutan or chios refer to the 1044 basic electoral precincts of Bhutan. Chiwogs are also former third-level administrative divisions of Bhutan below geos. Until 2009, they were the equivalent of municipalities or parishes, containing clusters of villages and hamlets. There are generally 5 or 6 chios in each geo, and in turn several geos in each dzongkha (district). To illustrate, there are 50 chios in Paro District alone. The majority of chios are small rural communities; more densely populated areas tend to be separate thromdes, or municipalities. A Chiwog Disaster Management Plan (CDMP) exists in some chios to form an effective responsive to any local disasters. Often, participants in the CDMP are also trained at a geo level for better coordination.

Sephu Gewog (Dzongkha: སྲས་ཕུག་, also transliterated as Saephoog Gewog is a gewog of Wangdue Phodrang District, Bhutan.

Dragteng Gewog is a gewog of Trongsa District, Bhutan.

Langthil Gewog is a gewog of Trongsa District, Bhutan.

Nubi Gewog is a gewog of Trongsa District, Bhutan.

Tangsibji Gewog is a gewog of Trongsa District, Bhutan.
Kangpar Gewog is a gewog of Trashigang District, Bhutan. Kangpara Gewog, along with Thrimshing Gewog, comprises Thrimshing Dungkhag (sub-district). Kangpara is one of the remotest gewogs under Trashigang Dzongkhag(district). The gewog is 341.9 square kilometers and shares borders with other gewogs like Gomdar, Thrimshing, Shongphu, Khaling, Shingkhar Lauri and Merak. Kangpara is popular for housing some sacred monasteries like Lamai Goenpa, Sikhar Goenpa et al., and is also popular for their belief in deities like Ama Jomo and Meme Dangling.

A thromde is a second-level administrative division in Bhutan. The legal administrative status of thromdes was most recently codified under the Local Government Act of 2009, and the role of thromdes in elections in Bhutan was defined in the Election Act of 2008
Nyenkha is an East Bodish language spoken by about 10,000 people in the eastern, northern, and western areas of the Black Mountains. Speakers live primarily between the Tang Chuu to the east and Mangde Chhu to the west, from the town of Trongsa in Trongsa District; along Black River passes in the Trongsa District villages of Taktse and Usar; to in Ridha and Tashiding villages, and Phobji, Dangchu, and Sephu Gewogs and surrounding villages in southeast Wangdue Phodrang District.











