
Wangdue Phodrang District is a Thromde and dzongkhag (district) of central Bhutan. This is also the name of the dzong which dominates the district. The name is said to have been given by the Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal who was searching for the best location for a dzong to prevent incursions from the south. The word "wangdue" means unification of Country, and "Phodrang" means Palace in Dzongkha.

Haa District is one of the 20 dzongkhag or districts comprising Bhutan. An alternative name for the district is "Hidden-Land Rice Valley." It the second least-populated dzongkhag in the country after Gasa.

Trashigang District is Bhutan's easternmost dzongkhag (district).

Paro District is a district (dzongkhag), valley, river and town in Bhutan. It is one of the most historic valleys in Bhutan. Both trade goods and invading Tibetans came over the pass at the head of the valley, giving Paro the closest cultural connection with Tibet of any Bhutanese district. The dominant language in Paro is Dzongkha, the national language.

Gasa District or Gasa Dzongkhag is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. The capital of Gasa District is Gasa Dzong near Gasa. It is located in the far north of the county and spans the Middle and High regions of the Tibetan Himalayas. The dominant language of the district is Dzongkha, which is the national language. Related languages, Layakha and Lunanakha, are spoken by semi-nomadic communities in the north of the district. The People's Republic of China claims the northern part of Gasa District.

Lhuntse District is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. It consists of 2506 households. Located in the northeast, Lhuentse is one of the least developed dzhongkhags of Bhutan. There are few roads, the first gas station was opened in September 2005, electricity is not well distributed, and the difficult terrain makes distribution of social welfare problematic. Despite its favorable climate, farming is hindered by the lack of infrastructure.

Mongar District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. Mongar is the fastest-developing dzongkhag in eastern Bhutan. A regional hospital has been constructed and the region is bustling with many economic activities. Mongar is noted for its lemon grass, a plant that can be used to produce an essential oil. It also has a hydroelectric power-plant on the Kuri Chhu river. Mongar is notable for having the longest work time in all the dzongkhags of Bhutan.

PemagatshelDistrict is one of the 20 Dzongkhags (districts) in Bhutan.
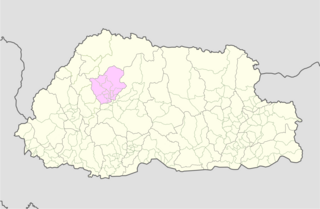
Punakha District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Thimphu, Gasa, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts. The dominant language in the district is Dzongkha, the national language.

Samtse District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It comprises two subdistricts (dungkhags): Tashicholing and Dophuchen. They are further subdivided into 15 gewogs. The Samtse district covers a total area of 1304 km2.

Tsirang District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) of Bhutan. The administrative center of the district is Damphu.
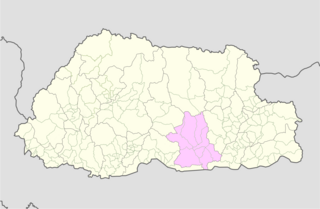
Zhemgang District, is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Sarpang, Trongsa, Bumthang, Mongar and Pemagatshel Districts, and borders Assam in India to the south. The administrative center of the district is Zhemgang.
Lunana is a remote village in Gasa District in northwestern Bhutan. It is the capital of Lunana Gewog, which had a 2014 population of 810.

The Jigme Dorji National Park (JDNP), named after the late Jigme Dorji Wangchuck, is the second-largest National Park of Bhutan.
Bji Gewog is a gewog of Haa District, Bhutan. It is the northernmost gewog of the Haa District, bordering China's Chumbi Valley. The gewog has mostly mountainous terrain, with rivers flowing into Amo Chu in the west and the Ha Chu in the east. China claims a large part of the gewog as its territory and has recently started building roads and villages in the border areas.
Laya Gewog is a gewog of Gasa District, Bhutan. The capital of gewog is the town Laya.

Merag Gewog is a gewog of Trashigang District, Bhutan. Merak and Sakten Gewogs comprise Sakten Dungkhag (sub-district).

Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park covers an area of 1,730 square kilometres (670 sq mi) in central Bhutan. It protects a large area of the Black Mountains, a sub−range of the Himalayan Range System.
The Lunana language, Lunanakha is a Tibetic language spoken in Bhutan by some 700 people in 1998. Most are yak-herding pastoralists. Lunana is a variety of Dzongkha, the national language of Bhutan.

The lakes of Bhutan comprise its glacial lakes and its natural mountain lakes. Bhutanese territory contains some 2,674 high altitude glacial lakes and subsidiary lakes, out of which 25 pose a risk of GLOFs. There are also more than 59 natural non-glacial lakes in Bhutan, covering about 4,250 hectares (16.4 sq mi). Most are located above an altitude of 3,500 metres (11,500 ft), and most have no permanent human settlements nearby, though many are used for grazing yaks and may have scattered temporary settlements.















