
The Quadi were a Germanic people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its border on the River Danube just to the south of the Quadi. They associated the Quadi with their neighbours the Marcomanni, and described both groups as having entered the region after the Celtic Boii had left it deserted. The Quadi may later have contributed to the "Suebian" group who crossed the Rhine with the Vandals and Alans in the 406 Crossing of the Rhine, and later founded a kingdom in northwestern Iberia.

Legio III Italica was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 165 AD by the emperor Marcus Aurelius for his campaign against the Marcomanni tribe. The cognomen Italica suggests that the legion's original recruits were drawn for the defence of Italy. The legion was still active in Raetia and other provinces in the early 5th century.
The equites constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an eques.

The Vangiones appear first in history as an ancient Germanic tribe of unknown provenance. They threw in their lot with Ariovistus in his bid of 58 BC to invade Gaul through the Doubs river valley and lost to Julius Caesar in a battle probably near Belfort. After some Celts evacuated the region in fear of the Suebi, the Vangiones, who had made a Roman peace, were allowed to settle among the Mediomatrici in northern Alsace.. They gradually assumed control of the Celtic city of Burbetomagus, later Worms.
Auxilia palatina were infantry units of the Late Roman army, first raised by Constantine I as part of the new field army he created in about 325 AD.

The Marcomannic Wars were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against principally the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts with several other Germanic, Sarmatian and Gothic peoples along both sides of the whole length of the Roman Empire's northeastern European border, the river Danube.

The auxilia were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 27 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of infantry as the legions and, in addition, provided almost all of the Roman army's cavalry and more specialised troops. The auxilia thus represented three-fifths of Rome's regular land forces at that time. Like their legionary counterparts, auxiliary recruits were mostly volunteers, not conscripts.

The Scholae Palatinae were an elite military imperial guard unit, usually ascribed to the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great as a replacement for the equites singulares Augusti, the cavalry arm of the Praetorian Guard. The Scholae survived in Roman and later Byzantine service until they disappeared from the historical record in the late 11th century, during the reign of Alexios I Komnenos.

The Taifals or Tayfals were a people group of Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fragmented history, for the most part in association with various Gothic peoples, and alternately fighting against or for the Romans. In the late fourth century some Taifali were settled within the Roman Empire, notably in western Gaul in the modern province of Poitou. They subsequently supplied mounted units to the Roman army and continued to be a significant source of cavalry for early Merovingian armies. By the sixth century their region of western Gaul had acquired a distinct identity as Thifalia.
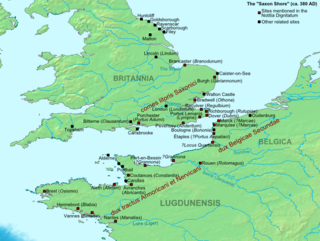
The Saxon Shore was a military command of the Late Roman Empire, consisting of a series of fortifications on both sides of the Channel. It was established in the late 3rd century and was led by the "Count of the Saxon Shore". In the late 4th century, his functions were limited to Britain, while the fortifications in Gaul were established as separate commands. Several well-preserved Saxon Shore forts survive in east and south-east England.

In modern scholarship, the "late" period of the Roman army begins with the accession of the Emperor Diocletian in AD 284, and ends in 480 with the death of Julius Nepos, being roughly coterminous with the Dominate. During the period 395–476, the army of the Roman Empire's western half progressively disintegrated, while its counterpart in the East, known as the East Roman army remained largely intact in size and structure until the reign of Justinian I.

The Eastern Roman army refers to the army of the eastern section of the Roman Empire, from the empire's definitive split in 395 AD to the army's reorganization by themes after the permanent loss of Syria, Palestine and Egypt to the Arabs in the 7th century during the Byzantine-Arab Wars. The East Roman army was the continuation of the Late Roman army of the 4th century, until it gradually transformed into what is now called the Byzantine army from the 7th century onwards.
The palatini were elite units of the Late Roman army mostly attached to the comitatus praesentales, or imperial escort armies. In the elaborate hierarchy of troop-grades, the palatini ranked below the scholares, but above the comitatenses and the limitanei.
Defence-in-depth is the term used by American political analyst Edward Luttwak to describe his theory of the defensive strategy employed by the Late Roman army in the third and fourth centuries AD.

The Imperial Roman army was the military land force of the Roman Empire from 27 BC to 476 AD, and the final incarnation in the long history of the Roman army. This period is sometimes split into the Principate and the Dominate (284–476) periods.

The Batavi was an auxilia palatina (infantry) unit of the late Roman army, active between the 4th and the 5th century. It was composed by 500 soldiers and was the heir of those ethnic groups that were initially used as auxiliary units of the Roman army and later integrated in the Roman Empire after the Constitutio Antoniniana. Their name was derived from the people of the Batavi.

The Primani was a legio palatina of the Late Roman army, active in the 4th and 5th century.

The Cornuti ("horned") was an auxilia palatina unit of the Late Roman army, active in the 4th and 5th century. It was probably related to the Cornuti seniores and the Cornuti iuniores.

The Dux Belgicae secundae was a senior officer in the army of the Late Roman Empire who was the commander of the limitanei and of a naval squadron on the so-called Saxon Shore in Gaul.
The Catalauni were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the modern Champagne region during the Roman period. The Catalauni probably belonged to a larger tribe, either the Remi in the north or the Lingones in the south. The Catuvellauni, who migrated to southern Britain in the 1st century BC, are likely part of the same tribal group.














