
Lancashire is a ceremonial county and geographical area in North West England. The ceremonial county's administrative centre is Preston, while Lancaster is still the county town. The borders of the ceremonial county were created by the Local Government Act 1972 and enclose a population of 1,449,300 and an area of 1,189 square miles (3,080 km2).

Roger the Poitevin was born in Normandy in the mid-1060s and died before 1140. He was an Anglo-Norman aristocrat, possessing large holdings in both England and through his marriage in France.

The River Ribble runs through North Yorkshire and Lancashire in Northern England. It starts close to the Ribblehead Viaduct in North Yorkshire, and is one of the few that start in the Yorkshire Dales and flow westwards towards the sea.
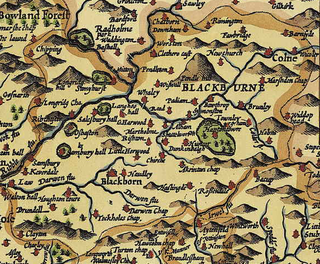
Blackburn Hundred is a historic sub-division of the county of Lancashire, in northern England. Its chief town was Blackburn, in the southwest of the hundred. It covered an area similar to modern East Lancashire, including the current districts of Ribble Valley, Pendle, Burnley, Rossendale, Hyndburn, Blackburn with Darwen, and South Ribble.

The West Derby Hundred is one of the six subdivisions of the historic county of Lancashire, in northern England. Its name alludes to its judicial centre being the township of West Derby.

The Amounderness Hundred is one of the six subdivisions of the historic county of Lancashire in North West England, but the name is older than the system of hundreds first recorded in the 13th century and might best be described as the name of a Norse wapentake. In the Domesday Book, it was used for some territories north of the River Ribble included together with parts of Yorkshire. The area eventually became part of Lancashire, sitting geographically between the Rivers Lune and Ribble, in the strip of coast between the Irish Sea and Bowland Forest.

The Rebellion of 1088 occurred after the death of William the Conqueror and concerned the division of lands in the Kingdom of England and the Duchy of Normandy between his two sons William Rufus and Robert Curthose. Hostilities lasted from 3 to 6 months starting around Easter of 1088.

The history of Cheshire can be traced back to the Hoxnian Interglacial, between 400,000 and 380,000 years BP. Primitive tools that date to that period have been found. Stone Age remains have been found showing more permanent habitation during the Neolithic period, and by the Iron Age the area is known to have been occupied by the Celtic Cornovii tribe and possibly the Deceangli.

Lancashire is a county of England, in the northwest of the country. The county did not exist in 1086, for the Domesday Book, and was apparently first created in 1182, making it one of the youngest of the traditional counties.

Great Eccleston is a village and civil parish in the English county of Lancashire, situated on a coastal plain called the Fylde. The village lies to the south of the River Wyre and the A586 road, approximately 10 miles (16 km) upstream from the port of Fleetwood. At the 2001 United Kingdom census, the parish had a population of 1,473, rising slightly to 1,486 at the Census 2011.

Conksbury is the site of a deserted medieval settlement between Over Haddon and Youlgreave in Derbyshire, England.
The Hundreds of Cheshire, as with other Hundreds in England, were the geographic divisions of Cheshire for administrative, military and judicial purposes. They were introduced in Cheshire some time before the Norman conquest. Later on, both the number and names of the hundreds changed by processes of land being lost from Cheshire, and merging or amalgamation of remaining hundreds. The Ancient parishes of Cheshire were usually wholly within a specific hundred, although a few were divided between two hundreds.

The Honour of Lancaster was a medieval English honour located primarily in the north-west of England, between 1066 to the 15th century.

The extent of the medieval district of Craven, in the north of England is a matter of debate. The name Craven is either pre-Celtic Britain, Britonnic or Romano-British in origin. However, its usage continued following the ascendancy of the Anglo-Saxons and the Normans – as was demonstrated by its many appearances in the Domesday Book of 1086. Places described as being In Craven in the Domesday Book fell later within the modern county of North Yorkshire, as well as neighbouring areas of West Yorkshire, Lancashire and Cumbria. Usage of Craven in the Domesday Book is, therefore, circumstantial evidence of an extinct, British or Anglo-Saxon kingdom or subnational entity.
The honour of Pontefract, also known as the feudal barony of Pontefract, was an English feudal barony. Its origins lie in the grant of a large, compact set of landholdings in Yorkshire, made between the Norman conquest of England in 1066 and the completion of the Domesday Survey in 1086. An expansive set of landholdings spanning sixty parishes and six wapentakes in Yorkshire, the honour was created primarily to serve a strategic, defensive function in a potentially hostile frontier zone. The first lord was Ilbert de Lacy, who built a castle at Pontefract which became the caput of the honour. Alongside the Yorkshire holdings, a smaller number of dispersed possessions elsewhere in England belonged to the honour.
Robert of Aumale was one of the Devon Domesday Book tenants-in-chief of King William the Conqueror (1066-1087). His lands, comprising 17 entries in the Domesday Book of 1086, later formed part of the very large Feudal barony of Plympton, whose later barons were the Courtenay family, Earls of Devon.
Nicholas the Bowman (fl.1086), also known as Nicholas de la Pole, was a servant of King William the Conqueror (1066-1087) and was one of that king's Devon Domesday Book tenants-in-chief. He was also a tenant-in-chief in Warwickshire and at some time between 1095 and 1100 he exchanged his manor of Ailstone in Warwickshire for the manor of Plymtree in Devon, held by St Peter's Abbey, Gloucester.

The Domesday Book of 1086 AD lists King William the Conqueror's tenants-in-chief in Derbyscire (Derbyshire), following the Norman Conquest of England:

The Domesday Book of 1086 AD lists King William the Conqueror's tenants-in-chief in Snotinghscire (Nottinghamshire), following the Norman Conquest of England:

The Domesday Book of 1086 AD identifies King William the Conqueror's tenants-in-chief in Cestrescire (Cheshire), following the Norman Conquest of England. At the time, the County of Cheshire included South Lancashire and most of modern Flintshire and Wrexham counties in north Wales.


















