
The greater bulldog bat or fisherman bat is a species of fishing bat native to Latin America. The bat uses echolocation to detect water ripples made by the fish upon which it preys, then uses the pouch between its legs to scoop the fish up and its sharp claws to catch and cling to it. It is not to be confused with the lesser bulldog bat, which, though belonging to the same genus, merely catches water insects, such as water striders and water beetles.

The New World leaf-nosed bats (Phyllostomidae) are found from southern North America to South America, specifically from the Southwest United States to northern Argentina. They are ecologically the most varied and diverse family within the order Chiroptera. Most species are insectivorous, but the phyllostomid bats include within their number true predatory species and frugivores. For example, the spectral bat, the largest bat in the Americas, eats vertebrate prey, including small, dove-sized birds. Members of this family have evolved to use food groups such as fruit, nectar, pollen, insects, frogs, other bats, and small vertebrates, and in the case of the vampire bats, even blood.

The New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat is a small-sized omnivorous mammal endemic to the islands of New Zealand. It is one of two extant and three overall terrestrial mammal species unique to New Zealand. The NZ lesser short-tailed bat's closest relative, M. robusta, was last seen in 1965 and is presumed extinct due to intense predation from ship rats introduced in the last few centuries. These bats are also commonly referred to as pekapeka, their Te Reo Māori name. Lesser short-tailed bats have unique adaptations that differentiate them from bats found in other parts of the world. For example, they are fully capable of moving along the ground to search for food, and the males sing to attract partners, taking turns to do so. Lesser short-tailed bats are a vulnerable species, so extensive conservation work and research are being done to prevent extinction.

Emballonuridae is a family of microbats, many of which are referred to as sac-winged or sheath-tailed bats. They are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. The earliest fossil records are from the Eocene.

The greater horseshoe bat is an insectivorous bat of the genus Rhinolophus. Its distribution covers Europe, Northern Africa, Central Asia and Eastern Asia. It is the largest of the horseshoe bats in Europe and is thus easily distinguished from other species. The species is sedentary, typically travelling up to 30 kilometres (19 mi) between the winter and summer roosts, with the longest recorded movement being 180 km (110 mi). The frequencies used by this bat species for echolocation lie between 69–83 kHz, have most energy at 81 kHz and have an average duration of 37.4 ms.

The Jamaican, common or Mexican fruit bat is a fruit-eating bat native to Mexico, through Central America to northwestern South America, as well as the Greater and many of the Lesser Antilles. It is also an uncommon resident of the Southern Bahamas. Populations east of the Andes in South America are now usually regarded a separate species, the flat-faced fruit-eating bat. The distinctive features of the Jamaican fruit bat include the absence of an external tail and a minimal, U-shaped interfemoral membrane.

The greater sac-winged bat is a bat of the family Emballonuridae native to Central and South America.

The northern ghost bat is a bat species from South America, Trinidad, and Central America. It is a relatively rare, completely white, insectivorous bat, with an unusual sac at the base of its tail.
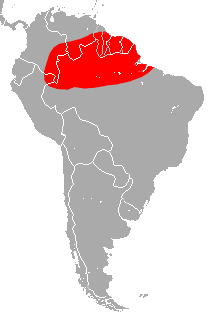
The lesser ghost bat is a bat species found in South America. It is one of six bat species worldwide to have white fur.

The dwarf dog-faced bat is a species of free-tailed bat from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Paraguay and Uruguay, typically at lower elevations. It is one of two species in the genus Molossops, the other being the rufous dog-faced bat. Three subspecies are often recognized, though mammalogist Judith Eger considers it monotypic with no subspecies. It is a small free-tailed bat, with a forearm length of 28.9–32.5 mm (1.14–1.28 in) and a weight of 5–8 g (0.18–0.28 oz); males are larger than females. It is brown, with paler belly fur and darker back fur. Its wings are unusual for a free-tailed bat, with exceptionally broad wingtips. Additionally, it has low wing loading, meaning that it has a large wing surface area relative to its body weight. Therefore, it flies more similarly to a vesper bat than to other species in its own family. As it forages at night for its insect prey, including moths, beetles, and others, it uses two kinds of frequency-modulated echolocation calls: one type is to navigate in open areas and to search for prey, while the other type is used for navigating in cluttered areas or while approaching a prey item.

The large slit-faced bat is a species of slit-faced bat with a broad distribution in forest and savanna habitats in West, Central, and East Africa. N. marica, is the available name for the southern savanna species if it is recognized as distinct from this species.

The Hawaiian hoary bat, also known as ʻōpeʻapeʻa, is a species of bat endemic to the islands of Hawaiʻi. Whereas the mainland hoary bat is found throughout North America, the Hawaiian hoary bat is distributed only among the major volcanic islands of Hawaiʻi, making it the only extant and native terrestrial mammal in the state; although some studies also posit that the mainland hoary bat lives in sympatry on the Hawaiian Islands alongside the Hawaiian hoary bat, this has been disputed. The Hawaiian hoary bat was officially named the state land mammal of Hawaiʻi in 2015. It is a federally listed endangered taxon of the United States.

The gray sac-winged bat is a species in the family Emballonuridae which comprises the 51 species of sac-winged bats. It is found in Mexico from Baja California Sur and Sonora to Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and northern Colombia, at elevations up to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft).

The lesser bamboo bat or lesser flat-headed bat is one of the smallest species of vesper bat, and is native to Southeast Asia.

The golden-tipped bat is a species of Microchiropteran in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Papua New Guinea and in Australia, especially scattered along the eastern part of Australia. The species is considered uncommon, and is listed as endangered in Australia.

The yellow-bellied sheath-tailed bat, also known as the yellow-bellied sheathtail or yellow-bellied pouched bat, is a microbat species of the family Emballonuridae found extensively in Australia and less commonly in parts of Papua New Guinea.

The naked-rumped pouched bat, also known as the pouched tomb bat, is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae.

The Mauritian tomb bat is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae that is found in central and southern Africa and Madagascar. It was discovered in 1818 by Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, and is characterized by an all-white ventral surface, grizzled dorsal coloration, and conical face. It has exceptionally good eyesight, a trait which is common in old world bats and enables it to find roosting locations. It has adapted itself to a wide range of habitats including subarid scrub to semi-tropical savanna and can be found throughout much of Africa south of the Sahara, including many of the surrounding islands. They often seek out refuge in cool dry areas. Mauritian tomb bats help control pest populations, including insects that carry human diseases. These bats tend to be nocturnal hunters and their normal prey consists of moths, butterflies, and termites. Not prone to large-scale roosting, T. mauritianus is most often spotted on the sides of buildings or on the trunks of trees in groups of around five individuals. They breed on average once or twice a year and rear usually one pup, though twins are occasionally reported. They usually deposit their hungry offspring in areas where they can feed ferociously, most often in berry bushes. This species is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due their wide distribution and stable population.

The white-striped free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. Its echolocation calls are audible to humans, which is a characteristic found in only a few microbat species. The species was formerly classified as Tadarida australis.

The Seychelles sheath-tailed bat is a sac-winged bat found in the central granitic islands of the Seychelles. They are nocturnal insectivores that roost communally in caves. The species was previously abundant across much of the archipelago, but has since seen a substantial loss of habitat. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed the species as being critically endangered, due to population decline. This is mainly due to an increase in land development and the introduction of invasive species.






















