| Proboscis bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Emballonuridae |
| Genus: | Rhynchonycteris Peters, 1867 |
| Species: | R. naso |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchonycteris naso (Wied-Neuwied, 1820) | |
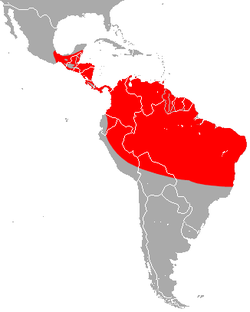 | |
| Proboscis bat range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The proboscis bat (Rhynchonycteris naso) is a species of bat found in South America and Central America. Other common names include long-nosed proboscis bat, sharp-nosed bat, [2] Brazilian long-nosed bat, [3] and river bat. [4] It is the only species in the genus Rhynchonycteris.
Contents
This species is in the family Emballonuridae, the sac-winged or sheath-tailed bats. Like most bats, it is nocturnal. It is found from southern Mexico to Belize, Peru, Venezuela, Bolivia and Brazil, as well as in Trinidad. [1] [5] [6]




