
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically, which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, translation, etc. It is a lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data.
Lexicography is the study of lexicons and the art of compiling dictionaries. It is divided into two separate academic disciplines:
Lexicology is the branch of linguistics that analyzes the lexicon of a specific language. A word is the smallest meaningful unit of a language that can stand on its own, and is made up of small components called morphemes and even smaller elements known as phonemes, or distinguishing sounds. Lexicology examines every feature of a word – including formation, spelling, origin, usage, and definition.
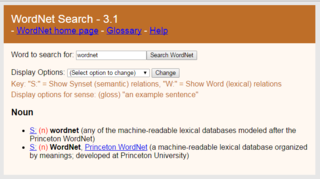
WordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words that links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into synsets with short definitions and usage examples. It can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. While it is accessible to human users via a web browser, its primary use is in automatic text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. It was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD style license and are freely available for download from that WordNet website. Until about 2024 the English WordNet could be used as an online dictionary/lexical database, and references with links to single words could be made, but thereafter one have to download the database to use it. There are now WordNets in more than 200 languages.

An idiom dictionary is a dictionary or phrase book that lists and explains idioms – distinctive words or phrases having a figurative meaning that goes beyond the original semantics of the words.
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A term is a word, compound word, or multi-word expression that in specific contexts is given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (terms), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings.
Computer-aided translation (CAT), also referred to as computer-assisted translation or computer-aided human translation (CAHT), is the use of software, also known as a translator, to assist a human translator in the translation process. The translation is created by a human, and certain aspects of the process are facilitated by software; this is in contrast with machine translation (MT), in which the translation is created by a computer, optionally with some human intervention.
A specialized dictionary is a dictionary that covers a relatively restricted set of phenomena. The definitive book on the subject includes chapters on some of the dictionaries included below:

The Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, often called the University of Thessaloniki, is the second oldest tertiary education institution in Greece. Named after the philosopher Aristotle, who was born in Stageira, about 55 kilometres (34 mi) east of Thessaloniki, it is the largest university in Greece and its campus covers 230,000 square metres (2,500,000 sq ft) in the centre of Thessaloniki, with additional educational and administrative facilities elsewhere.
A translation management system (TMS), formerly globalization management system (GMS), is a type of software for automating many parts of the human language translation process and maximizing translator efficiency. The idea of a translation management system is to automate all repeatable and non-essential work that can be done by software/systems and leaving only the creative work of translation and review to be done by human beings. A translation management system generally includes at least two types of technology: process management technology to automate the flow of work, and linguistic technology to aid the translator.

An electronic dictionary is a dictionary whose data exists in digital form and can be accessed through a number of different media. Electronic dictionaries can be found in several forms, including software installed on tablet or desktop computers, mobile apps, web applications, and as a built-in function of E-readers. They may be free or require payment.

A bilingual dictionary or translation dictionary is a specialized dictionary used to translate words or phrases from one language to another. Bilingual dictionaries can be unidirectional, meaning that they list the meanings of words of one language in another, or can be bidirectional, allowing translation to and from both languages. Bidirectional bilingual dictionaries usually consist of two sections, each listing words and phrases of one language alphabetically along with their translation. In addition to the translation, a bilingual dictionary usually indicates the part of speech, gender, verb type, declension model and other grammatical clues to help a non-native speaker use the word. Other features sometimes present in bilingual dictionaries are lists of phrases, usage and style guides, verb tables, maps and grammar references. In contrast to the bilingual dictionary, a monolingual dictionary defines words and phrases instead of translating them.
Beryl T. "Sue" Atkins was a British lexicographer, specialising in computational lexicography, who pioneered the creation of bilingual dictionaries from corpus data.

Emmanuel G. Kriaras was a Greek lexicographer, philologist, professor and linguist. He was Professor Emeritus of the School of Philosophy at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. He was a student of Jean Psychari and the practice and ideology of demotic Greek.
In digital lexicography, natural language processing, and digital humanities, a lexical resource is a language resource consisting of data regarding the lexemes of the lexicon of one or more languages e.g., in the form of a database.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to knowledge:
The Terminology Coordination Unit (TermCoord) is a supporting unit to the translation units of the Directorate-General for Translation of the European Parliament. TermCoord was created in 2008 by Rodolfo Maslias, professor at the Universities Luxembourg and Savoie-Mont Blanc, to stimulate and coordinate the terminology work of the 24 translation units of the European Parliament in Luxembourg.

Sketch Engine is a corpus manager and text analysis software developed by Lexical Computing since 2003. Its purpose is to enable people studying language behaviour to search large text collections according to complex and linguistically motivated queries. Sketch Engine gained its name after one of the key features, word sketches: one-page, automatic, corpus-derived summaries of a word's grammatical and collocational behaviour. Currently, it supports and provides corpora in over 90 languages.
The Dictionary of Standard Modern Greek is a monolingual dictionary of Modern Greek published by the Institute of Modern Greek Studies , at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in 1998. It is also called the University of Thessaloniki Dictionary, and is known to the public as Triantafyllidis Dictionary.
OntoLex is the short name of a vocabulary for lexical resources in the web of data (OntoLex-Lemon) and the short name of the W3C community group that created it.







