The Canadian Rockies or Canadian Rocky Mountains comprise the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. They are the eastern part of the Canadian Cordillera, which is a system of multiple ranges of mountains which runs from the Canadian Prairies to the Pacific Coast. The Canadian Rockies mountain system comprises the southeastern part of this system, lying between the Interior Plains of Alberta and Northeastern British Columbia on the east to the Rocky Mountain Trench of BC on the west. The southern end borders Idaho and Montana of the United States. In geographic terms the boundary is at the Canada/US border, but in geological terms it might be considered to be at Marias Pass in northern Montana. The northern end is at the Liard River in northern British Columbia.

The Black Mountains are a group of hills spread across parts of Powys and Monmouthshire in southeast Wales, and extending across the England–Wales border into Herefordshire. They are the easternmost of the four ranges of hills that comprise the Brecon Beacons National Park, and are frequently confused with the westernmost, which is known as the Black Mountain. The Black Mountains may be roughly defined as those hills contained within a triangle defined by the towns of Abergavenny in the southeast, Hay-on-Wye in the north and the village of Llangors in the west. Other gateway towns to the Black Mountains include Talgarth and Crickhowell. The range of hills is well known to walkers and ramblers for the ease of access and views from the many ridge trails, such as that on the Black Hill (Herefordshire) at the eastern edge of the massif.

The Judith Mountains are located in central Montana in Fergus County just to the northeast of Lewistown, Montana.

The Tobacco Root Mountains lie in the northern Rocky Mountains, between the Jefferson and Madison Rivers in southwest Montana. The highest peak is Hollowtop at 10,604 feet (3,232 m). The range contains 43 peaks rising to elevations greater than 10,000 feet.

The Madison Limestone is a thick sequence of mostly carbonate rocks of Mississippian age in the Rocky Mountain and Great Plains areas of western United States. The rocks serve as an important aquifer as well as an oil reservoir in places. The Madison and its equivalent strata extend from the Black Hills of western South Dakota to western Montana and eastern Idaho, and from the Canada–United States border to western Colorado and the Grand Canyon of Arizona.

The Black Hills are a small and isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk Peak, which rises to 7,244 feet (2,208 m), is the range's highest summit. The Black Hills encompass the Black Hills National Forest. The name "Black Hills" is a translation of the Lakota Pahá Sápa. The hills were so-called because of their dark appearance from a distance, as they were covered in trees.

The Little Belt Mountains are a section of the Rocky Mountains in the U.S. state of Montana. Situated mainly in the Lewis and Clark National Forest, the mountains are used for logging and recreation for the residents of Great Falls, Montana. Showdown is a ski area located within the mountains located off US Highway 89 which splits the mountains in half connecting White Sulphur Springs and Belt, MT. The highest point in the Little Belt Range is Big Baldy Mountain at 9,175 feet (2,797 m).

The Mokattam, also known as the Mukattam Mountain or Hills, is the name of a range of hills and a suburb in them, located in southeastern Cairo, Egypt.
The Big Snowy Group is a stratigraphical unit of Chesterian age in the Williston Basin.
The Limestone Alps are a mountain ranges system of the Alps in Central Europe.

The Castle Mountains, highest point Elk Peak, el. 8,589 feet (2,618 m), are an island range east of White Sulphur Springs in Meagher County, Montana, United States. About 30,000 acres of the Castles were roadless as of 1995. The western portion of the Castles are moist, while the eastside is dry, porous limestone hills. The range gets its name from "castle turrets", 50-foot high igneous rock spires on the western slopes. The range was the focus of mining activity in the previous century; crumbling remains of old miners' cabins and diggings are present throughout the area. The landscape is characterized by a central cluster of peaks over 8,000 feet and extensive grassy parks surrounded by lodgepole pine and limber pine. The Castles are lightly used by recreationists except for hunters in the fall. On the peak of Castle Mountain itself is a login book for the few who reach the top. There is no trail that leads to the peak.

The Henrys Lake Mountains, highest point Sheep Point, el. 10,609 feet (3,234 m), are a small mountain range northwest of West Yellowstone, Montana in Madison County, Montana. These mountains are also referred to as the Lionhead Mountains, and straddle the Continental Divide along the Idaho-Montana border. On the northwest corner of these mountains is Quake Lake, created when the 1959 Hebgen Lake earthquake caused a massive landslide and dammed the Madison River. Nine subalpine lakes sit in high cirques in the higher reaches, with several peaks topping 10,000'. Coffin Lake is the largest and most popular, on the Montana side. About 32,000 acres are roadless in the Montana portion, with an unknown amount in Idaho. Dense forests, pristine streams, rolling tundra, and grassy parks provide year-round habitat for grizzly bears, elk, and bighorn sheep. Rocks and soils are inherently unstable, a factor in the landslide that caused much loss of life in 1959. The instability exists because the range is basically limestone blocks sitting on top of shale and Yellowstone volcanic rocks.

The Little Snowy Mountains are a small mountain range in central Montana about 25 miles (40 km) southeast of Lewistown. The range lies mostly in Fergus County, but the southern part of the range extends into Golden Valley and Musselshell counties.

The Pryor Mountains are a mountain range in Carbon and Big Horn counties of Montana. They are located on the Crow Indian Reservation and the Custer National Forest, and portions of them are on private land. They lie south of Billings, Montana, and north of Lovell, Wyoming.

In Montana, the South Hills are the small foothills in various Montana communities, most notably those at el. 3,592 feet (1,095 m), south of Missoula, Montana in Missoula County, Montana. Several districts of Missoula, Montana are, also, in the South Hills.

The Scratchgravel Hills, el. 5,233 feet (1,595 m) are a small summit of hills northwest of Helena in Lewis and Clark County, Montana. The area has seen increased development and a drop in water level in recent years. The Scratchgravel Hills have alluvial deposits on top of faulted granitic bedrock. There was extensive mining in the area in late 1800s through the 1930s. The northern part of the region has folding shale, sandstone and limestone from the Algonkian (Belt) age. Adjacent granite has altered them into quartz-mica schist and related rocks. The southern and central portions of the region contains quartz monzonite. Bitterroot and conifers are common in the area.
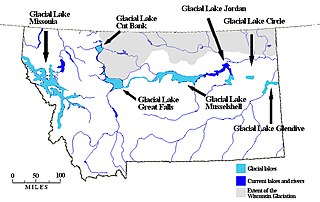
Lake Chouteau was a glacial lake formed during the late Pleistocene along the Teton River. After the Laurentide ice sheet retreated, water melting off the glacier accumulated between the Rocky Mountains and the ice sheet. The lake drained along the front of the ice sheet, eastward towards the Judith River and the Missouri River.