
Haleakalā, or the East Maui Volcano, is a massive, active shield volcano that forms more than 75% of the Hawaiian Island of Maui. The western 25% of the island is formed by another volcano, Mauna Kahalawai, also referred to as the West Maui Mountains.
Located about 2,300 miles (3,680 km) from the nearest continental shore, the Hawaiian Islands are the most isolated group of islands on the planet. The plant and animal life of the Hawaiian archipelago is the result of early, very infrequent colonizations of arriving species and the slow evolution of those species—in isolation from the rest of the world's flora and fauna—over a period of at least 5 million years. As a consequence, Hawai'i is home to a large number of endemic species. The radiation of species described by Charles Darwin in the Galapagos Islands which was critical to the formulation of his theory of evolution is far exceeded in the more isolated Hawaiian Islands.

Haleakalā National Park is a national park of the United States located on the island of Maui, Hawaii. Named after Haleakalā, a dormant volcano within its boundaries, the park covers an area of 33,265 acres, of which 24,719 acres is a wilderness area. The land was designated a national park in 1976 and its boundaries expanded in 2005.
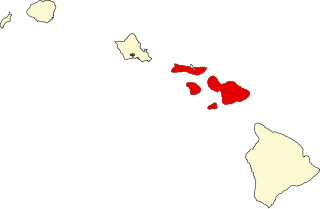
Maui Nui is a modern geologists' name given to a prehistoric Hawaiian island and the corresponding modern biogeographic region. Maui Nui is composed of four modern islands: Maui, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, and Kahoʻolawe. Administratively, the four modern islands comprise Maui County. Long after the breakup of Maui Nui, the four modern islands retained plant and animal life similar to each other. Thus, Maui Nui is not only a prehistoric island but also a modern biogeographic region.

The Hawaiian lobelioids are a group of flowering plants in the bellflower family, Campanulaceae, subfamily Lobelioideae, all of which are endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. This is the largest plant radiation in the Hawaiian Islands, and indeed the largest on any island archipelago, with over 125 species. The six genera involved can be broadly separated based on growth habit: Clermontia are typically branched shrubs or small trees, up to 7 metres (23 ft) tall, with fleshy fruits; Cyanea and Delissea are typically unbranched or branching only at the base, with a cluster of relatively broad leaves at the apex and fleshy fruits; Lobelia and Trematolobelia have long thin leaves down a single, non-woody stem and capsular fruits with wind-dispersed seeds; and the peculiar Brighamia have a short, thick stem with a dense cluster of broad leaves, elongate white flowers, and capsular fruits. The relationships among the genera and sections remains unsettled as of April 2022.

Acacia koaia, known as koaiʻa or koaiʻe in Hawaiian, is a species of acacia that is endemic to Hawaii. It is closely related to koa, and is sometimes considered to be the same species.

Hosmer's Grove is an example of experimental forestation from Hawaii's territorial days. Located just inside Haleakala National Park near the summit of Haleakala in Maui, Hawaii, it includes a campsite and several hiking trails. The grove is well known amongst birdwatchers due to the abundance of endemic honeycreepers at the site, including Iiwi, Apapane, Hawaii Amakihi, and the Maui Alauahio.

Moʻomomi is a Nature Conservancy preserve located on the northwestern shore of Molokaʻi in Hawaii. It was established in 1988. This area is dry and hot, primarily denuded of soil due to overgrazing and poor land use practices over the last 150 years.
Kokia kauaiensis, the Kauai treecotton or Kauaʻi Kokiʻo, is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family, Malvaceae, that is endemic to Kauaʻi, Hawaii.

Schiedea adamantis, commonly known as Diamond Head schiedea, is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae, that is endemic to the island of Oʻahu in Hawaii. It inhabits low shrublands on steep slopes along the northwest rim of Diamond Head Crater. Associated plants include nehe, kāwelu, ʻakoko, and ʻilima. There are only about 30 individuals remaining, and they are threatened by habitat loss.

Lipochaeta, common name nehe, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae that is endemic to Hawaii.

Melanthera, is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to the tropical and subtropical Americas.
Udea despecta, the Hawaiian sweetpotato leafroller, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is endemic to the Hawaiian islands of Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Maui, Lanai and Hawaii.

Geranium arboreum is a rare species of geranium known by the common names Hawaiian red-flowered geranium and Hawaii red cranesbill. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it is known only from the island of Maui. It was federally listed as an endangered species in 1992. Like other Hawaiian geraniums, this plant is known as hinahina and nohoanu.

Lipochaeta fauriei known by the common name Olokele Canyon nehe, is a rare species of flowering plant in the aster family.

Lipochaeta lobata is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name shrubland nehe. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it can be found in coastal dry shrublands and dry forests on Oʻahu, Maui, and Niʻihau.

Lipochaeta micrantha, known by the common name Kauai nehe, is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.

Lipochaeta tenuifolia is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common names Waianae Range nehe and slender-leaf nehe.
Lipochaeta venosa is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name spreading nehe. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it is known only from the island of Hawaii. It is federally listed as an endangered species of the United States.
Lipochaeta waimeaensis is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name Waimea Canyon nehe. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it is known only from the island of Kauai. It is federally listed as an endangered species of the United States.















