Related Research Articles
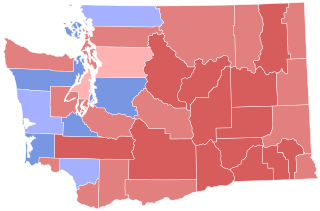
The 2004 Washington gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 2004. The race gained national attention for its legal twists and extremely close finish, among the closest political races in United States election history. Republican Dino Rossi was declared the winner in the initial automated count and again in a subsequent automated recount, but after a second recount done by hand, Democrat Christine Gregoire took the lead by a margin of 129 votes.

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Washington is the federal district court whose jurisdiction comprises the following counties of the state of Washington: Adams, Asotin, Benton, Chelan, Columbia, Douglas, Ferry, Franklin, Garfield, Grant, Kittitas, Klickitat, Lincoln, Okanogan, Pend Oreille, Spokane, Stevens, Walla Walla, Whitman, and Yakima.
The Superior Court is the state court in the U.S. state of New Jersey, with statewide trial and appellate jurisdiction. The New Jersey Constitution of 1947 establishes the power of the New Jersey courts. Under the State Constitution, "'judicial power shall be vested in a Supreme Court, a Superior Court, County Courts and inferior courts of limited jurisdiction.'" The Superior Court has three divisions: the Appellate Division is essentially an intermediate appellate court while the Law and Chancery Divisions function as trial courts. The State Constitution renders the New Jersey Superior Court, Appellate Division the intermediate appellate court, and "[a]ppeals may be taken to the Appellate Division of the Superior Court from the law and chancery divisions of the Superior Court and in such other causes as may be provided by law." Each division is in turn divided into various parts. "The trial divisions of the Superior Court are the principal trial courts of New Jersey. They are located within the State's various judicial geographic units, called 'vicinages,' R. 1:33-2(a), and are organized into two basic divisions: the Chancery Division and the Law Division".

The government of the State of New Jersey is separated into three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The powers of the State of New Jersey are vested by the Constitution of New Jersey, enacted in 1947, in a bicameral state legislature, the Governor, and the state courts, headed the New Jersey Supreme Court. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of the state legislature, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court.

The state government of Georgia is the U.S. state governmental body established by the Georgia State Constitution. It is a republican form of government with three branches: the legislature, executive, and judiciary. Through a system of separation of powers or "checks and balances", each of these branches has some authority to act on its own, some authority to regulate the other two branches, and has some of its own authority, in turn, regulated by the other branches. The seat of government for Georgia is located in Atlanta.

Superior courts in California are the state trial courts with general jurisdiction to hear and decide any civil or criminal action which is not specially designated to be heard in some other court or before a governmental agency. As mandated by the California Constitution, there is a superior court in each of the 58 counties in California. The superior courts also have appellate divisions which hear appeals from decisions in cases previously heard by inferior courts.

The Washington Court of Appeals is the intermediate level appellate court for the state of Washington. The court is divided into three divisions. Division I is based in Seattle, Division II is based in Tacoma, and Division III is based in Spokane.

Elected judicial positions in Washington State are nonpartisan; in 1912, Washington voters amended the constitution, adopting nonpartisan elections as the way to select judges.

The District of Columbia has a mayor–council government that operates under Article One of the United States Constitution and the District of Columbia Home Rule Act. The Home Rule Act devolves certain powers of the United States Congress to the local government, which consists of a mayor and a 13-member council. However, Congress retains the right to review and overturn laws created by the council and intervene in local affairs.
Thomas Samuel Zilly is a senior United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington in Seattle, Washington.

The Superior Court of Los Angeles County is the California Superior Court located in Los Angeles County. It is the largest single unified trial court in the United States.
The government of Washington State is the governmental structure of the State of Washington, United States, as established by the Constitution of the State of Washington. The executive is composed of the Governor, several other statewide elected officials and the Governor's cabinet. The Washington State Legislature consists of the House of Representatives and State Senate. The judiciary is composed of the Washington Supreme Court and lower courts. There is also local government, consisting of counties, municipalities and special districts.
The Judiciary of California or the Judicial Branch of California is defined under the California Constitution as holding the judicial power of the state of California which is vested in the Supreme Court, the Courts of Appeal and the Superior Courts. The judiciary has a hierarchical structure with the California Supreme Court at the top, California Courts of Appeal as the primary appellate courts, and the California Superior Courts as the primary trial courts.
Edward Michael Connelly was a federal prosecutor and justice of the Washington Supreme Court from 1946 to 1947. He was appointed to the Supreme Court by Governor Monrad Wallgren, and served less than one year. In 1946, he was defeated in the election, losing to King County Superior Court judge Matthew W. Hill. After leaving the court, Connelly returned to private practice in Spokane, Washington.

Initiative 1639 was a Washington state ballot initiative concerning firearms regulation that was passed into law on November 6, 2018. The initiative altered the gun laws in Washington by defining the term "semiautomatic assault rifle" to include all semiautomatic rifles, raising the minimum age for purchasing semiautomatic rifles from 18 to 21. It also imposes a 10-day waiting period before being allowed to claim a rifle from a firearms dealer, and expanded background checks to include medical records requiring a waiver of HIPAA rights.

Janice Niemi was an American lawyer and politician who served in the Washington House of Representatives from the 43rd district from 1983 to 1987 and in the Washington State Senate from the 43rd district from 1987 to 1995.
Verda M. Colvin is an associate justice of the Supreme Court of Georgia and former judge of the Georgia Court of Appeals.

The 2021 Seattle City Attorney election was held on November 2, 2021. Incumbent City Attorney Pete Holmes sought reelection to a fourth term in office, but came third place in the officially nonpartisan August 3 primary election and failed to advance to the general election, with both Nicole Thomas-Kennedy and Ann Davison finishing ahead of Holmes in the primary. Davison defeated Thomas-Kennedy in the general election.
References
- ↑ "Superior Courts". Washington State Administrative Office of the Courts. Retrieved January 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Washington State Constitution". Washington State Legislature. Retrieved January 5, 2019.