 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
Adduction is an anatomical term of motion referring to a movement which brings a part of the anatomy closer to the middle sagittal plane of the body.
 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
Adduction is an anatomical term of motion referring to a movement which brings a part of the anatomy closer to the middle sagittal plane of the body.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" and "carpal" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.
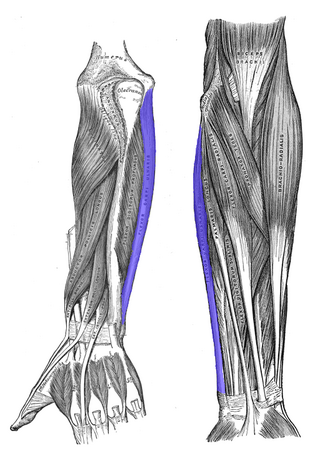
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint.

In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.
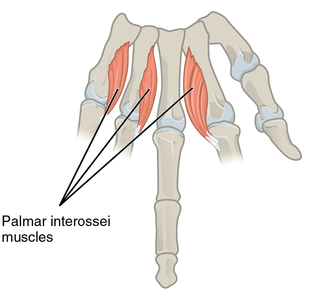
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.

In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four groups according to their orientation around the hip joint: the gluteal group; the lateral rotator group; the adductor group; and the iliopsoas group.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.

The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand, where they exert their action. Extrinsic denotes their location outside the hand. Extensor denotes their action which is to extend, or open flat, joints in the hand. They include the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL), extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), extensor pollicis longus (EPL), and extensor indicis (EI).