 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
Elevation, is an anatomical term of motion for movement in a superior direction.
It is the opposite of depression.
 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
Elevation, is an anatomical term of motion for movement in a superior direction.
It is the opposite of depression.

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle is, translated from Latin, the "lifter of both the upper lip and of the wing of the nose". The muscle is attached to the upper frontal process of the maxilla and inserts into the skin of the lateral part of the nostril and upper lip. At 44 characters, its name is longer than any other muscle's.
A snarl is a sound, often a growl or vicious utterance, often accompanied by a facial expression, where the upper lip is raised, and the nostrils widen, generally indicating hate, anger or pain. In addition to humans, other mammals including monkeys, rabbits and dogs snarl, often to warn others of their potential bite. In humans, snarling uses the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle. The threatening vocalizations of snarling are often accompanied by or used synonymously with threatening facial expressions.

The dorsal scapular nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus, usually derived from the ventral ramus of cervical nerve C5. It provides motor innervation to the rhomboid major muscle, rhomboid minor muscle, and levator scapulae muscle.

The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the cervical nerves C3-C4, and frequently also by the dorsal scapular nerve. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

The rhomboid major is a skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column. It originates from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae T2–T5 and supraspinous ligament; it inserts onto the lower portion of the medial border of the scapula. It acts together with the rhomboid minor to keep the scapula pressed against thoracic wall and to retract the scapula toward the vertebral column.
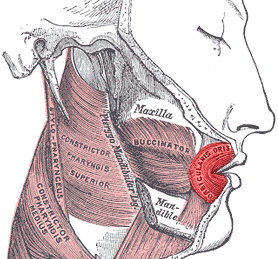
In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is not a true sphincter, as was once thought, as it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.
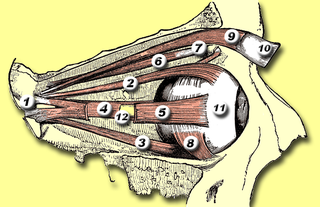
The levator palpebrae superioris is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the upper eyelid.

The lips are a horizontal pair of soft appendages attached to the jaws and are the most visible part of the mouth of many animals, including humans. Vertebrate lips are soft, movable and serve to facilitate the ingestion of food and the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are also a somatosensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.
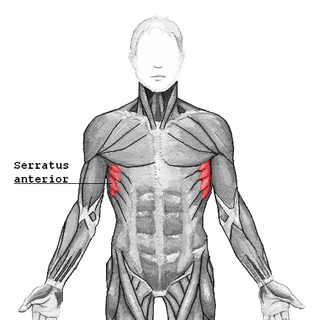
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve from the brachial plexus. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax.

The zygomaticus minor muscle is a muscle of facial expression. It originates from the zygomatic bone, lateral to the rest of the levator labii superioris muscle, and inserts into the outer part of the upper lip. It draws the upper lip backward, upward, and outward and is used in smiling. It is innervated by the facial nerve (VII).

The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It travels through the orbit, then enters and traverses the infraorbital canal, exiting the canal at the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face.

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates. They are the only muscles that attach to the dermis.
Levator muscle can refer to:
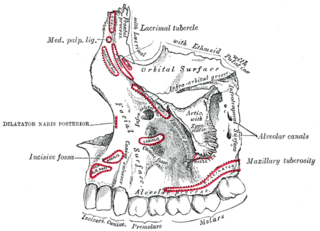
The canine space, is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a thin potential space on the face, and is paired on either side. It is located between the levator anguli oris muscle inferiorly and the levator labii superioris muscle superiorly. The term is derived from the fact that the space is in the region of the canine fossa, and that infections originating from the maxillary canine tooth may spread to involve the space. Infra-orbital is derived from infra- meaning below and orbit which refers to the eye socket.
Quadratus is Latin for square and quadratus muscle may refer to:

Gummy smile, also known as excessive gingival display, is a smile that shows gum under the upper lip. It is a common clinical condition, which can be caused by an abnormal dental eruption, hyperfunction of the upper lip elevator muscle, excessive vertical growth of the maxilla bone, over-eruption of the maxillary anterior teeth, or a combination of the above described factors. Several treatment options have been proposed to enhance the smile display and to reduce the gingival exposure.