This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2024) |
This is a partial list of molecules that contain 40 to 49 carbon atoms.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2024) |
This is a partial list of molecules that contain 40 to 49 carbon atoms.
| Chemical formula | Synonyms | CAS number |
|---|---|---|
| C40H24 | tetranaphthylene [1] | 116204-83-2 |
| C40H26 | 1,3,6,8-Tetraphenylpyrene | 13638-82-9 |
| C40H44N4O16 | uroporphyrinogen III | 1976-85-8 |
| C40H46N4O17 | hydroxymethylbilane | 73023-76-4 |
| C40H48 | isorenieratene | 524-01-6 |
| C40H49ClN8O12 | microsclerodermin D | 206535-30-0 |
| C40H50 | tetracyclohexylpyrene | |
| C40H50O | tedaniaxanthin [2] | 63893-29-8 |
| C40H50O2 | rhodoxanthin | 116-30-3 |
| C40H52O2 | canthaxanthin | 514-78-3 |
| C40H52O3 | flavoxanthin | 512-29-8 |
| C40H52O4 | Astaxanthin | 472-61-7 |
| C40H54 | torulene | |
| C40H54O3 | diadinoxanthin | 18457-54-0 |
| C40H54O4 | halocynthiaxanthin | 81306-52-7 |
| C40H56 | β-carotene | 7235-40-7 |
| C40H56O | Cyptoxanthin | 472-70-8 |
| C40H56O2 | zeaxanthin | 144-68-3 |
| C40H56O3 | antheraxanthin and flavoxanthin | - |
| C40H56O4 | violaxanthin | 126-29-4 |
| C40H58O | rhodopin | 105-92-0 |
| C40H58O2 | cucumariaxanthin B | 167818-24-8 |
| C40H58O4 | oryzanol A | 21238-33-5 |
| C40H60 | zeta-Carotene | |
| C40H60O2 | cucumariaxanthin C | 167818-25-9 |
| C40H62 | phytofluene | 27664-65-9 |
| C40H62O | phytofluenol | 29753-46-6 |
| C40H64 | phytoene | |
| C40H64O12 | nonactin | 6833-84-7 |
| C40H66 | lycopersene | 502-62-5 |
| C40H68O11 | nigericin | 28380-24-7 |
| C40H70O14 | halityloside B | 102075-01-5 |
| C40H78O4 | dioctadecyl succinate | 26720-12-7 |
| C40H78O5 | diethylene glycol distearate | 109-30-8 |
| C40H80 | cyclotetracontane | 297-54-1 |
| C40H80O2 | docosyl stearate | 22413-03-2 |
| C40H80NO8P | lecithin | 8002-43-5 |
| C40H82 | tetracontane | 4181-95-7 |
| C40H84NBr | tetrakis(decyl)ammonium bromide | 14937-42-9 |
| C40H87NSi2 | dioctadecyl tetramethylsilaxane | 82356-82-9 |
| C40H90O13Ti4 | decabutoxytetratitanoxane | 7393-48-8 |
| C41H42N4O8 | verteporfin | 129497-78-5 |
| C41H60N8O10 | nodularin | 118399-22-7 |
| C41H63NO14 | protoveratrine a | 1360-61-8 |
| C41H63NO15 | protoveratrine b | 124-97-0 |
| C41H64O13 | digitoxin | 71-63-6 |
| C41H67NO15 | troleandomycin | 2751-09-9 |
| C41H70O9Ca | ionomycin | 56092-81-0 |
| C41H72O2 | cholesteryl myristate | 1989-52-2 |
| C41H74N7O17P3S | phytanoyl-CoA | 146622-45-9 |
| C41H76N2O15 | roxithromycin | 80214-83-1 |
| C41H80O4 | dioctadecyl gluatarate | 26720-18-3 |
| C41H84 | hentetracontane | 7194-87-8 |
| C42H28O | tetraphenylnaphthacene monoxide | 127257-80-1 |
| C42H28O2 | pseudooxytetraphenyl naphthacene | 38118-83-1 |
| C42H51N6NiO13 | cofactor F430 | 73145-13-8 |
| C42H53NO15 | aclarubicin | 57576-44-0 |
| C42H58O5 | dinoxanthin | 54369-12-9 |
| C42H58O6 | fucoxanthin | 3351-86-8 |
| C42H62O16 | glycyrrhizin | 1405-68-3 |
| C42H69NO15 | josamycin | 16846-24-5 |
| C42H70O11 | salinomycin | 53003-10-4 |
| C42H71NO14 | rokitamycin | 74014-51-0 |
| C42H78N2O14 | dirithromycin | 62013-14-1 |
| C42H84 | cyclodotetracontane | 297-58-5 |
| C42H84N14O36S3 | streptomycin sulfate | 3810-74-0 |
| C42H87N | trimyristylamine | 27911-72-4 |
| C42H87Al | tritetradecylaluminium | 1529-58-4 |
| C42H90N2Br2 | hexanediaminium dihexadecyl tetramethyl dichloride | 15590-96-2 |
| C43H51N3O11 | rifaximin | 80521-81-4 |
| C43H53NO14 | docetaxel | 114977-28-5 |
| C43H54N4O8 | vinorelbine | 71486-22-1 |
| C43H55N5O7 | vindesine | 59917-39-4 |
| C43H58N4O12 | rifampcin | 13292-46 |
| C43H65N11O12S2 | demoxytocin | 113-78-0 |
| C43H66N12O12S2 | oxytocin | 50-56-6 |
| C43H67N15O12S2 | vasotocin | 113-80-4 |
| C43H68ClNO11 | pimecrolimus | 137071-32-0 |
| C43H72O11 | narasin | 55134-13-9 |
| C43H74N2O14 | spiramycin | 8025-81-8 |
| C43H76O2 | cholesteryl palmitate | 601-34-3 |
| C43H88 | tritetracontane | 7098-21-7 |
| C44H30N4 | tetraphenylporphyrin | 917-23-7 |
| C44H30N4O12S4 | tetraphenylporphine sulfonate | |
| C44H32N4O4 | temoporfin | 122341-38-2 |
| C44H50Cl2N6O2 | XF-73 | 718638-68-7 |
| C44H57NO17 | ortataxel | 186348-23-2 |
| C44H69NO12 | tacrolimus | 104987-11-3 |
| C44H82O13 | sucrose dipalmitate | 248917-86-4 |
| C44H86PNO8 | stearoyloleoylglycerophosphatidylcholine | 6753-56-6 |
| C45H44N3NaO7S2 | coomassie brilliant blue | 6104-59-2 |
| C45H52N4O18 | bilirubin diglucuronide | 17459-92-6 |
| C45H54N4O8 | vinorelbine | 71486-22-1 |
| C45H54F2N4O8 | vinflunine | 162652-95-1 |
| C45H57NO14 | cabazitaxel | 183133-96-2 |
| C45H57NO16 | larotaxel | 156294-36-9 |
| C45H64O | 2-Isopentenyl-3,4-dehydrorhodopin | |
| C45H69N5O8S | apratoxin A | 350791-64-9 |
| C45H69N11O12S | carbetocin | 37025-55-1 |
| C45H73NO14 | chaconine | 20562-03-2 |
| C45H73NO15 | solanine | 20562-02-1 |
| C45H74O | solanesol | 13190-97-1 |
| C45H75NO15 | miocamycin | 55881-07-7 |
| C45H78O2 | cholesteryl oleate | 303-43-5 |
| C45H80O2 | cholesteryl stearate | 1184-05-0 |
| C45H80O2 | cholesteryl stearate | 35602-69-8 |
| C45H83NO9 | ophidiacerebroside A | 152247-26-2 |
| C45H86O6 | trimyristin | 555-45-3 |
| C45H90 | cyclopentatetracontane | 297-60-9 |
| C46H56N4O10 | vincristine | 57-22-7 |
| C46H58N4O9 | vinblastine | 865-21-4 |
| C46H60FN3O13 | tesetaxel | 333754-36-2 |
| C46H62N4O11 | rifabutin | 72559-06-9 |
| C46H71BrN10O13 | symplocamide A | 1007391-44-7 |
| C46H77NO17 | tylosin | 1401-69-0 |
| C46H80O3 | cholesteryl oleyl carbonate | 17110-51-9 |
| C46H82O2 | cholesteryl nonadecanoate | 25605-90-7 |
| C46H85NO9 | ophidiacerebroside B | 152247-27-3 |
| C46H94 | hexatetracontane | 7098-24-0 |
| C47H51NO14 | paclitaxel | 33069-62-4 |
| C47H64N4O12 | rifapentine | 61379-65-5 |
| C47H73NO17 | amphotericin B | 1397-89-3 |
| C47H75NO17 | nystatin | 1400-61-9 |
| C47H84O2 | cholesteryl eicosanoate | 2573-03-7 |
| C48H40O4Si4 | octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane | 546-56-5 |
| C48H89NO9 | ophidiacerebroside D | 152247-28-4 |
| C48H94O4 | didocosyl succinate | 13475-47-3 |
| C48H96 | cyclooctatetracontane | 36355-90-5 |
| C48H99N | trihexadecylamine | 28947-77-5 |
| C48H100ClP | hexyl tris(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride | |
| C49H64N10O11S2 | octreotate | |
| C49H66N10O10S2 | octreotide | 83150-76-9 |
| C49H71N7O17 | cilofungin | 79404-91-4 |
| C49H74N10O12 | microcystin-LR | 101043-37-2 |
| C49H80O2 | cholesteryladrenate | 14940-92-2 |
| C49H96O4 | didocosyl glutarate | 94278-09-8 |
| C49H97NO10 | agelasphin-11 | 152139-44-1 |

Carbon is a chemical element; it has symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, 12C and 13C being stable, while 14C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity.

Ethylene is a hydrocarbon which has the formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene.
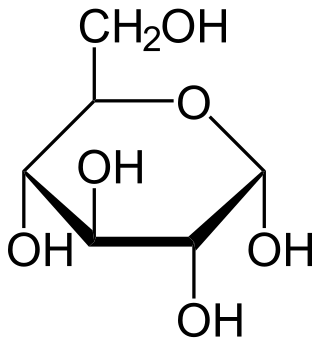
Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world.

Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as halides of carbon without carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon bonds, and certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen.
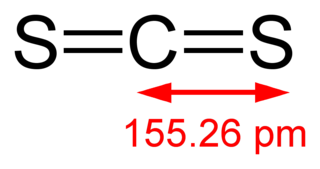
Carbon disulfide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CS2 and structure S=C=S. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as a building block in organic synthesis. Pure carbon disulfide has a pleasant, ether- or chloroform-like odor, but commercial samples are usually yellowish and are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.

A fashion week is a week-long fashion industry event where fashion designers, brands, or "houses" display their latest collections in runway fashion shows to buyers and the media which influences upcoming fashion trends for the current and approaching seasons.

A reseller is a company or individual (merchant) that purchases goods or services with the intention of selling them rather than consuming or using them. Individual resellers are often referred to as middle men. This is usually done for profit. One example can be found in the industry of telecommunications, where companies buy excess amounts of transmission capacity or call time from other carriers and resell it to smaller carriers. Resale can be seen in everyday life from yard sales to selling used cars.

Afforestation is the establishment of a forest or stand of trees (forestation) in an area where there was no recent tree cover. In comparison, reforestation means re-establishing forest that have either been cut down or lost due to natural causes, such as fire, storm, etc. There are three types of afforestation: Natural regeneration, agroforestry and commercial plantations. The intended benefits of afforestation are numerous. In the context of climate change, afforestation can be helpful for climate change mitigation through the route of carbon sequestration. Afforestation can also improve the local climate through increased rainfall and by being a barrier against high winds. The additional trees can also prevent or reduce topsoil erosion, floods and landslides. Finally, additional trees can be a habitat for wildlife, and provide employment and wood products.

Carbon offsetting is a carbon trading mechanism that allows entities such as governments or businesses to compensate for (i.e. “offset”) their greenhouse gas emissions. It works by supporting projects that reduce, avoid, or remove emissions elsewhere. In other words, carbon offsets work by offsetting emissions through investments in emission reduction projects. When an entity invests in a carbon offsetting program, it receives carbon credits. These "tokens" are then used to account for net climate benefits from one entity to another. A carbon credit or offset credit can be bought or sold after certification by a government or independent certification body. One carbon offset or credit represents a reduction, avoidance or removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide or its carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e).
Inert gas asphyxiation is a form of asphyxiation which results from breathing a physiologically inert gas in the absence of oxygen, or a low amount of oxygen, rather than atmospheric air. Examples of physiologically inert gases, which have caused accidental or deliberate death by this mechanism, are argon, helium, nitrogen and methane. The term "physiologically inert" is used to indicate a gas which has no toxic or anesthetic properties and does not act upon the heart or hemoglobin. Instead, the gas acts as a simple diluent to reduce the oxygen concentration in inspired gas and blood to dangerously low levels, thereby eventually depriving cells in the body of oxygen.

The BMW X6 is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV by German automaker BMW. The BMW X6 is the originator of the sports activity coupé (SAC), referencing its sloping rear roof design. It combines the attributes of an SUV with the stance of a coupé. It is built in BMW's North American plant in Greer, South Carolina alongside the BMW X5, whose platform it shares. Prior to the release of the X7, the X6 was considered a flagship SUV for BMW.

The Formula Regional Oceania Championship is New Zealand's premier formula racing category. The series includes races for every major trophy in New Zealand circuit racing including the New Zealand Motor Cup and the Denny Hulme Memorial Trophy. The cars are also the category for the New Zealand Grand Prix – one of only two races in the world with FIA approval to use the Grand Prix nomenclature outside Formula One. The series was formerly known as the Toyota Racing Series until 2023.

A freshwater marsh is a non-forested marsh wetland that contains shallow fresh water, and is continuously or frequently flooded. Freshwater marshes primarily consist of sedges, grasses, and emergent plants. Freshwater marshes are usually found near the mouths of rivers, along lakes, or are present in low lying areas with low drainage like abandoned oxbow lakes. Unlike its counterpart the salt marsh, which is regularly flushed with sea water, freshwater marshes receive the majority of their water from surface water.

Individual action on climate change can include personal choices in many areas, such as diet, travel, household energy use, consumption of goods and services, and family size. Individuals can also engage in local and political advocacy around issues of climate change. People who wish to reduce their carbon footprint, can take "high-impact" actions, such as avoiding frequent flying and petrol fuelled cars, eating mainly a plant-based diet, having fewer children, using clothes and electrical products for longer, and electrifying homes. Avoiding meat and dairy foods has been called "the single biggest way" an individual can reduce their environmental impact. Excessive consumption is more to blame for climate change than population increase. High consumption lifestyles have a greater environmental impact, with the richest 10% of people emitting about half the total lifestyle emissions.
The Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), formerly the Voluntary Carbon Standard, is a standard for certifying carbon credits to offset emissions. VCS is administered by Verra, a 501(c)(3) organization. Verra is the world's biggest certifier of voluntary carbon offsets. As of 2020 there were over 1,500 certified VCS projects covering energy, transport, waste, forestry, and other sectors. In 2021 Verra issued 300 MtCO2e worth of offset credits for 110 projects. There are also specific methodologies for REDD+ projects. Verra is the program of choice for most of the forest credits in the voluntary market, and almost all REDD+ projects.

The United Nations Climate Change Conferences are yearly conferences held in the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). They serve as the formal meeting of the UNFCCC parties – the Conference of the Parties (COP) – to assess progress in dealing with climate change, and beginning in the mid-1990s, to negotiate the Kyoto Protocol to establish legally binding obligations for developed countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Starting in 2005 the conferences have also served as the "Conference of the Parties Serving as the Meeting of Parties to the Kyoto Protocol" (CMP); also parties to the convention that are not parties to the protocol can participate in protocol-related meetings as observers. From 2011 to 2015 the meetings were used to negotiate the Paris Agreement as part of the Durban platform, which created a general path towards climate action. Any final text of a COP must be agreed by consensus.

An energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding supply and consumption. Currently, a transition to sustainable energy is underway to limit climate change. It is also called renewable energy transition. The current transition is driven by a recognition that global greenhouse-gas emissions must be drastically reduced. This process involves phasing-down fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon electricity. A previous energy transition took place during the industrial revolution and involved an energy transition from wood and other biomass to coal, followed by oil and most recently natural gas.

Climate change litigation, also known as climate litigation, is an emerging body of environmental law using legal practice to set case law precedent to further climate change mitigation efforts from public institutions, such as governments and companies. In the face of slow climate change politics delaying climate change mitigation, activists and lawyers have increased efforts to use national and international judiciary systems to advance the effort. Climate litigation typically engages in one of five types of legal claims: Constitutional law, administrative law, private law (challenging corporations or other organizations for negligence, nuisance, etc., fraud or consumer protection, or human rights.
Rattan Lal is a soil scientist. His work focuses on regenerative agriculture through which soil can help resolve global issues such as climate change, food security and water quality. He is considered a pioneer in soil-centric agricultural management to improve global food security and develop climate-resilient agriculture.
Carbon Design System is a free and open-source design system and library created by IBM, which implements the IBM Design Language, and licensed under Apache License 2.0. Its public development initially started on June 10, 2015. Their components have multiple implementations, which includes a vanilla JS and CSS implementation and React, while the community maintains the frameworks developed in Svelte, Vue.js, and Web Components. The official typeface to be used according to the guidelines is the IBM Plex typeface, with alternative typefaces for CJK scripts are Noto Sans CJK SC, Noto Sans CJK TC, and Noto Sans JP.