
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, and typhoid fever. Its use by mouth or by injection is only recommended when safer antibiotics cannot be used. Monitoring both blood levels of the medication and blood cell levels every two days is recommended during treatment.

Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic.
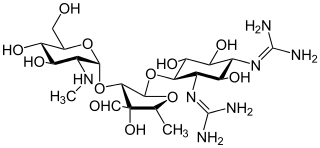
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer more generally to any organic molecule that contains amino sugar substructures. Aminoglycoside antibiotics display bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobes and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen but generally not against Gram-positive and anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria.

Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media, and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina.

Aztreonam, sold under the brand name Azactam among others, is an antibiotic used primarily to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This may include bone infections, endometritis, intra abdominal infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis. It is given by intravenous or intramuscular injection or by inhalation.

Tigecycline, sold under the brand name Tygacil, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication for a number of bacterial infections. It is a glycylcycline class drug that is administered intravenously. It was developed in response to the growing rate of antibiotic resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, and E. coli. As a tetracycline derivative antibiotic, its structural modifications has expanded its therapeutic activity to include Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, including those of multi-drug resistance.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. P. aeruginosa is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane - and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization P. aeruginosa poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of antibiotic resistance.

Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams.

Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces tenebrarius that is used to treat various types of bacterial infections, particularly Gram-negative infections. It is especially effective against species of Pseudomonas.
Ampicillin/sulbactam is a fixed-dose combination medication of the common penicillin-derived antibiotic ampicillin and sulbactam, an inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase. Two different forms of the drug exist. The first, developed in 1987 and marketed in the United States under the brand name Unasyn, generic only outside the United States, is an intravenous antibiotic. The second, an oral form called sultamicillin, is marketed under the brand name Ampictam outside the United States, and generic only in the United States. Ampicillin/sulbactam is used to treat infections caused by bacteria resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. Sulbactam blocks the enzyme which breaks down ampicillin and thereby allows ampicillin to attack and kill the bacteria.

Marbofloxacin is a carboxylic acid derivative third generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is used in veterinary medicine under the brand names Marbocyl, Forcyl, Marbo vet and Zeniquin. A formulation of marbofloxacin combined with clotrimazole and dexamethasone is available under the name Aurizon.
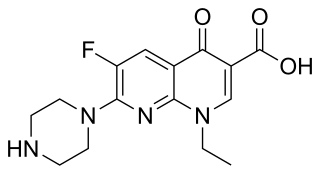
Enoxacin is an oral broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent used in the treatment of urinary tract infections and gonorrhea. Insomnia is a common adverse effect. It is no longer available in the United States.

Cefotiam is a parenteral third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It has broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. As a beta-lactam, its bactericidal activity results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via affinity for penicillin-binding proteins.

Doripenem is an antibiotic drug in the carbapenem class. It is a beta-lactam antibiotic drug able to kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

Boromycin is a bacteriocidal polyether-macrolide antibiotic. It was initially isolated from the Streptomyces antibioticus, and is notable for being the first natural product found to contain the element boron. It is effective against most Gram-positive bacteria, but is ineffective against Gram-negative bacteria. Boromycin kills bacteria by negatively affecting the cytoplasmic membrane, resulting in the loss of potassium ions from the cell. Boromycin has not been approved as a drug for medical use.

Cefditoren, also known as cefditoren pivoxil is an antibiotic used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. It is mainly used for treatment of community acquired pneumonia. It is taken by mouth and is in the cephalosporin family of antibiotics, which is part of the broader beta-lactam group of antibiotics.

Oleandomycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is synthesized from strains of Streptomyces antibioticus. It is weaker than erythromycin.

Fosfomycin, sold under the brand name Monurol among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat lower urinary tract infections. It is not indicated for kidney infections. Occasionally it is used for prostate infections. It is generally taken by mouth.

Polypeptide antibiotics are a chemically diverse class of anti-infective and antitumor antibiotics containing non-protein polypeptide chains. Examples of this class include actinomycin, bacitracin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Actinomycin-D has found use in cancer chemotherapy. Most other polypeptide antibiotics are too toxic for systemic administration, but can safely be administered topically to the skin as an antiseptic for shallow cuts and abrasions.
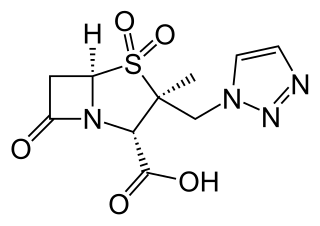
Ceftolozane/tazobactam, sold under the brand name Zerbaxa, (Merck) is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and complicated intra-abdominal infections in adults. Ceftolozane is a cephalosporin antibiotic, developed for the treatment of infections with gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to conventional antibiotics. It was studied for urinary tract infections, intra-abdominal infections and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia.



















