 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Netromycin |
| Other names | 1-N-Ethylsisomicin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605011 |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~0% |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.661 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
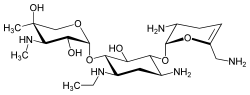
| Formula | C21H41N5O7 |
| Molar mass | 475.587 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Netilmicin (1-N-ethylsisomicin) is a semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic, and a derivative of sisomicin, produced by Micromonospora inyoensis . Aminoglycoside antibiotics have the ability to kill a wide variety of bacteria. Netilmicin is not absorbed from the gut and is therefore only given by injection or infusion. It is only used in the treatment of serious infections particularly those resistant to gentamicin.
Contents
It was patented in 1973 and approved for medical use in 1981. [2] It was approved for medical use in the UK in December 2019, for the treatment of external infections of the eye. [3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [4]