
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Monoamine oxidases (MAO) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase. The MAOs belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases.

Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth.
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an oxidoreductase (any enzyme that catalyzes a redox reaction) that uses dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Some oxidation reactions, such as those involving monoamine oxidase or xanthine oxidase, typically do not involve free molecular oxygen.

Furazolidone is a nitrofuran antibacterial agent and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). It is marketed by Roberts Laboratories under the brand name Furoxone and by GlaxoSmithKline as Dependal-M.

Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOA gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze the oxidative deamination of amines, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. A mutation of this gene results in Brunner syndrome. This gene has also been associated with a variety of other psychiatric disorders, including antisocial behavior. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed.
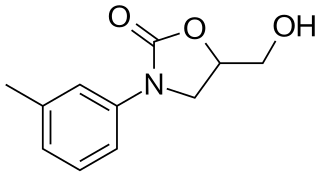
Toloxatone (Humoryl) is an antidepressant launched in 1984 in France by Sanofi Aventis for the treatment of depression. It was discontinued in 2002. It acts as a selective reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA).
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.

Brunner syndrome is a rare genetic disorder associated with a mutation in the MAOA gene. It is characterized by lower than average IQ, problematic impulsive behavior, sleep disorders and mood swings. It was identified in fourteen males from one family in 1993. It has since been discovered in additional families.

Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAO-B, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.

Flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases are a family of various amine oxidases, including maize polyamine oxidase (PAO), L-amino acid oxidases (LAO) and various flavin containing monoamine oxidases (MAO). The aligned region includes the flavin binding site of these enzymes. In vertebrates, MAO plays an important role in regulating the intracellular levels of amines via their oxidation; these include various neurotransmitters, neurotoxins and trace amines. In lower eukaryotes such as aspergillus and in bacteria the main role of amine oxidases is to provide a source of ammonium. PAOs in plants, bacteria and protozoa oxidise spermidine and spermine to an aminobutyral, diaminopropane and hydrogen peroxide and are involved in the catabolism of polyamines. Other members of this family include tryptophan 2-monooxygenase, putrescine oxidase, corticosteroid-binding proteins, and antibacterial glycoproteins.
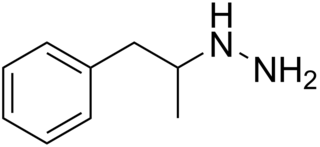
Pheniprazine, formerly sold under the brand names Catron and Cavodil, is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine group that was used as an antidepressant to treat depression in the 1960s. It was also used in the treatment of angina pectoris and schizophrenia. Pheniprazine has been largely discontinued due to toxicity concerns such as jaundice, amblyopia, and optic neuritis.

Eperezolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic.

Posizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic under investigation by AstraZeneca for the treatment of bacterial infections. At a concentration of 2 mg/L it inhibited 98% of all Gram-positive bacteria tested in vitro.
Metralindole (Inkazan) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) which was investigated in Russia as a potential antidepressant. It is structurally and pharmacologically related to pirlindole.

Radezolid is a novel oxazolidinone antibiotic being developed by Melinta Therapeutics, Inc. for the treatment of bacterial acne.

Amiflamine (FLA-336) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), thereby being a RIMA, and, to a lesser extent, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO), as well as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA). It is a derivative of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. The (+)-enantiomer is the active stereoisomer.

Almoxatone (MD-780,236) is a selective and reversible inhibitor of MAO-B. It was patented as an antidepressant and antiparkinsonian agent but was never marketed.
Tetrindole was a drug candidate that functions by reversibly inhibiting monoamine oxidase A; it was first synthesized in Moscow in the early 1990s. Tetrindole is similar in its chemical structure to pirlindole (Pyrazidol), and metralindole.

SU-11739 is an experimental monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that was never marketed.















