
Russia is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,192 km2, and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations.

In physical geography, a steppe is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees except near rivers and lakes.
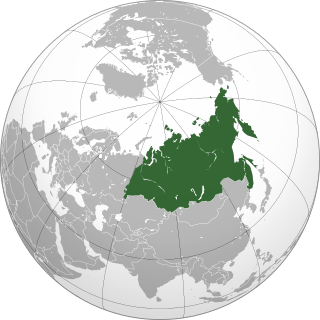
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographical terms and is coextensive with the Asian part of Russia, and consists of three Russian regions east of the Ural Mountains: Ural, Siberia, and the Russian Far East. North Asia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to its north; by Eastern Europe to its west; by Central and East Asia to its south; and by the Pacific Ocean and North America to its east. It covers an area of 13,100,000 square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), or 8.8% of Earth's total land area; and is the largest subregion of Asia by area, but is also the least populated, with a population of around 33 million, accounting for merely 0.74% of Asia's population.

The Daurian jackdaw is a bird in the crow family, Corvidae, native to eastern Asia. It is closely related to the western jackdaw. The name derives from the Dauria region of eastern Russia.

The Eurasian skylark is a passerine bird in the lark family, Alaudidae. It is a widespread species found across Europe and the Palearctic with introduced populations in New Zealand, Australia and on the Hawaiian Islands. It is a bird of open farmland and heath, known for the song of the male, which is delivered in hovering flight from heights of 50 to 100 metres. The sexes are alike. It is streaked greyish-brown above and on the breast and has a buff-white belly.

The greater short-toed lark is a small passerine bird. The current scientific name is from Ancient Greek. The genus name, Calandrella, is a diminutive of kalandros, the calandra lark, and brachydactila is from brakhus, "short", and daktulos, "toe".

Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain, and Vatican City.

The African paradise flycatcher is a medium-sized passerine bird. The two central tail feathers of the male are extended into streamers that commonly are more than twice as long as the body. The female tail feathers are of moderate length and without streamers. The upper parts of the male body, wings, and tail are boldly coloured in chestnut or rusty shades, but the underparts and the head are variably grey to blue-gray, with the head of the mature male being darker, commonly glossy black with greenish highlights. The beak and other bare areas, including a wattle ring round the eye, match the colour of the surrounding feathers. The female coloration is similar, though not so showy and glossy and with the head paler.

The KamchatkaPeninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long (777 mi) peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about 270,000 km2 (104,248 sq mi). The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10,500-metre-deep (34,449 ft) Kuril–Kamchatka Trench.

A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south are commonly used to define a subregion.

The Chukchi Peninsula, at about 66° N 172° W, is the easternmost peninsula of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. The Chukotka Mountains are located in the central/western part of the peninsula, which is bounded by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the east, where at its easternmost point it is only about 60 km (37 mi) from Seward Peninsula in Alaska; this is the smallest distance between the land masses of Eurasia and North America. The peninsula is part of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug of Russia.

A flyway is a flight path used by large numbers of birds while migrating between their breeding grounds and their overwintering quarters. Flyways generally span continents and often pass over oceans. Although applying to any species of migrating bird, the concept was first conceived and applied to waterfowl and shore birds. The flyways can be thought of as wide arterial highways to which the migratory routes of different species are tributaries. An alternative definition is that a flyway is the entire range of a migratory bird, encompassing both its breeding and non-breeding grounds, and the resting and feeding locations it uses while migrating. There are four major north–south flyways in North America and six covering Eurasia, Africa, and Australasia.

Lycaena phlaeas, the small copper, American copper, or common copper, is a butterfly of the Lycaenids or gossamer-winged butterfly family. According to Guppy and Shepard (2001), its specific name phlaeas is said to be derived either from the Greek φλέγω (phlégo), "to burn up", or from the Latin floreo, "to flourish".

Saturnia pyri, the giant peacock moth, great peacock moth, giant emperor moth or Viennese emperor, is a Saturniid moth which is native to Europe. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is the largest European moth, with a wingspan reaching 15–20 cm (6–8 in).

Heliothis ononis, the flax bollworm, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found in China, Kazakhstan, central Asia, northern Mongolia (Khangai), the Russian Far East, the Korean Peninsula, southern European part of Russia, southern and central Europe, southern and eastern Siberia and Turkey. In North America it is found from south-central Manitoba west to British Columbia, north to the Northwest Territories and Yukon and Alaska and south to Colorado.

Spialia orbifer, the orbed red-underwing skipper or Hungarian skipper is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found from south-eastern Europe and temperate Asia to Korea. The habitat consists of steppe on plains and grassy slopes in the mountains.

Lithostege fissurata is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was described by Jules Paul Mabille in 1888. It is found from western Algeria to Libya, south-eastern Egypt and Israel and from Saudi Arabia to south-eastern Iran and southern Iraq. It is also found on Malta.

Oeneis bore, the white-veined Arctic or Arctic grayling, is a butterfly, a species of Satyrinae that occurs in North America and Asia.



















