
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, as the impacting body is usually traveling at several kilometres a second, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.

The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore, but the crater is named after the onshore community of Chicxulub Pueblo. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when an asteroid, about ten kilometers in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be 200 kilometers in diameter and 1 kilometer in depth. It is believed to be the second largest impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research.
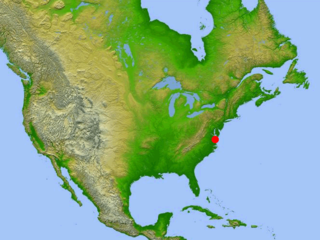
The Chesapeake Bay impact crater is a buried impact crater, located beneath the mouth of Chesapeake Bay, United States. It was formed by a bolide that struck the eastern shore of North America about 35.5 ± 0.3 million years ago, in the late Eocene epoch. It is one of the best-preserved "wet-target" impact craters in the world.
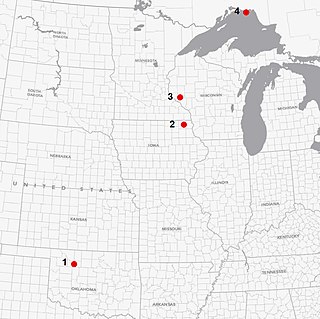
Ames crater is a meteorite crater (astrobleme) in Major County, Oklahoma, United States. Ames, Oklahoma is near the center of the structure, which is 30 miles (48 km) southwest of Enid, Oklahoma. Buried under a thick layer of sediment, it was not discovered until 1991. Subsequent drilling within the crater found a large amount of oil and gas. It is one of the largest of six meteor craters associated with oil-producing formations in the United States.

Aorounga is an eroded meteorite impact crater in Chad, Africa. The exposed remnant of the crater is 12.6 km (7.8 mi) in diameter and its age is estimated to be less than 345 million years.
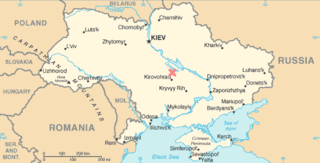
The Boltysh crater or Bovtyshka crater is a buried impact crater in the Kirovohrad Oblast of Ukraine, near the village of Bovtyshka. The crater is 24 kilometres (15 mi) in diameter and its age of 65.39 ± 0.14/0.16 million years, based on argon-argon dating techniques, less than 1 million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The Chicxulub impact is believed to have caused the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which included the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. The Boltysh crater is currently thought to be unrelated to the Chicxulub impact, and to have not generated major global environmental effects.
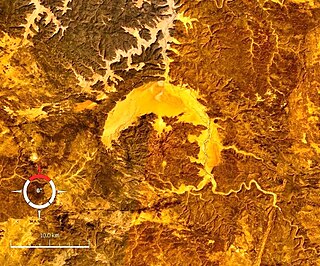
Gweni-Fada is a meteorite crater in the Ennedi Plateau, Chad.

Lappajärvi is a lake in Finland, in the municipalities of Lappajärvi, Alajärvi and Vimpeli. It is formed in a 23 km (14 mi) wide, partly eroded meteorite impact crater. The lake is part of Ähtävänjoki basin together with Lake Evijärvi that is located downstream (north) of it.
Obolon' crater is a 20 km (12 mi) diameter buried meteorite impact crater situated about 200 km (120 mi) southeast of Kyiv in Ukraine . The site has been drilled, which revealed the presence of shocked minerals and impact melt rock; the high chlorine content of the latter suggesting that the area was covered by shallow sea at the time of impact. One estimate puts the age at 169 ± 7 million years.

The Popigai impact structure is the eroded remnant of an impact crater in northern Siberia, Russia. It is tied with the Manicouagan structure as the fourth largest verified impact structure on Earth. A large bolide impact created the 100-kilometre (62 mi) diameter crater approximately 35 million years ago during the late Eocene epoch. It might be linked to the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event.

Rochechouart impact structure or Rochechouart astrobleme is an impact structure in France. Erosion has over the millions of years mostly destroyed its impact crater, the initial surface expression of the asteroid impact leaving highly deformed bedrock and fragments of the crater's floor as evidence of it.
Tookoonooka is a large meteorite impact structure (astrobleme) situated in South West Queensland, Australia. It lies deeply buried within Mesozoic sedimentary rocks of the Eromanga Basin and is not visible at the surface.

Vepriai is the largest impact crater in Lithuania, named after the town of Vepriai located at its center. The crater is not exposed to the surface, having been eroded and covered by sedimentary rocks during the last glacial period.

The Wetumpka impact crater is the only confirmed impact crater in Alabama, United States. It is located east of downtown Wetumpka in Elmore County. The crater is 4.7 miles (7.6 km) in diameter, and its age is estimated to be about 85 million years, based on fossils found in the youngest disturbed deposits, which belong to the Mooreville Chalk Formation.

Wolfe Creek Crater is a well-preserved meteorite impact crater (astrobleme) in Western Australia.

Woodleigh is a large meteorite impact structure (astrobleme) in Western Australia, centred on Woodleigh Station east of Shark Bay in the Gascoyne region. A team of four scientists at the Geological Survey of Western Australia and the Australian National University, led by Arthur J. Mory, announced the discovery in the 15 April 2000 issue of Earth and Planetary Science Letters.

Suevite is a rock consisting partly of melted material, typically forming a breccia containing glass and crystal or lithic fragments, formed during an impact event. It forms part of a group of rock types and structures that are known as impactites.

Christian Köberl is a professor of impact research and planetary geology at the University of Vienna, Austria. From June 2010 to May 2020 he was director general of the Natural History Museum in Vienna. He is best known for his research on meteorite impact craters.

A crater is a landform consisting of a hole or depression on a planetary surface, usually caused either by an object hitting the surface, or by geological activity on the planet. A crater has classically been described as: "a bowl-shaped pit that is formed by a volcano, an explosion, or a meteorite impact". On Earth, craters are "generally the result of volcanic eruptions", while "meteorite impact craters are common on the Moon, but are rare on Earth".




















