Related Research Articles
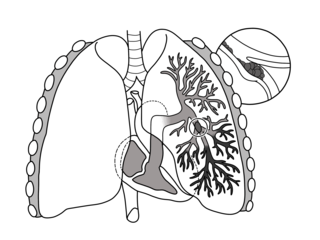
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to passing out, abnormally low blood pressure, and sudden death.
Venous thrombosis is thrombosis in a vein, caused by a thrombus. The most common form of venous thrombosis is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg. If the thrombus breaks off and flows towards the lungs, it can become a pulmonary embolism (PE), a blood clot in the lungs. This combination is called venous thromboembolism. Various other forms of venous thrombosis also exist; some of these can also lead to pulmonary embolism.
Factor V Leiden is a variant of human factor V, which causes an increase in blood clotting (hypercoagulability). Due to this mutation, protein C, an anticoagulant protein which normally inhibits the pro-clotting activity of factor V, is not able to bind normally to factor V, leading to a hypercoagulable state, i.e., an increased tendency for the patient to form abnormal and potentially harmful blood clots. Factor V Leiden is the most common hereditary hypercoagulability disorder amongst ethnic Europeans. It is named after the Dutch city Leiden, where it was first identified in 1994 by Prof R. Bertina under the direction of Prof P. Reitsma. Despite the increased risk of VTE, people with one copy of this gene have not been found to have shorter lives than the general population.

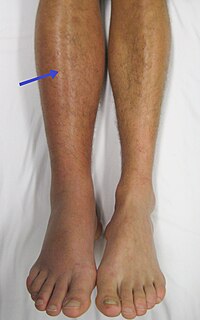
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to detach from the veins (embolize), travel through the right side of the heart, and become stuck in arteries that supply blood to the lungs. This is called pulmonary embolism (PE). Both DVT and PE are considered as part of the same overall disease process, which is called venous thromboembolism (VTE). VTE can occur as DVT only, as PE with DVT, or PE without DVT. The most frequent long-term complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Also, recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% of those in the ten years following an initial VTE.

Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis related to a thrombus. When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans.

In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adductor hiatus and is a continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the external iliac vein. The femoral vein bears valves which are mostly bicuspid and whose number is variable between individuals and often between left and right leg.
Lisker's sign is a clinical sign in which there is tenderness when the front, middle (anteromedial) part of the tibia is percussed. It can be found in people who have deep venous thrombosis.

May–Thurner syndrome (MTS), also known as the iliac vein compression syndrome, is a condition in which compression of the common venous outflow tract of the left lower extremity may cause discomfort, swelling, pain or clots in the iliofemoral veins.

Compression stockings are a specialized hosiery designed to help prevent the occurrence of, and guard against further progression of, venous disorders such as edema, phlebitis and thrombosis. Compression stockings are elastic compression garments worn around the leg, compressing the limb. This reduces the diameter of distended veins and increases venous blood flow velocity and valve effectiveness. Compression therapy helps decrease venous pressure, prevents venous stasis and impairments of venous walls, and relieves heavy and aching legs.
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), also called postphlebitic syndrome and venous stress disorder is a medical condition that may occur as a long-term complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
The term venous translucence has been used in phlebology since 1996 by surgeon Pedro Fernandes Neto during ambulatory clinical exams in Brazil. His results were published in the annals of the national and international congresses of angiology. Venous translucence is the process of reflective image visualization of veins by light, which reaches up to the superficial venous system. It is a non-invasive method. Since it is a simple, low-cost technique it can be repeated as needed, which is useful in disease-process monitoring. It is a new diagnostic procedure, still undergoing investigation; more analysis is necessary to hone its technical aspects. Venous translucence is based on optical physics. It is caused by the refraction, absorption and reflection of light. The color which is not absorbed is reflected, and is the one that is seen. Therefore, venous translumination is based on the incidence of luminosity on the vein, where part of the light is absorbed and another reflected.

Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which blood pools in the veins, straining the walls of the vein. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux which is a treatable condition. As functional venous valves are required to provide for efficient blood return from the lower extremities, this condition typically affects the legs. If the impaired vein function causes significant symptoms, such as swelling and ulcer formation, it is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is sometimes called chronic peripheral venous insufficiency and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome in which the deep veins have been damaged by previous deep vein thrombosis.
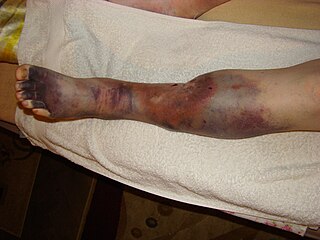
Superficial thrombophlebitis is a thrombosis and inflammation of superficial veins which presents as a painful induration with erythema, often in a linear or branching configuration forming cords.
Bancroft's sign, also known as Moses' sign, is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis of the lower leg involving the posterior tibial veins. The sign is positive if pain is elicited when the calf muscle is compressed forwards against the tibia, but not when the calf muscle is compressed from side to side. Like other clinical signs for deep vein thrombosis, such as Homans sign and Lowenberg's sign, this sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of thrombosis.
Louvel's sign is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis. The sign is defined as pain in the distribution of the affected vein which occurs during coughing or sneezing, and which disappears when the vein is compressed proximally.
Rose's sign is a clinical sign in which the skin of one leg feels warm and stiff when pinched. It can occur in people with deep vein thrombosis due to oedema in the affected leg.
Blood clots are a relatively common occurrence in the general population and are seen in approximately 1-2% of the population by age 60. Typically blood clots develop in the deep veins of the lower extremities, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or as a blood clot in the lung, pulmonary embolism (PE). A very small number of people who develop blood clots have a more serious and often life-threatening condition, known as Thrombotic Storm (TS). TS is characterized by the development of more than one blood clot in a short period of time. These clots often occur in multiple and sometimes unusual locations in the body and are often difficult to treat. TS may be associated with an existing condition or situation that predisposes a person to blood clots such as injury, infection, or pregnancy. In many cases a risk assessment will identify interventions that will prevent the formation of blood clots.
Peabody's sign is a clinical sign which may be found in patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The sign is positive when calf muscle spasm occurs on raising the affected leg with the foot extended. The sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of DVT.

Kazi Mobin-Uddin was an American surgeon specializing in vascular surgery research.
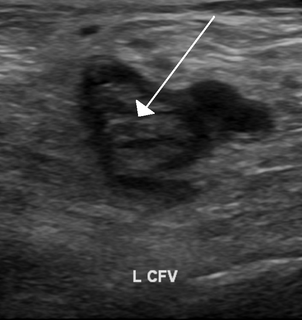
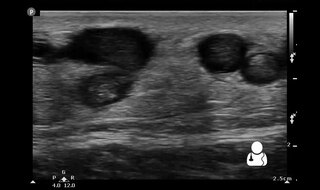
Ultrasonography in suspected deep vein thrombosis focuses primarily on the femoral vein and the popliteal vein, because thrombi in these veins are associated with the greatest risk of harmful pulmonary embolism.
References
- ↑ "Chapter 18: History, Physical Examination, and Diagnostic Approach". Manual of Vascular Diseases. Sanjay Rajagopalan, Debabrata Mukherjee, Emile R. Mohler. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2004. p. 258. ISBN 978-0-7817-4499-7.CS1 maint: others (link)
- ↑ Assessment of the Elderly Patient: The Peripheral Vascular Examination: Venous Examinations at Medscape.
- ↑ Lowenberg, R. I. (1954). "Early Diagnosis of Phlebo Thrombosis with Aid of a New Clinical Test". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 155 (18): 1566–70. doi:10.1001/jama.1954.03690360018005. PMID 13183782.
| | This medical sign article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |