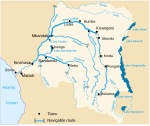
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is the largest country of sub-Saharan Africa, occupying some 2,344,858 square kilometres (905,355 sq mi). Most of the country lies within the vast hollow of the Congo River basin. The vast, low-lying central area is a plateau-shaped basin sloping toward the west, covered by tropical rainforest and criss-crossed by rivers. The forest center is surrounded by mountainous terraces in the west, plateaus merging into savannas in the south and southwest. Dense grasslands extend beyond the Congo River in the north. High mountains of the Ruwenzori Range are found on the eastern borders with Rwanda and Uganda.

The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo–Lualaba–Luvua–Luapula–Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

Sir Henry Morton Stanley was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author and politician who was famous for his exploration of Central Africa and his search for missionary and explorer David Livingstone. Besides his discovery of Livingstone, he is mainly known for his search for the sources of the Nile and Congo rivers, the work he undertook as an agent of King Leopold II of the Belgians which enabled the occupation of the Congo Basin region, and his command of the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition. He was knighted in 1897, and served in Parliament as a Liberal Unionist member for Lambeth North from 1895 to 1900.

David Livingstone was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livingstone, from the prominent 18th-century Moffat missionary family. Livingstone came to have a mythic status that operated on a number of interconnected levels: Protestant missionary martyr, working-class "rags-to-riches" inspirational story, scientific investigator and explorer, imperial reformer, anti-slavery crusader, and advocate of British commercial and colonial expansion. As a result, Livingstone became one of the most popular British heroes of the late 19th-century Victorian era.
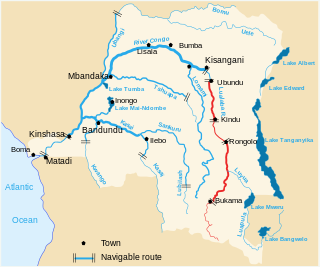
The Lualaba River flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi. The Lualaba is 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) long. Its headwaters are in the country's far southeastern corner near Musofi and Lubumbashi in Katanga Province, next to the Zambian Copperbelt.

The Luvua River is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for 350 kilometres (220 mi) to its confluence with the Lualaba River opposite the town of Ankoro. The Lualaba becomes the Congo River below the Boyoma Falls.

The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu (Zambia), which are fed by the Chambeshi River. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo before emptying into Lake Mweru. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province.

Livingstone Falls, named for British explorer David Livingstone, are a succession of enormous rapids on the lower course of the Congo River in west equatorial Africa, downstream from Malebo Pool in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Colonization of the Congo Basin refers to the European colonization of the Congo Basin of tropical Africa. It was the last part of the continent to be colonized. By the end of the 19th century, the Basin had been carved up by European colonial powers, into the Congo Free State, the French Congo and the Portuguese Congo.

The Ruzizi is a river, 117 kilometres (73 mi) long, that flows from Lake Kivu to Lake Tanganyika in Central Africa, descending from about 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) to about 770 metres (2,530 ft) above sea level over its length. The steepest gradients occur over the first 40 kilometres (25 mi), where hydroelectric dams have been built. Further downstream, the Ruzizi Plain, the floor of the Western Rift Valley, has gentle hills, and the river flows into Lake Tanganyika through a delta, with one or two small channels splitting off from the main channel.

The Lukuga River is a tributary of the Lualaba River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that drains Lake Tanganyika. It is unusual in that its flow varies not just seasonally but also due to longer term climate fluctuations.

The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tanganyika. The geographical term includes the valley and the surrounding mountains.

Nyangwe is a town on the right bank of the Lualaba River, in the Maniema Province in the east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In the second half of the 19th century, it was an important Swahili–Arab hub for trade goods like ivory, gold, iron and slaves, remaining one of the main slave trading centres until the Congo Arab war.

The Malagarasi River is a river in western Tanzania, flowing through Kigoma Region, although one of its tributaries comes from southeastern Burundi. The river also forms the western border of Tabora Region, the southern border of Kagera Region and the southwestern border of Geita Region. It is the second-longest river in Tanzania behind the Rufiji—Great Ruaha, and has the largest watershed of any river flowing into Lake Tanganyika. The Malagarasi-Muyovozi Wetlands are a designated a Ramsar site. Local tribes have nicknamed the Malagarasi as "the river of bad spirits".

Between 1874 and 1877 Henry Morton Stanley traveled Central Africa east to west, exploring Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and the Lualaba and Congo rivers. He covered 7,000 miles (11,000 km) from Zanzibar in the east to Boma at the mouth of the Congo in the west. The expedition resolved several open questions concerning the geography of Central Africa, including identifying the source of the Nile, which he proved was not the Lualaba and is in fact the source of the Congo River.

Congo is a 2001 BBC nature documentary series for television on the natural history of the Congo River of Central Africa. In three episodes, the series explores the variety of animals and habitats that are to be found along the river's 4,700 km (2,922 mi) reach.

The Congo–Arab war or Arab war was a colonial war fought between the Congo Free State and Arab-Swahili warlords associated with the Arab slave trade in the eastern regions of the Congo basin between 1892 and 1894.
The Elila River is a tributary of the Lualaba River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It rises in Mwenga Territory of Sud-Kivu Province and flows west through Shabunda Territory and then Pangi Territory in Maniema Province, entering the Lualaba just downstream of Kindu.

The Rutshuru River is a river in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo that drains Lake Mutanda in the foothills of the Virunga Mountains in Uganda, flowing northward into Lake Rutanzige. For most of its length it runs through the Rutshuru Territory in North Kivu province.

The Congo–Nile Divide or the Nile–Congo Watershed is the continental divide that separates the drainage basins of the Congo and Nile rivers. It is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) long.