The Faboideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. An acceptable alternative name for the subfamily is Papilionoideae, or Papilionaceae when this group of plants is treated as a family.

Acosmium is a South America genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. Three species are currently recognized. Most Acosmium species have been recently transferred to Leptolobium and one species to the South American Guianodendron while the genus Acosmium itself has been transferred from the tribe Sophoreae to the tribe Dalbergieae in a monophyletic clade informally known as the Pterocarpus clade.

Camoensia is a genus of 2 species of lianas in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, native to the Gulf of Guinea, Africa. C. scandens is cultivated as an ornamental plant; it has one of the largest leguminous flowers, up to 20 cm across. The genus has classically been assigned to the tribe Sophoreae, but was recently assigned to its own monophyletic tribe, Camoensieae, on the basis of molecular phylogenetic evidence. Species of Camoensia are known to produce quinolizidine alkaloids, consistent with their placement in the genistoid clade.

Airyantha is a small genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It was named after the botanist Herbert Kenneth Airy Shaw. It was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae; however, recent molecular phylogenetic analyses reassigned Airyantha into the Baphieae tribe.

Amphimas is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It is a west African tree used for medicine and for wood. Amphimas was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae; however, recent molecular phylogenetic analyses reassigned Amphimas into an unspecified position in the Meso-Papilionoideae.
Leucomphalos is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It contains a single species, Leucomphalos capparideus, a climbing perennial shrub native to the Guineo-Congolian forest of Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Gulf of Guinea Islands. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. Leucomphalos was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae; however, recent molecular phylogenetic analyses reassigned Leucomphalos to the Baphieae tribe.
Sweetia fruticosa is a species of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is a tree native to eastern, southern, and west-central Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and northeastern Argentina. It is the only member of the genus Sweetia. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae, mainly on the basis of flower morphology; recent molecular phylogenetic analyses assigned Sweetia fruticosa into an informal, monophyletic clade called the "vataireoids".

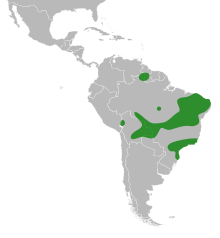
Vatairea is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes eight species of tall trees native to the tropical Americas, ranging from southern Mexico to Bolivia and southern Brazil. Seven species are native to northern South America, with the center of diversity in Amazonia. Vatairea lundellii ranges from southern Mexico to Panama. Most species grow in tropical rain forest, often in the inundated forests known as igapó and varzea, where they are emergent trees, growing above the forest canopy. V. macrocarpa grows in seasonally-dry forest, cerrado, and caatinga.

The tribe Brongniartieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae, primarily found in tropical regions of the Americas and in Australia The members of this tribe consistently form a monophyletic clade in molecular phylogenetic analyses. The tribe does not currently have a node-based definition, but morphological synapomorphies have been identified:
"stamens united by filaments in an adaxially open tube; anthers alternately long and basifixed, short and versatile; anther connective inconspicuous; septa present between seeds in pods; aril lateral lobe present and fitting into heel of funicle; fine red glandular processes present in axils; and pollen tricolporate with opercula and no definite endoaperture."

The tribe Dalbergieae is an early-branching clade within the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae. Within that subfamily, it belongs to an unranked clade called the dalbergioids. It was recently revised to include many genera formerly placed in tribes Adesmieae and Aeschynomeneae and to be included in a monophyletic group informally known as the dalbergioids sensu lato. The members of this tribe have a distinctive root nodule morphology, often referred to as an "aeschynomenoid" or "dalbergioid" nodule.

The tribe Dipterygeae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae. It was recently recircumscribed to include the following genera:

The tribe Sophoreae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae. Traditionally this tribe has been used as a wastebasket taxon to accommodate genera of Faboideae which exhibit actinomorphic, rather than zygomorphic floral symmetry and/or incompletely differentiated petals and free stamens. Various morphological and molecular analyses indicated that Sophoreae as traditionally circumscribed was polyphyletic. This led to a re-circumscription of Sophoreae, which resulted in the transfer of many genera to other tribes. This also necessitated the inclusion of two former tribes, Euchresteae and Thermopsideae, in the new definition of Sophoreae. Tribe Sophoreae, as currently circumscribed, consistently forms a monophyletic clade in molecular phylogenetic analyses. The Sophoreae arose 40.8 ± 2.4 million years ago.

The tribe Swartzieae is an early-branching monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae or Papilionaceae. Traditionally this tribe has been used as a wastebasket taxon to accommodate genera of Faboideae which exhibit actinomorphic, rather than zygomorphic floral symmetry and/or incompletely differentiated petals and free stamens. It was recently revised and most of its genera were redistributed to other tribes. Under its new circumscription, this clade is consistently resolved in molecular phylogenies. Members of this tribe possess "non-papilionate swartzioid flowers[…]largely characterized by a tendency to lack petals combined with a profusion and elaboration of free stamens" and a "lack of unidirectional order in the initiation of the stamens". They also have "complete or near complete fusion of sepals resulting from intercalary growth early in development, relatively numerous stamens, and a single or no petal, with other petals not at all apparent in development." The tribe is predicted to have diverged from the other legume lineages 48.9±2.8 million years ago.

The vataireoids are an early-branching monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae that are mostly found in northern South America, primarily Brazil.

The non-protein amino acid-accumulating clade, also known as the Canavanine-accumulating clade is a clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae that includes the majority of agriculturally-cultivated legumes. It is characterized by the accumulation of the non-proteinogenic amino acid canavanine in the seeds—a deterrent against herbivory. This phylogenetic trait was first recognized in the early 1980s. This clade is consistently resolved in molecular phylogenies. It contains many economically important genera, including Cicer, Glycine, Medicago, Phaseolus, Trifolium, Vicia, and Vigna.
Steinbachiella leptoclada is recently reinstated species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is a tree endemic to Bolivia. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Steinbachiella. The genus is assigned to the informal monophyletic Dalbergia clade of the Dalbergieae.

The Cladrastis clade is a monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae that is found in eastern Asia and southern North America. It is consistently resolved in molecular phylogenies and is sister to the Meso-Papilionoideae. Evidence for the existence of this clade was first proposed based on morphological (floral), cytological, and biochemical evidence. It is predicted to have diverged from the other legume lineages 47.4±2.6 million years ago.
The Andira clade is a predominantly Neotropical, monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae. The members of this clade were formerly included in tribe Dalbergieae, but this placement was questioned due to differences in wood anatomy and fruit, seed, seedling, floral, and vegetative characters. Recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown that they belong to a unique evolutionary lineage. It is predicted to have diverged from the other legume lineages in the late Eocene).
The tribe Ormosieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae, primarily found in tropical regions of the Americas, but also in southeast Asia and northern Australia. The members of this tribe were formerly included in tribe Sophoreae, but were recently circumscribed into a new tribe. The members of this tribe consistently form a monophyletic clade in molecular phylogenetic analyses. The tribe does not currently have a node-based definition, but morphological synapomorphies have been tentatively identified: "mostly dehiscent pods with woody valves" and "tufts of minute colleter-like glands in the axils of bract and bracteoles". Like other genistoids, members of tribe Ormosieae are known to produce quinolizidine alkaloids.
Bowringia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family (Fabaceae), found in tropical Africa and southeastern Asia. It includes four species native to western and central Africa and Madagascar, and to Borneo, Indochina, and southern China.