
Sarcosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform and distant relative of living crocodilians that lived during the Early Cretaceous, from the late Hauterivian to the early Albian, 133 to 112 million years ago of what is now Africa and South America. The genus name comes from the Greek σάρξ (sarx) meaning flesh and σοῦχος (souchus) meaning crocodile. It was one of the largest pseudosuchians, with the largest specimen of S. imperator reaching approximately 9–9.5 metres (29.5–31.2 ft) long and weighing up to 3.45–4.3 metric tons. It is known from two species; S. imperator from the early Albian Elrhaz Formation of Niger, and S. hartti from the Late Hauterivian of northeastern Brazil. Other material is known from Morocco and Tunisia and possibly Libya and Mali.
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Period. It lasted from 387.7 million years ago to 382.7 million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian Stage and followed by the Frasnian Stage. It is named after the town of Givet in France. The oldest forests occurred during the late Givetian. The lower GSSP is located at Jebel Mech Irdane, Tafilalt, Morocco.

Cheirolepis is an extinct genus of marine and freshwater ray-finned fish that lived in the Devonian period of Europe and North America. It is the only genus yet known within the family Cheirolepididae and the order Cheirolepidiformes. It was among the most basal of the Devonian actinopterygians and is considered the first to possess the "standard" dermal cranial bones seen in later actinopterygians.
Anhanguera is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Early Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of Brazil and the Late Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of Morocco. This pterosaur is closely related to Ornithocheirus, but belongs in the family Anhangueridae. The generic name comes from the Tupi words añanga, meaning "spirit protector of the animals" + wera "bygone".

Eldredgeops is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, known from the late Middle and earliest Upper Devonian of Morocco and the USA.
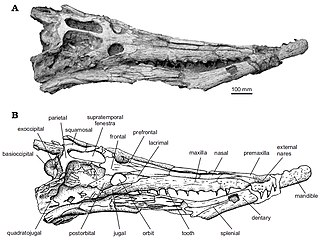
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Campanian to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine, with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
The Kačák Event, also known as the Kačák-otomari Event, is a widely recognised bioevent or series of events that occurred close to the end of the Eifelian Age of the Middle Devonian Epoch. It involved a global eustatic rise in sea level and ecological turnover. It was named for the Kačák Member of the Srbsko Formation in Bohemia, where it is represented by a black shale interval within a sequence of limestone. In marine environments, this appears as an anoxic event, often forming potential hydrocarbon source rocks such as the Marcellus Shale. Within the Old Red Sandstone continent, it is represented by the Achanarras lake, the deepest and most widespread lake that developed within the Orcadian Basin. The event is associated with significant extinctions, particularly amongst the Ammonoidea.

Argochampsa is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, usually regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian, related to modern gharials. It lived in the Paleocene of Morocco. Described by Hua and Jouve in 2004, the type species is A. krebsi, with the species named for Bernard Krebs. Argochampsa had a long narrow snout, and appears to have been marine in habits.
Ocepesuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian, related to modern gharials. Ocepesuchus is the oldest known crocodilian of Africa, and is known only from a single species, O. eoafricanus. It lived in Morocco during the late Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous.

Holonema is an extinct genus of relatively large, barrel-shaped arthrodire placoderms that were found in oceans throughout the world from the Mid to Late Devonian, when the last species perished in the Frasnian-Fammian extinction event. Most species of the genus are known from fragments of their armor, but the Gogo Reef species, H. westolli, is known from whole, articulated specimens.

Quasipetalichthys haikouensis is the type and only known species of the extinct petalichthid placoderm, Quasipetalichthys. Fossil remains of Quasipetalichthys have been found in the Middle Devonian, Givetian faunal stage of China.
Atlantosuchus is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from Morocco. One defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other long-snouted dyrosaurids was its proportionally elongate snout, the longest in proportion to body size of any dyrosaurid. Rhabdognathus, a hyposaurine dyrosaurid, is believed to have been the closest relative of the genus.
Sebecosuchia is an extinct group of mesoeucrocodylian crocodyliforms that includes the families Sebecidae and Baurusuchidae. The group was long thought to have first appeared in the Late Cretaceous with the baurusuchids and become extinct in the Miocene with the last sebecids, but Razanandrongobe pushes the origin of Sebecosuchia to the Middle Jurassic. Fossils have been found primarily from South America but have also been found in Europe, North Africa, Madagascar, and the Indian subcontinent.

Arganarhinus is an extinct genus of phytosaur known from the late Triassic period of Argana Basin in Morocco. It is known from a skull which is housed at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle. It was first named as a species of Paleorhinus in 1977b by Jean Michel Dutuit and it was named as a separate genus by Long and Murry in 1995. The type species is the original Paleorhinus magnoculus and the combinatio nova is Arganarhinus magnoculus. Its closest relative was Paleorhinus.

Holonematidae is an extinct family of relatively large arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Almost all fossil specimens are of armor fragments, though, all have distinctive ornamentation, often of unique arrangements and patterns of tubercles, that are diagnostic of the family. The trunkshield is very elongated, giving the armor an overall "barrel" like appearance.

Hollardosteus marocanus is a brachythoracid arthrodire placoderm from the Middle Devonian of Morocco. Its scrappy remains were found in Eifelian-aged strata from the Tafilat-Maider Valley.

Apatorhamphus is an extinct genus of azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Kem Kem Group of Morocco. It might have been part of the Chaoyangopteridae. It is only known from a few snout fragments and it likely had a wingspan of between 3–7 metres (9.8–23.0 ft)

Machimosauridae is an extinct family of teleosauroid thalattosuchian crocodyliforms. The family was first identified in 2016, when fossils of teleosauroid thalattosuchians, including an indeterminate close relative of Lemmysuchus and Machimosaurus, were described from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) of Morocco. The family was largely expanded in 2020 when the systematics of Teleosauroidea were re-reviewed. Members of this family generally were larger than the teleosaurids.

Watsonosteus is an extinct genus of coccosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Givetian stage of the Middle Devonian period. Fossils are found in the Orkney Islands, Scotland. It was a small placoderm with a total body length of 57 cm (22 in), with the largest individuals reaching lengths of 1 m (39 in). It is one of the few arthrodires for which complete body fossils are known.

Phoebodus is an extinct genus of phoebodontiform total group elasmobranch, known from over a dozen species found worldwide spanning the middle to late Devonian, making it one of the oldest known total group elasmobranchs. Most species are only known from their isolated tricuspid teeth, but one species, Phoebodus saidselachus from the Late Devonian of Morocco, is known from a complete skeleton, estimated to have been 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) in total length in life, which shows that it had a slender body superficially similar to that of the living frilled shark. The teeth of Phoebodus and frilled sharks are also morphologically similar, and are designed for grasping prey. Phoebodus probably consumed small prey items that were capable of being swallowed whole.






















