This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2020) |
![Martin Gottlieb Klauer; portrait by Jakob Samuel Beck [de] (1775) Beck-Klauer.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/51/Beck-Klauer.jpg/300px-Beck-Klauer.jpg)

Martin Gottlieb Klauer (29 August 1742, Rudolstadt - 4 April 1801, Weimar) was a German sculptor, and one of the first teachers at the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2020) |
![Martin Gottlieb Klauer; portrait by Jakob Samuel Beck [de] (1775) Beck-Klauer.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/51/Beck-Klauer.jpg/300px-Beck-Klauer.jpg)

Martin Gottlieb Klauer (29 August 1742, Rudolstadt - 4 April 1801, Weimar) was a German sculptor, and one of the first teachers at the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School.
His father, Johann Michael Klauer, was a tailor. He learned his trade in his hometown, from the Court Sculptor, Karl Adolph Kändler . He probably worked in Gera and Potsdam. From 1769, he was an independent craftsman in Rudolstadt. In 1772, he married Johanna Kapler, the daughter of a winery manager. She died while giving birth to their first child, who also died.
In 1773, he was appointed a Court Sculptor in Weimar, by Duchess Anna Amalia. He also worked in Bad Berka, which was a major source of high quality sandstone. During this time, he became acquainted with Goethe. In 1776, he became one of the first teachers at the new Drawing school. Three years later, he made a trip to study the ancient plaster casts in Mannheim. His friendship with Johann Joachim Christoph Bode has led to speculation that he was a member of the Illuminati. [1]
He was admired for his lifelike, monumental portrait busts. In addition to Goethe, he is known for definitive busts of Friedrich Schiller, Johann Gottfried Herder and Christoph Martin Wieland, as well as many other less familiar notables. In 1789, together with Friedrich Justin Bertuch, he opened an ornamental brick factory and produced small works in Terracotta; keeping a detailed catalog of everything produced there. He also did a few larger works; notably the statue of Neptune in the fountain at Weimar's marketplace. Although the great majority of his works are in Weimar, he occasionally went elsewhere; for example, four stone figures at the village church in Flurstedt.
He remarried in 1778, but nothing is known about his wife. They had two sons; one who died in infancy, and Johann Christian Ludwig , who also became a sculptor.
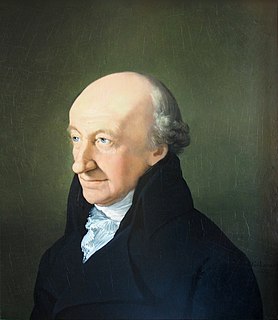
Christoph Martin Wieland was a German poet and writer. He is best-remembered for having written the first Bildungsroman, as well as the epic Oberon, which formed the basis for Carl Maria von Weber's opera of the same name. His thought was representative of the cosmopolitanism of the German Enlightenment, exemplified in his remark: "Only a true cosmopolitan can be a good citizen."

Friedrich Christoph Oetinger was a German Lutheran theologian and theosopher.

Anna Amalia of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, was a German princess and composer. She became the duchess of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, by marriage, and was also regent of the states of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach from 1758 to 1775. She transformed her court and its surrounding into the most influential cultural center of Germany.

Weimar Classicism was a German literary and cultural movement, whose practitioners established a new humanism from the synthesis of ideas from Romanticism, Classicism, and the Age of Enlightenment. It was presumably named after the city of Weimar, Germany, because the leading authors of Weimar Classicism lived there.

Johann Wolfgang von Goethe was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature and aesthetic criticism, and treatises on botany, anatomy, and colour. He is considered to be the greatest German literary figure of the modern era.

Ferdinand Jagemann was a German painter; known primarily for his portraits.

Georg Melchior Kraus was a German painter. He was a co-founder of the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School, together with Friedrich Justin Bertuch, in 1776.

The Weimar Princely Free Drawing School was an art and literature educational establishment. It was set up in 1776 in Weimar by the scholar and ducal private-secretary Friedrich Justin Bertuch (1747–1822) and the painter Georg Melchior Kraus (1737–1806), as part of Weimar Classicism. It was financed by the young Charles Augustus, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach and heavily promoted by Goethe, who also taught there. Among its pupils were Charles Augustus's future mistress Karoline Jagemann. It lasted until 1930.

Friedrich Johann Justin Bertuch was a German publisher and patron of the arts. He co-founded the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School with the painter Georg Melchior Kraus in 1776. He was the father of the writer and journalist Karl Bertuch.

Johann Heinrich Meyer was a Swiss painter, engraver and art critic. He served as the second Director of the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School. A close associate of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, he was often referred to as "Goethemeyer".

Johann Martin Miller was a German theologian and writer. He is best known for his novel Siegwart, which became one of the most successful books at the time.

Charlotte Luise Antoinette von Schiller was the wife of German poet Friedrich Schiller.

Johann Friedrich Bause was a German copper engraver; primarily of portraits.

Prince Frederick Ferdinand Constantin of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach was a titular Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach and a major general in the army of the Electorate of Saxony. He lived during the Age of Enlightenment.

The Seyler Theatre Company, also known as the Seyler Company, was a theatrical company founded in 1769 by Abel Seyler, a Hamburg businessman originally from Switzerland who became "the leading patron of German theatre" in his lifetime. It was largely a continuation of the Hamburgische Entreprise, whose dramaturge was Gotthold Ephraim Lessing and whose main owner was Seyler. The Seyler theatrical company became one of the most famous theatrical companies of Europe in the 18th century, attracting some of Germany's leading actors, playwrights and composers. It originally comprised around 60 members, including an orchestra, a ballet, house dramatists and set designers. Between 1777 and 1778 Seyler employed some 230 actors, singers and musicians. The company was originally contracted by the Hanoverian court with performing at Hanover and other cities of the kingdom. The company would eventually perform all across Germany, and performed for three years at the Weimar Schlosstheater, invited by Duchess Anna Amalia of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. When Anna Amalia succeeded in engaging the Seyler Company, this was "an extremely fortunate coup. The Seyler Company was the best theatre company in Germany at that time." The company had an important role in the development of German opera in the late 18th century.

Schloss Weimar is a Schloss (palace) in Weimar, Thuringia, Germany. It is now called Stadtschloss to distinguish it from other palaces in and around Weimar. It was the residence of the dukes of Saxe-Weimar and Eisenach, and has also been called Residenzschloss. Names in English include Palace at Weimar, Grand Ducal Palace, City Palace and City Castle. The building is located at the north end of the town's park along the Ilm river, Park an der Ilm. It forms part of the World Heritage Site "Classical Weimar".

Adolf Brütt was a German sculptor. He was the founder of the Weimarer Bildhauerschule and its accompanying bronze foundry.

Johann Ernst Heinsius was a German portrait painter and miniaturist.

The Weimar courtyard of the muses is a term, that had emerged during the 19th century. It refers to an elite fellowship of people in Classical Weimar (1772-1805), that was made up of nobles and commoners, courtiers, civil servants, writers, artists and scientists, who congregated around the central character, Duchess Anna Amalia of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, pioneer of Weimar Classicism and patroness of the arts. Duchess Anna Amalia was the mother and from 1758 until 1775 regent for the infant Grand Duke Karl August von Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach. Among the poets living in Weimar were the most famous German authors of their time, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Schiller, Christoph Martin Wieland and Johann Gottfried Herder.
Christian Johann Christoph Schreiber was a German theologian, philologist, philosopher, and poet. He was also the Superintendent of the dioceses of Lengsfeld and Dermbach. He was connected in friendship or correspondence to writers and philosophers of his time, and published poetry, sermons, historical and philosophical works.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Martin Gottlieb Klauer . |