In computing, cross-platform software is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms.
A software development kit (SDK) is a collection of software development tools in one installable package. They facilitate the creation of applications by having a compiler, debugger and sometimes a software framework. They are normally specific to a hardware platform and operating system combination. To create applications with advanced functionalities such as advertisements, push notifications, etc; most application software developers use specific software development kits.
Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for one or more mobile devices, which can include personal digital assistants (PDA), enterprise digital assistants (EDA), or mobile phones. Such software applications are specifically designed to run on mobile devices, taking numerous hardware constraints into consideration. Common constraints include CPU architecture and speeds, available memory (RAM), limited data storage capacities, and considerable variation in displays and input methods. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing or delivered as web applications, using server-side or client-side processing to provide an "application-like" experience within a web browser.

Adobe AIR is a cross-platform runtime system currently developed by Harman International, in collaboration with Adobe Inc., for building desktop applications and mobile applications, programmed using Adobe Animate, ActionScript, and optionally Apache Flex. It was originally released in 2008. The runtime supports installable applications on Windows, macOS, and mobile operating systems, including Android, iOS, and BlackBerry Tablet OS.

The iOS SDK, formerly the iPhone SDK, is a software development kit (SDK) developed by Apple Inc. The kit allows for the development of mobile apps on Apple's iOS and iPadOS operating systems.
Apache Cordova is a mobile application development framework created by Nitobi. Adobe Systems purchased Nitobi in 2011, rebranded it as PhoneGap, and later released an open-source version of the software called Apache Cordova. Apache Cordova enables software programmers to build hybrid web applications for mobile devices using CSS3, HTML5, and JavaScript, instead of relying on platform-specific APIs like those in Android, iOS, or Windows Phone. It enables the wrapping up of CSS, HTML, and JavaScript code depending on the platform of the device. It extends the features of HTML and JavaScript to work with the device. The resulting applications are hybrid, meaning that they are neither truly native mobile application nor purely Web-based. They are not native because all layout rendering is done via Web views instead of the platform's native UI framework. They are not Web apps because they are packaged as apps for distribution and have access to native device APIs. Mixing native and hybrid code snippets has been possible since version 1.9.
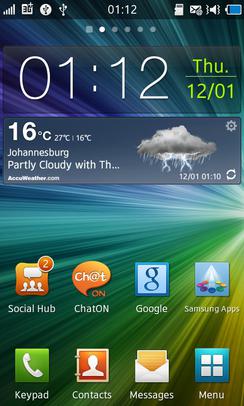
Bada was a mobile operating system developed by Samsung Electronics for devices such as mid- to high-end smartphones and tablet computers. The name is derived from "바다 (bada)", meaning "ocean" or "sea" in Korean. All phones running Bada were branded with the name Wave, unlike Samsung's Android devices which are branded as Galaxy.

Wikitude was a mobile augmented reality (AR) technology provider based in Salzburg, Austria. Founded in 2008, Wikitude initially focused on providing location-based augmented reality experiences through the Wikitude World Browser App. In 2012, the company restructured its proposition by launching the Wikitude SDK, a development framework that uses image recognition and tracking, and geolocation technology.
Junaio was an augmented reality browser designed for 3G and 4G mobile devices. It was developed by Munich-based company Metaio GmbH. It provided a Creator application and an API for developers and content providers to generate mobile Augmented Reality experiences for end-users. The smartphone app, for Android and iPhone platforms, and API were free to use.
Aurasma, later known as HP Reveal, was an augmented reality platform launched by HP Autonomy on May 5, 2011. Available as both a software development kit (SDK) and an application for Android and iOS, it leveraged mobile device cameras to overlay digital content—such as animations, videos, 3D models, or web pages—onto the physical world. In October 2011, HP acquired the platform and rebranded it as HP Reveal.
An app store, also called an app marketplace or app catalog, is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software called applications, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not include the running of the computer itself. Complex software designed for use on a personal computer, for example, may have a related app designed for use on a mobile device. Today apps are normally designed to run on a specific operating system—such as the contemporary iOS, macOS, Windows, Linux or Android—but in the past mobile carriers had their own portals for apps and related media content.

Recon Instruments was a Canadian technology company that produced smartglasses and wearable displays marketed by the company as "heads-up displays" for sports. Recon's products delivered live activity metrics, GPS maps, and notifications directly to the user's eye. Recon's first heads-up display offering was released commercially in October 2010, roughly a year and a half before Google introduced Google Glass.
A mobile application or app is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device.
Vuforia is an augmented reality software development kit (SDK) for mobile devices that enables the creation of augmented reality applications. It uses computer vision technology to recognize and track planar images and 3D objects in real time. This image registration capability enables developers to position and orient virtual objects, such as 3D models and other media, in relation to real world objects when they are viewed through the camera of a mobile device. The virtual object then tracks the position and orientation of the image in real-time so that the viewer's perspective on the object corresponds with the perspective on the target. It thus appears that the virtual object is a part of the real-world scene.

Sailfish OS is a paid Linux-based operating system based on free software, and open source projects such as Mer as well as including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.
Microsoft mobile services are a set of proprietary mobile services created specifically for mobile devices; they are typically offered through mobile applications and mobile browser for Windows Phone platforms, BREW, and Java. Microsoft's mobile services are typically connected with a Microsoft account and often come preinstalled on Microsoft's own mobile operating systems while they are offered via various means for other platforms. Microsoft started to develop for mobile computing platforms with the launch of Windows CE in 1996 and later added Microsoft's Pocket Office suite to their Handheld PC line of PDAs in April 2000. From December 2014 to June 2015, Microsoft made a number of corporate acquisitions, buying several of the top applications listed in Google Play and the App Store including Acompli, Sunrise Calendar, Datazen, Wunderlist, Echo Notification Lockscreen, and MileIQ.
This is a comparison of mobile operating systems. Only the latest versions are shown in the table below, even though older versions may still be marketed.
iOnRoad is a free augmented reality driving safety app owned by Harman. It received the International CES 2012 innovation award. The program uses the GPS feature, gyroscope and video camera stream of the native mobile device to monitor a vehicle’s position on the road, alerting drivers of lane departures and potential collisions with audio and visual cues. iOnRoad has been downloaded by over 500,000 people.
WebAR, previously known as the Augmented Web, is a web technology that allows for augmented reality functionality within a web browser. It is a combination of HTML, Web Audio, WebGL, and WebRTC. From 2020s more known as web-based Augmented Reality or WebAR, which is about the use of augmented reality elements in browsers.

A progressive web application (PWA), or progressive web app, is a type of web app that can be installed on a device as a standalone application. PWAs are installed using the offline cache of the device's web browser.







