Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) B27 is a class I surface antigen encoded by the B locus in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6 and presents antigenic peptides to T cells. HLA-B27 is strongly associated with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and other associated inflammatory diseases referred to as "spondyloarthropathies". Diseases associated with the HLA-B27 subtype can be remembered with the mnemonic PAIR, and include Psoriasis, Ankylosing spondylitis, Inflammatory bowel disease, and Reactive arthritis.
Blood proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors. Contrary to popular belief, haemoglobin is not a blood protein, as it is carried within red blood cells, rather than in the blood serum.

β2 microglobulin also known as B2M is a component of MHC class I molecules, MHC class I molecules have α1, α2, and α3 proteins which are present on all nucleated cells. In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein is encoded by the B2M gene.

Beta globulins are a group of globular proteins in plasma that are more mobile in alkaline or electrically charged solutions than gamma globulins, but less mobile than alpha globulins.
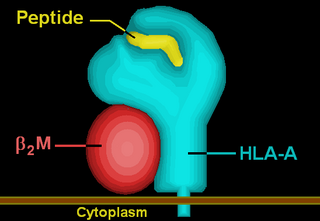
HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are coded for by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3. HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen specific to humans. HLA-A is one of three major types of human MHC class I cell surface receptors. The others are HLA-B and HLA-C. The receptor is a heterodimer, and is composed of a heavy α chain and smaller β chain. The α chain is encoded by a variant HLA-A gene, and the β chain (β2-microglobulin) is an invariant β2 microglobulin molecule. The β2 microglobulin protein is coded for by a separate region of the human genome.

HLA-A43 (A43) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α43 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A43, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*43 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*4301. A43 and A*43 are almost synonymous in meaning. A43 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A10. A43 is a sister serotype of A25, A26, A34, and A66.

HLA-A66 (A66) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α66 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A66, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*66 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. A66 and A*66 are almost synonymous in meaning. A66 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A10. A66 is a sister serotype of A25, A26, A34, and A43.

HLA-A74 (A74) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α74 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A74, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*74 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. A74 and A*74 are almost synonymous in meaning. A74 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A19. A74 is a sister serotype of A29, A30, A31, A32, and A33.

HLA-A31 (A31) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α31 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A31, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*31 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*3101. A31 and A*31 are almost synonymous in meaning. A31 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A19. A31 is a sister serotype of A29, A30, A32, A33, and A74.

HLA-A29 (A29) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α29 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A29, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*29 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*2902. A29 and A*29 are almost synonymous in meaning. A29 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A19. A29 is a sister serotype of A30, A31, A32, A33, and A74.
Allovectin-7 is a substance that is being studied as a gene therapy agent in the treatment of cancer, such as malignant melanoma. It is a plasmid/lipid complex containing the DNA sequences encoding HLA-B7 and ß2 microglobulin - two components of major histocompatibility complex. It increases the ability of the immune system to recognize cancer cells and kill them.

Protein AMBP is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AMBP gene.

Collagen alpha-1(XXVI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EMID2 gene.
Haemodialysis-associated amyloidosis is a form of systemic amyloidosis associated with chronic kidney failure.
Alpha-1-microglobulin is a microglobulin, a small globular protein. It is found in all vertebrates, including humans, and is distributed in blood plasma and extravascular tissues of all organs. It is synthesized in most cells of the body, but mainly in the liver from a gene that codes for the alpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor.
Placental alpha microglobulin-1 (PAMG-1) is a human protein that was first isolated in 1975 from amniotic fluid. PAMG-1 is an important biomarker for the detection of premature rupture of fetal membrane (PROM) The high concentration of PAMG-1 in amniotic fluid means it can be used to detect if this fluid is present in the cervico-vaginal discharge of pregnant women; the presence of PAMG-1 in the discharge suggests that amniotic fluid is present, and therefore suggests that PROM has occurred. PAMG-1 was originally referred to as specific alpha-1 globulin of placenta.
Beta-2-microglobulin regulator is a protein in humans that is encoded by the B2MR gene.
Cuprophane is a membrane made of cellulose, commonly used for hemodialysis. Cuprophane is a synthetic non-biocompatible membrane. It has been associated with hemodialysis-associated amyloidosis.