Related Research Articles

The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.

Lysine is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain lysyl, classifying it as a basic, charged, aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the S configuration.

Sprouting is the natural process by which seeds or spores germinate and put out shoots, and already established plants produce new leaves or buds, or other structures experience further growth.
The globulins are a family of globular proteins that have higher molecular weights than albumins and are insoluble in pure water but dissolve in dilute salt solutions. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune system. Globulins, albumins, and fibrinogen are the major blood proteins. The normal concentration of globulins in human blood is about 2.6-3.5 g/dL.

Soy milk, also known as soya milk or soymilk, is a plant-based drink produced by soaking and grinding soybeans, boiling the mixture, and filtering out remaining particulates. It is a stable emulsion of oil, water, and protein. Its original form is an intermediate product of the manufacture of tofu. Originating in China, it became a common beverage in Europe and North America in the latter half of the 20th century, especially as production techniques were developed to give it a taste and consistency more closely resembling that of dairy milk. Soy milk may be used as a substitute for dairy milk by individuals who are vegan or lactose intolerant.

A coffee bean is a seed from the Coffea plant and the source for coffee. It is the pit inside the red or purple fruit. This fruit is often referred to as a coffee cherry, and like the cherry, it is a fruit with a pit. Even though the coffee beans are not technically beans, they are referred to as such because of their resemblance to true beans. The fruits most commonly contain two stones with their flat sides together. A small percentage of cherries contain a single seed, called a "peaberry". Peaberries make up only around 10% to 15% of all coffee beans. It is a fairly common belief that they have more flavour than normal coffee beans. Like Brazil nuts and white rice, coffee beans consist mostly of endosperm.

Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) or sex steroid-binding globulin (SSBG) is a glycoprotein that binds to androgens and estrogens. When produced by the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis, it is called androgen-binding protein (ABP).
Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans and their ability to digest it.
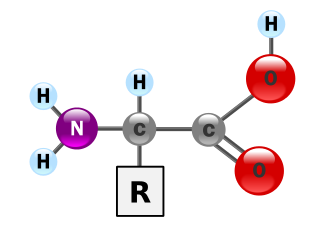
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the building blocks of body tissue and can also serve as a fuel source. As a fuel, proteins provide as much energy density as carbohydrates: 4 kcal per gram; in contrast, lipids provide 9 kcal per gram. The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition.

Soy protein is a protein that is isolated from soybean. It is made from soybean meal that has been dehulled and defatted. Dehulled and defatted soybeans are processed into three kinds of high protein commercial products: soy flour, concentrates, and isolates. Soy protein isolate has been used since 1959 in foods for its functional properties.

Tofu is a food prepared by coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: silken, soft, firm, extra firm. Tofu is also known as bean curd in English. It is a traditional component of East Asian and Southeast Asian cuisines that has also been consumed in China for over 2,000 years. In modern Western cooking, it is sometimes used as a meat substitute.
Legumin is family of globular proteins obtained from beans, peas, lentils, vetches, hemp and other leguminous seeds. Garden peas are a common nutritional source for humans that contains legumin.

The cupin superfamily is a diverse superfamily of proteins named after its conserved barrel domain. The superfamily includes a wide variety of enzymes as well as non-enzymatic seed storage proteins.

Pea protein is a food product and protein supplement derived and extracted from yellow and green split peas, Pisum sativum. It can be used as a dietary supplement to increase an individual's protein or other nutrient intake, or as a substitute for other food products. As a powder, it is used as an ingredient in food manufacturing, such as a thickener, foaming agent, or an emulsifier.
Canavalin is a plant protein found in the jack bean, sword bean, and related plants. It is the major storage protein found in these plants' seeds, and is one of four proteins readily isolated from the seeds; the others are concanavalin A, concanavalin B, and urease. Canavalin is a vicilin protein homologous to phaseolin.
Vicilin is a legumin-associated globulin protein. It is a storage protein found in legumes such as the pea or lentil that protects plants from fungi and microorganism. It is believed to be an allergen in pea and peanut allergy responses.
Protein quality is the digestibility and quantity of essential amino acids for providing the proteins in correct ratios for human consumption. There are various methods that rank the quality of different types of protein, some of which are outdated and no longer in use, or not considered as useful as they once were thought to be. The Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS), which was recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), became the industry standard in 1993. FAO has recently recommended the newer Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) to supersede PDCAAS.

Hemp protein is a plant-derived protein from the cannabis plant and is isolated from hemp seeds.
Soy formula is a substitute for human breast milk. It is a commercial product based on the proteins found in soybeans. Soy infant formula uses processed soybeans as its source of protein, and comes in powdered or liquid form. Usually lactose-free, soy infant formula contains a different sugar. Infants who are intolerant of cows' milk protein may also be intolerant of soy protein. It differs from human breast milk in a number of ways. Soy protein inhibits the absorption of iron. The soy-based formulas discussed by the World Health Organization reports that soy formula is fortified with iron to compensate for this effect. One naturally occurring plant-based compound found in soy-based infant formula is phytic acid. It is also a strong inhibitor of iron absorption, though it can be removed in processing. It is not known how many manufacturers of soy-based formula incorporate this practice. China and Vietnam have regulated soy-based infant formulas to include NaFeEDTA to fortify the formula and enhance the absorption of iron by the infant. When iron compounds are added to soy-based infant formula, the iron compound is encapsulated to prevent it from making the formula dark.
Cruciferin is one of the two most abundant seed storage proteins in mustard and rapeseed. They are classified as 11S globulins based on their sedimentation coefficient, and are salt soluble neutral glycoproteins. Their molecular weights range from 20 to 40 kDa. They comprise up to 50–70% of the total seed protein. Cruciferin is a comparatively larger seed storage protein than napin. It is composed of two polypeptide chains α and β. The α-chain has a mass of 30 kDa and the β-chain weighs in at 20 kDa. They are held together by a disulphide bond.
References
- 1 2 "Pulse Proteins" (PDF). Pulsecanada.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-03-05. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ↑ Michael C. Lawrence (1999). "Structural Relationships of 7S and 11S Globulins". Seed Proteins. pp. 517–541. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4431-5_22. ISBN 978-94-010-5904-6.
- ↑ Motoyasu Adachi; Jiro Kanamori; Taro Masuda; Kazuhiro Yagasaki; Keisuke Kitamura; Bunzo Mikami; Shigeru Utsumi (2003). "Crystal structure of soybean 11S globulin : Glycinin A3B4 homohexamer". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (12): 7395–7400. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.7395A. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0832158100 . PMC 165886 . PMID 12771376.