
Serum protein electrophoresis is a laboratory test that examines specific proteins in the blood called globulins. The most common indications for a serum protein electrophoresis test are to diagnose or monitor multiple myeloma, a monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS), or further investigate a discrepancy between a low albumin and a relatively high total protein. Unexplained bone pain, anemia, proteinuria, chronic kidney disease, and hypercalcemia are also signs of multiple myeloma, and indications for SPE. Blood must first be collected, usually into an airtight vial or syringe. Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique in which the blood serum is applied to either an acetate membrane soaked in a liquid buffer, or to a buffered agarose gel matrix, or into liquid in a capillary tube, and exposed to an electric current to separate the serum protein components into five major fractions by size and electrical charge: serum albumin, alpha-1 globulins, alpha-2 globulins, beta 1 and 2 globulins, and gamma globulins.

Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) is a globulin protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINA7 gene. TBG binds thyroid hormones in circulation. It is one of three transport proteins (along with transthyretin and serum albumin) responsible for carrying the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) in the bloodstream. Of these three proteins, TBG has the highest affinity for T4 and T3 but is present in the lowest concentration relative to transthyretin and albumin, which also bind T3 and T4 in circulation. Despite its low concentration, TBG carries the majority of T4 in the blood plasma. Due to the very low concentration of T4 and T3 in the blood, TBG is rarely more than 25% saturated with its ligand. Unlike transthyretin and albumin, TBG has a single binding site for T4/T3. TBG is synthesized primarily in the liver as a 54-kDa protein. In terms of genomics, TBG is a serpin; however, it has no inhibitory function like many other members of this class of proteins.
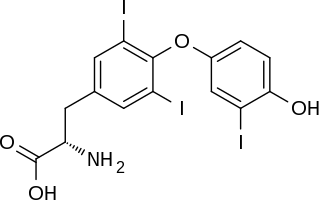
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
The globulins are a family of globular proteins that have higher molecular weights than albumins and are insoluble in pure water but dissolve in dilute salt solutions. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune system. Globulins, albumins, and fibrinogen are the major blood proteins. The normal concentration of globulins in human blood is about 2.6-3.5 g/dL.

Transcortin, also known as corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG) or serpin A6, is a protein produced in the liver in animals. In humans it is encoded by the SERPINA6 gene. It is an alpha-globulin.

Serpins are a superfamily of proteins with similar structures that were first identified for their protease inhibition activity and are found in all kingdoms of life. The acronym serpin was originally coined because the first serpins to be identified act on chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. They are notable for their unusual mechanism of action, in which they irreversibly inhibit their target protease by undergoing a large conformational change to disrupt the target's active site. This contrasts with the more common competitive mechanism for protease inhibitors that bind to and block access to the protease active site.
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors. Contrary to popular belief, haemoglobin is not a blood protein, as it is carried within red blood cells, rather than in the blood serum.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).

Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) or sex steroid-binding globulin (SSBG) is a glycoprotein that binds to androgens and estrogens. When produced by the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis, it is called androgen-binding protein (ABP).

Beta globulins are a group of globular proteins in plasma that are more mobile in alkaline or electrically charged solutions than gamma globulins, but less mobile than alpha globulins.
Orosomucoid (ORM) or alpha-1-acid glycoprotein is an acute phase protein found in plasma. It is an alpha-globulin glycoprotein and is modulated by two polymorphic genes. It is synthesized primarily in hepatocytes and has a normal plasma concentration between 0.6–1.2 mg/mL. Plasma levels are affected by pregnancy, burns, certain drugs, and certain diseases, particularly HIV.

Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-associated protein 1 also known as LRPAP1 or RAP is a chaperone protein which in humans is encoded by the LRPAP1 gene.

Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8 (LRP8), also known as apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP8 gene. ApoER2 is a cell surface receptor that is part of the low-density lipoprotein receptor family. These receptors function in signal transduction and endocytosis of specific ligands. Through interactions with one of its ligands, reelin, ApoER2 plays an important role in embryonic neuronal migration and postnatal long-term potentiation. Another LDL family receptor, VLDLR, also interacts with reelin, and together these two receptors influence brain development and function. Decreased expression of ApoER2 is associated with certain neurological diseases.
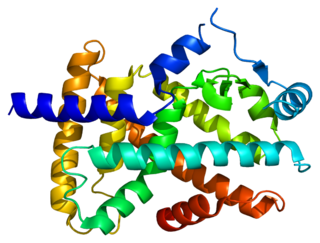
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), also known as NR1C1, is a nuclear receptor protein functioning as a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the PPARA gene. Together with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PPAR-alpha is part of the subfamily of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. It was the first member of the PPAR family to be cloned in 1990 by Stephen Green and has been identified as the nuclear receptor for a diverse class of rodent hepatocarcinogens that causes proliferation of peroxisomes.

Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), also known as alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor (A2MR), apolipoprotein E receptor (APOER) or cluster of differentiation 91 (CD91), is a protein forming a receptor found in the plasma membrane of cells involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis. In humans, the LRP1 protein is encoded by the LRP1 gene. LRP1 is also a key signalling protein and, thus, involved in various biological processes, such as lipoprotein metabolism and cell motility, and diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, atherosclerosis, and cancer.

Pregnancy zone protein (PZP), also known as the pregnancy-associated α2-glycoprotein, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PZP gene on chromosome 12. PZP is part of the alpha-2 globulin family of proteins. It is often associated with pregnancy, during which it can be the most abundant among the plasma proteins. PZP is believed to play a role in immune-regulation during pregnancy, however many aspects of its mechanism, function and structure are yet to be determined. Recent research has largely focused on determining how dysregulated PZP levels can act as a markers of various diseases.
The liver plays the major role in producing proteins that are secreted into the blood, including major plasma proteins, factors in hemostasis and fibrinolysis, carrier proteins, hormones, prohormones and apolipoprotein:

7α-Thiospironolactone is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogen of the spirolactone group and a minor active metabolite of spironolactone. Other important metabolites of spironolactone include 7α-thiomethylspironolactone, 6β-hydroxy-7α-thiomethylspironolactone (6β-OH-7α-TMS), and canrenone (SC-9376).

7α-Thioprogesterone is a synthetic, steroidal, and potent antimineralocorticoid (putative) and antiandrogen which was developed by G. D. Searle & Co and was described in the late 1970s and early 1980s but was never developed or introduced for medical use. It is a derivative of progesterone (pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione) with a thio (sulfur) substitution at the C7α position, and is related to the spirolactone group of drugs but lacks a γ-lactone ring.














