The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory fibers that create a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves, each containing about 100,000 fibres—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem.
Articles related to anatomy include:

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve that originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.

The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and left. The right and left nerves are not symmetrical, with the left nerve looping under the aortic arch, and the right nerve looping under the right subclavian artery then traveling upwards. They both travel alongside the trachea. Additionally, the nerves are among the few nerves that follow a recurrent course, moving in the opposite direction to the nerve they branch from, a fact from which they gain their name.

The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

The scalene muscles are a group of three muscles on each side of the neck, identified as the anterior, the middle, and the posterior. They are innervated by the third to the eighth cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8).

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of vagus nerve and additionally also receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.

The cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.

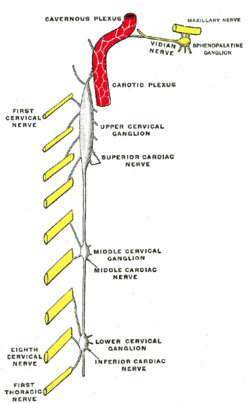
The middle cervical ganglion is the smallest of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It presumably represents the merging of the sympathetic ganglia of cervical segments C5–C6. It is usually situated at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.

The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.

The inferior cervical cardiac nerve arises from the stellate ganglion, or from the ansa subclavia of the cervical sympathetic trunk. It passes along the posterior aspect of the brachiocephalic trunk on the right side of the body, and of the internal carotid artery on the left side. It terminates by joining the deep cardiac plexus.

The superior cardiac nerve arises by two or more branches from the superior cervical ganglion, and occasionally receives a filament from the trunk between the first and second cervical ganglia. It runs down the neck behind the common carotid artery, and in front of the Longus colli muscle; and crosses in front of the inferior thyroid artery, and recurrent nerve. The course of the nerves on the two sides then differs.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The cardiac branches of the vagus nerve are two sets of nerves found in the upper torso, in close proximity to the larynx. The specific branches are the cervical cardiac branches of vagus nerve and the thoracic cardiac branches of vagus nerve.