
Guam is a U.S. territory in the western Pacific Ocean, at the boundary of the Philippine Sea. It is the southernmost and largest member of the Mariana Islands archipelago, which is itself the northernmost group of islands in Micronesia. The closest political entity is the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), another U.S. territory. Guam shares maritime boundaries with CNMI to the north and the Federated States of Micronesia to the south. It is located approximately one quarter of the way from the Philippines to Hawaii. Its location and size make it strategically important. It is the only island with both a protected harbor and land for multiple airports between Asia and Hawaii, on an east–west axis, and between Papua New Guinea and Japan, on a north–south axis.

Mount Mitchell is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and the highest peak in mainland North America east of the Mississippi River. It is located near Burnsville in Yancey County, North Carolina in the Black Mountain subrange of the Appalachians about 19 miles (31 km) northeast of Asheville. It is protected by Mount Mitchell State Park and surrounded by the Pisgah National Forest. Mount Mitchell's elevation is 6,684 feet (2,037 m) above sea level. Mount Mitchell is ranked 31st by topographic isolation.

Mount Whitney is the highest mountain in the contiguous United States, with an elevation of 14,505 feet (4,421 m). It is in East–Central California, in the Sierra Nevada, on the boundary between California's Inyo and Tulare counties, and 84.6 miles (136.2 km) west-northwest of North America's lowest topographic point, Badwater Basin in Death Valley National Park, at 282 ft (86 m) below sea level. The mountain's west slope is in Sequoia National Park and the summit is the southern terminus of the John Muir Trail, which runs 211.9 mi (341.0 km) from Happy Isles in Yosemite Valley. The eastern slopes are in Inyo National Forest in Inyo County. Mount Whitney is ranked 18th by topographic isolation.

Mount Elbert is the highest summit of the Rocky Mountains of North America. With an elevation of 14,440 feet (4401.2 m), it is also the highest point in the U.S. state of Colorado and the second-highest summit in the contiguous United States after Mount Whitney, which is slightly taller. The ultra-prominent fourteener is the highest peak in the Sawatch Range, as well as the highest point in the entire Mississippi River drainage basin. Mount Elbert is located in San Isabel National Forest, 12.1 miles (19.4 km) southwest of the city of Leadville in Lake County, Colorado.

Mount Massive is the second-highest summit of the Rocky Mountains of North America and the U.S. state of Colorado. The prominent 14,428-foot (4,398 m) fourteener of the Sawatch Range is located in the Mount Massive Wilderness of San Isabel National Forest, 10.6 miles (17.1 km) west-southwest of the City of Leadville in Lake County, Colorado, United States. Mount Massive edges out the third-highest summit of the Rockies, Mount Harvard, by 7 feet (2.1 m), but falls short of Mount Elbert by 12 feet (3.7 m). It ranks as the third-highest peak in the contiguous United States after Mount Whitney and Mount Elbert.

Mount Cleveland is the highest mountain in Glacier National Park, located in Montana, United States. It is also the highest point in the Lewis Range, which spans part of the northern portion of the park and extends into Canada. It is located approximately 3 mi (4.8 km) southeast of the southern end of Waterton Lake, and approximately 5 mi (8.0 km) south of the US–Canada border. The east side of the future national park was purchased by the federal government from the Blackfoot Confederacy in 1895 during the second term of President Grover Cleveland. According to the United States Board on Geographic Names, the mountain is named for the former president.

Humåtak is a village on the southwestern coast of the United States territory of Guam. The month of March in the Chamorro language is "Umatalaf," or "to catch guatafi," which is believed to be the root word of Umatac. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census, and it is by far the least populated village on the island.

Mount Augusta, also designated Boundary Peak 183, is a high peak in the state of Alaska.

Mount Williamson, at an elevation of 14,379 feet (4,383 m), is the second-highest mountain in both the Sierra Nevada range and the state of California, and the sixth-highest peak in the contiguous United States.

Mount Jefferson is the highest mountain in both the Toquima Range and Nye County in Nevada, United States. It is the sixth highest mountain in the state. As the high point of a range which is well separated from other ranges by low basins, Mount Jefferson has a high topographic prominence of 5,861 feet (1,786 m). This makes it the most prominent peak in Nye County and the third most prominent peak in Nevada. For similar reasons, it is also the highest mountain for over 90 miles in all directions. It is located about 50 miles (80 km) northeast of the county seat of Tonopah within the Alta Toquima Wilderness of the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest, near the smaller towns of Carvers and Round Mountain. Three distinct summits are located on a broad area of subalpine tundra: North Summit rises to 11,820 feet (3,603 m), Middle Summit to 11,692 feet (3,564 m), and South Summit to 11,949 feet (3,642 m). During the Pleistocene, alpine glaciers eroded several cirques east of the summit plateau.

Mount Süphan is a stratovolcano located in eastern Turkey, immediately north of Lake Van. It is the second highest volcano in Turkey, with an elevation of 4,058 metres, and has the third highest prominence of the Armenian Highlands, after Mount Ararat and Mount Aragats.

Thor Peak is in the northern Teton Range, Grand Teton National Park, in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Mount Moran is 1 mile (1.6 km) to the east. The summit is the eighth-highest in the Teton Range. Several semi-permanent snowfields as well as the Triple Glaciers are located on the east and northern slopes of the mountain. While the easiest route up the mountain, the south slope, is only rated a class 4, the mountain's remoteness and difficulty of approach make it a challenging mountain to summit.
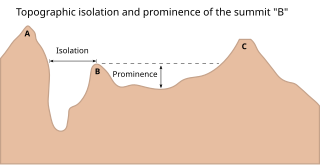
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major mountain peaks and can even be calculated for submarine summits. Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth, has an undefined isolation, since there are no higher points to reference.

Mount Lamlam is a peak on the United States island of Guam. It is located near the village of Agat, in the south-west of the island.

Mount Jumullong Manglo is a peak in the south-west of the island of the United States territory of Guam.

Typhoon Andy, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Iliang, was an intense tropical cyclone that made landfall in Taiwan. Andy formed along the northern edge of the monsoon trough south of Guam on July 22, 1982. It became a tropical storm the next day, although this system was initially poorly organized. Andy moved steadily west during the first few days of its life. After looping south of Guam, the cyclone moved northwest and strengthened. Andy turned westward near the 18th parallel on July 25. The system became a strong typhoon for a prolonged period on July 27 and July 28 while attaining a peak intensity of 185 km/h (115 mph). However, the typhoon struck Southern Taiwan on July 29. Continuing westward through the Formosa Strait, the storm made its final landfall in southern China on July 30 and dissipated inland two days later.
















