
Hagåtña, formerly Agana or Agaña, is a coastal village and the capital of the United States territory of Guam. From the 18th through mid-20th century, it was Guam's population center, but today, it is the second smallest of the island's 19 villages in both area and population. However, it remains one of the island's major commercial districts in addition to being the seat of government.

Tamuning, also known as Tamuning-Tumon-Harmon, is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The village of Tamuning is the economic center of Guam, containing tourist center Tumon, Harmon Industrial Park, and other commercial districts. Its central location along Marine Corps Drive, the island's main thoroughfare, has aided in its development.

Asan-Maina is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The municipality combines the names of the coastal community of Asan with Maina, a community along the slopes of the Fonte River valley to the east. Asan was the northern landing site for United States Marines during Guam's liberation from the Japanese during World War II. Asan Beach Park is part of the War in the Pacific National Historic Park. The third community comprising Asan-Maina is Nimitz Hill Annex in the hills above Asan and Maina, which is the location of the Joint Region Marianas headquarters. Asan-Maina is located in the Luchan (Western) District.
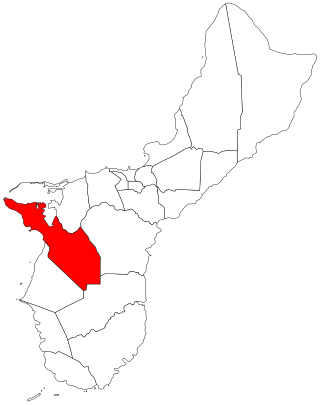
Sånta Rita-Sumai, formerly Santa Rita and encompassing the former municipality of Sumay, is a village located on the southwest coast of the United States territory of Guam with hills overlooking Apra Harbor. According to the 2020 census it has a population of 6,470, which is up slightly from 6,084 in 2010 but down from 11,857 in 1990. Santa Rita is the newest village in Guam, having been established after the Second World War.

Piti is a village located on the central west coast of the United States territory of Guam. It contains northern and eastern coastlines of Apra Harbor, including Cabras Island, which has the commercial Port of Guam and the island's largest power plants. Piti was a pre-Spanish CHamoru village and, after Spanish colonization, became the primary port town on Guam. The town was largely destroyed during the 1944 liberation of Guam and the population relocated during the wartime construction of Apra Harbor.

Yona is a village in the United States territory of Guam.

Agana Heights is one of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña, in the central part of the island. United States Naval Hospital Guam is located in this largely residential village.

Sinajana is the smallest of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam by area. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña. The village's name may have come from the word "china-jan," cookware used to cook wild yams that once grew in the area.

The Guam Department of Education (GDOE), formerly the Guam Public School System, is a school district that serves the United States territory of Guam. The school district can be thought of as analogous to the school districts of other cities and communities in the United States, but in some manners, it can also be thought of as analogous to the state education agencies of other states and territories.

Mongmong-Toto-Maite is a municipality in the United States territory of Guam composed of three separate villages east of Hagåtña that experienced development after the Second World War.

George Washington High School is a public secondary school located at 298 Washington Drive in Mangilao, in the United States territory of Guam.
The Guam Department of Corrections is an agency of the government of the United States territory of Guam that operates the island's correctional facilities.

Talo'fo'fo, formerly Talofofo, is a village located in the southern part of the United States territory of Guam, on the east coast. The village center is located in the hills above the coast, while the smaller coastal community below the cliff is known as Ipan.

Inalåhan is a village located on the southeastern coast of the United States territory of Guam. The village's original Chamoru name, Inalåhan, was altered when transliterated during Spanish control of the island.

Dededo is the most populated village in the United States territory of Guam. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Dededo's population was just under 45,000 in 2020. The village is located on the coral plateau of Northern Guam. The greater Dededo-Machanao-Apotgan Urban Cluster had a population of 139,825 as of the 2010 census, making up 87.7% of Guam's population and 29.8% of its area.

Yigo, Guam is the northernmost village of the United States territory of Guam, and is the location of Andersen Air Force Base. The municipality of Yigo is the largest village on the island in terms of area. It contains a number of populated places, including Asatdas and Agafo Gumas.

Chalan Pago-Ordot is a village in the United States territory of Guam, containing the communities of Chalan Pago and Ordot. It is located in the eastern-central part of the island and is part of the Kattan (Eastern) District. The village's population has increased slightly since the island's 2010 census.

Barrigada is a village in the United States territory of Guam. A largely residential municipality, its main village is located south of the Antonio B. Won Pat International Airport near the intersections of Routes 8, 10, and 16. The community east of the airport known as Barrigada Heights is considered an affluent neighborhood on the island, where homes have excellent views overlooking much of Guam including the island's airport and hotels along Tumon Bay. Another significant location is Mount Barrigada, nearly 200 meters above sea level. Its location in the center of the island means it houses most of the island's radio masts and towers; the position and height make it easier for radio signals to reach the entire island.

Malesso' is the southernmost village in the United States territory of Guam. Cocos Island is a part of the municipality. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census.




















