
Wireless broadband is a telecommunications technology that provides high-speed wireless Internet access or computer networking access over a wide area. The term encompasses both fixed and mobile broadband.

The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction over the areas of broadband access, fair competition, radio frequency use, media responsibility, public safety, and homeland security.

An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides myriad services related to accessing, using, managing, or participating in the Internet. ISPs can be organized in various forms, such as commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or otherwise privately owned.

The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) is a bureau of the United States Department of Commerce that serves as the president's principal adviser on telecommunications policies pertaining to the United States' economic and technological advancement and to regulation of the telecommunications industry.

Internet access is a facility or service that provides connectivity for a computer, a computer network, or other network device to the Internet, and for individuals or organizations to access or use applications such as email and the World Wide Web. Internet access is offered for sale by an international hierarchy of Internet service providers (ISPs) using various networking technologies. At the retail level, many organizations, including municipal entities, also provide cost-free access to the general public. Types of connections range from fixed-line cable to mobile and satellite.

A wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider with a network based on wireless networking. Technology may include commonplace Wi-Fi wireless mesh networking, or proprietary equipment designed to operate over open 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 4.9, 5, 24, and 60 GHz bands or licensed frequencies in the UHF band, LMDS, and other bands from 6 GHz to 80 GHz.
Municipal broadband is broadband Internet access offered by public entities. Services are often provided either fully or partially by local governments to residents within certain areas or jurisdictions. Common connection technologies include unlicensed wireless, licensed wireless, and fiber-optic cable. Many cities that previously deployed Wi-Fi based solutions, like Comcast and Charter Spectrum, are switching to municipal broadband. Municipal fiber-to-the-home networks are becoming more prominent because of increased demand for modern audio and video applications, which are increasing bandwidth requirements by 40% per year. The purpose of municipal broadband is to provide internet access to those who cannot afford internet from internet service providers and local governments are increasingly investing in said services for their communities.
The Universal Service Fund (USF) is a system of telecommunications subsidies and fees managed by the United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to promote universal access to telecommunications services in the United States. The FCC established the fund in 1997 in compliance with the Telecommunications Act of 1996. Originally designed to subsidize telephone service, since 2011 the fund has expanded its goals to supporting broadband universal service. The Universal Service Fund's budget ranges from $5–8 billion per year depending on the needs of the telecommunications providers. These needs include the cost to maintain the hardware needed for their services and the services themselves. In 2022 disbursements totaled $7.4 billion, split across the USF's four main programs: $2.1 billion for the E-rate program, $4.2 billion for the high-cost program, $0.6 billion for the Lifeline program, and $0.5 billion for the rural health care program.
Bandwidth allocation is the process of assigning radio frequencies to different applications. The radio spectrum is a finite resource, which means there is great need for an effective allocation process. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission or FCC has the responsibility of allocating discrete portions of the spectrum, or bands, to various industries. The FCC did this recently, when it shifted the location of television broadcasting on the spectrum in order to open up more space for mobile data. Different bands of spectrum are able to transmit more data than others, and some bands of the spectrum transmit a clearer signal than others. Bands that are particularly fast or that have long range are of critical importance for companies that intend to operate a business involving wireless communications.

The Internet in the United States grew out of the ARPANET, a network sponsored by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the U.S. Department of Defense during the 1960s. The Internet in the United States of America in turn provided the foundation for the worldwide Internet of today.
In telecommunications, white spaces refer to radio frequencies allocated to a broadcasting service but not used locally. National and international bodies assign frequencies for specific uses and, in most cases, license the rights to broadcast over these frequencies. This frequency allocation process creates a bandplan which for technical reasons assigns white space between used radio bands or channels to avoid interference. In this case, while the frequencies are unused, they have been specifically assigned for a purpose, such as a guard band. Most commonly however, these white spaces exist naturally between used channels, since assigning nearby transmissions to immediately adjacent channels will cause destructive interference to both.
Rural Internet describes the characteristics of Internet service in rural areas, which are settled places outside towns and cities. Inhabitants live in villages, hamlets, on farms and in other isolated houses. Mountains and other terrain can impede rural Internet access.

Julius Genachowski is an American lawyer and businessman. He became the Federal Communications Commission Chairman on June 29, 2009. On March 22, 2013, he announced he would be leaving the FCC in the coming weeks. On January 6, 2014, it was announced that Genachowski had joined The Carlyle Group. He transitioned from Partner and Managing Director to Senior Advisor in early 2024.

A national broadband plan is a national plan to deploy broadband Internet access. Broadband is a term normally considered to be synonymous with a high-speed connection to the internet. Suitability for certain applications, or technically a certain quality of service, is often assumed. For instance, low round trip delay would normally be assumed to be well under 150ms and suitable for Voice over IP, online gaming, financial trading especially arbitrage, virtual private networks and other latency-sensitive applications. This would rule out satellite Internet as inherently high-latency. In some applications, utility-grade reliability or security are often also assumed or defined as requirements. There is no single definition of broadband and official plans may refer to any or none of these criteria.
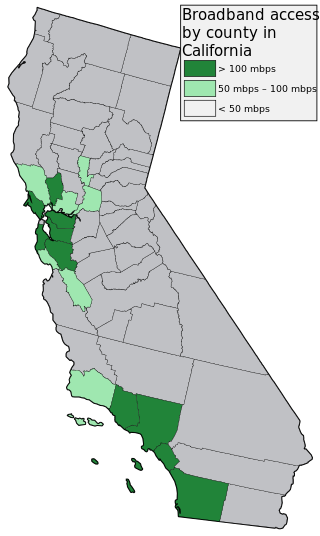
Broadband mapping in the United States are efforts to describe geographically how Internet access service from telephone and cable TV companies is available in terms of available speed and price. Mapping has been done on the national as well as the state level. The efforts are seen as preliminary steps towards broadband universal service.
Tiered service structures allow users to select from a small set of tiers at progressively increasing price points to receive the product or products best suited to their needs. Such systems are frequently seen in the telecommunications field, specifically when it comes to wireless service, digital and cable television options, and broadband internet access.
The Federal Communications Commission Open Internet Order of 2010 is a set of regulations that move towards the establishment of the internet neutrality concept. Some opponents of net neutrality believe such internet regulation would inhibit innovation by preventing providers from capitalizing on their broadband investments and reinvesting that money into higher quality services for consumers. Supporters of net neutrality argue that the presence of content restrictions by network providers represents a threat to individual expression and the rights of the First Amendment. Open Internet strikes a balance between these two camps by creating a compromised set of regulations that treats all internet traffic in "roughly the same way". In Verizon v. FCC, the Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit vacated portions of the order that the court determined could only be applied to common carriers.
Policies promoting wireless broadband are policies, rules, and regulations supporting the "National Wireless Initiative", a plan to bring wireless broadband Internet access to 98% of Americans.
Broadband universal service, also known as universal service obligation (USO) or universal broadband service, refers to government efforts to ensure all citizens have access to the internet. Universal voice service obligations have been expanded to include broadband service obligations in Switzerland, Finland, Spain and the UK.

The Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) was a United States government-sponsored program that provided internet access to low-income households. Several companies signed on to participate in the program, including Verizon Communications, Frontier Communications, T-Mobile, Spectrum, Cox, AT&T, Xfinity, Optimum and Comcast. The program was administered by the Federal Communications Commission. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $14.2 billion in funding for $30 subsidies for those with low incomes, and $75 subsidies on tribal lands. As of June 2024, the program has ended.










