
Ficus macrophylla, commonly known as the Moreton Bay fig or Australian banyan, is a large evergreen banyan tree of the Mulberry Family (Moraceae) native to eastern Australia, from the Wide Bay–Burnett region in the north to the Illawarra in New South Wales, as well as Lord Howe Island where the subspecies F. m. columnaris is a banyan form covering 2.5 acres or more of ground. Its common name is derived from Moreton Bay in Queensland, Australia. It is best known for its imposing buttress roots.

Lord Howe Island is an irregularly crescent-shaped volcanic remnant in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It lies 600 km (320 nmi) directly east of mainland Port Macquarie, 780 km (420 nmi) northeast of Sydney, and about 900 km (490 nmi) southwest of Norfolk Island. It is about 10 km (6.2 mi) long and between 0.3 and 2.0 km wide with an area of 14.55 km2, though just 3.98 km2 of that comprise the low-lying developed part of the island. The island is named after Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe.

Elaeocarpus is a genus of nearly five hundred species of flowering plants in the family Elaeocarpaceae native to the Western Indian Ocean, Tropical and Subtropical Asia, and the Pacific. Plants in the genus Elaeocarpus are trees or shrubs with simple leaves, flowers with four or five petals usually, and usually blue fruit.

Olearia, most commonly known as daisy-bush, is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae, the largest of the flowering plant families in the world. Olearia are found in Australia, New Guinea and New Zealand. The genus includes herbaceous plants, shrubs and small trees. The latter are unusual among the Asteraceae and are called tree daisies in New Zealand. All bear the familiar daisy-like composite flowerheads in white, pink, mauve or purple.

Dracophyllum is a genus of plants belonging to the family Ericaceae, formerly Epacridaceae. There are 61 species in the genus, mostly shrubs, but also cushion plants and trees, found in New Zealand, Australia, Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia. The name Dracophyllum, meaning dragon-leaf, refers to their strong outward similarity to the unrelated Dracaena, sometimes known as dragon tree. Although dicotyledonous, they resemble primitive monocots with their slender leaves concentrated in clumps at the ends of the branches; they are sometimes called grass-trees.

Myoporum insulare, commonly known as common boobialla, native juniper, is a species of flowering plant in the figwort family Scrophulariaceae and is endemic to coastal areas of Australia. It is a shrub or small tree which grows on dunes and coastal cliffs, is very salt tolerant and widely used in horticulture.

Zanthoxylum brachyacanthum, known as thorny yellow-wood, satinwood, satin tree or scrub mulga, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to north-eastern Australia. It is a rainforest shrub or tree with thick, cone-shaped spines on the trunk and prickles on the branches, pinnate leaves, and male and female flowers arranged in panicles.

Helicia glabriflora is a species of rainforest shrubs or small trees occurring in eastern Australia. Common names include smooth or pale helicia, pale, leather or brown oak. They grow naturally in a variety of different rainforest types from the Illawarra, New South Wales to the Townsville area, Queensland. Of all the global diversity of approximately one hundred Helicia species, this one species naturally grows the furthest south, in the Minnamurra Rainforest and the Robertson area, Illawarra, New South Wales, there observed more on the relatively fertile basalt and alluvial soils.

Drypetes deplanchei is a tree of eastern and northern Australia. It also occurs in New Caledonia and Lord Howe Island. The genus is derived from the Greek, dryppa meaning "olive fruit". The species named after Dr. Emile Deplanche, who collected this plant at New Caledonia. Common names include yellow tulip, grey boxwood, white myrtle, grey bark and yellow tulipwood.

Rhabdothamnus solandri is a small shrub of the family Gesneriaceae endemic to New Zealand. It is the only plant of the genus Rhabdothamnus, and the only member of Gesneriaceae native to New Zealand. Its common names are New Zealand gloxinia and, in the Māori language, taurepo, mātātā, and waiū-atua.

Syzygium fullagarii, commonly known as the scalybark, is a relatively large tree in the family Myrtaceae. It is found only on Lord Howe Island. It grows to 20 metres tall, up to an altitude of 400 metres above sea level in sheltered areas, often in rainforest. The bark is reddish brown, usually flaking to the touch. The base of the tree is often heavily buttressed. Known for many years as Cleistocalyx fullagarii, however, in recent times it has been placed in the large genus Syzygium.
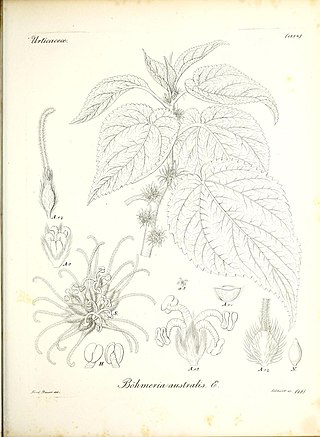
Pouzolzia australis, synonyms including Boehmeria australis and Boehmeria calophleba, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant family Urticaceae. It is endemic to small islands belonging to Australia and New Zealand – Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, and the Kermadec Islands. The population on Norfolk island, sometimes treated as a distinct subspecies, is critically endangered. In the Kermadec Islands, it was described in 2018 as "threatened – nationally endangered".

Metrosideros nervulosa, commonly known as the mountain rose, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae. It is endemic to Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It occurs in shrubland or low forest, mainly at altitudes of 300–875 m on the main peaks of the island. It prefers sunny positions on exposed ridges or in the forest canopy.
Leichhardtia tubulosa is a species of plant of unknown habit in the dogbane family, first described by Ferdinand von Mueller in 1875 as Marsdenia tubulosa. It is endemic to Australia's subtropical Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea. It is known only from a single collection, made in 1871 on the summit of Mount Gower, and is believed to be extinct.
Xylosma parvifolia, commonly known as mountain xylosma, is a plant in the family Salicaceae. It is endemic to the mountains of Australia's Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea.

Zygogynum howeanum, commonly known as hotbark or hot bark, is a species of plant in the family Winteraceae. It is endemic to Australia’s subtropical Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea. The specific epithet refers to the locality.

Olearia mooneyi, commonly known as pumpkin bush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae and is endemic to Lord Howe Island. It is a shrub or small tree with hairy, elliptic to egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and white and pale yellow, daisy-like inflorescences.

Corokia carpodetoides, simply known locally as corokia, is a flowering plant in the Argophyllaceae family. The specific epithet derives from a resemblance to the genus Carpodetus, with the addition of the Latin suffix -oides (“resembling”).
Planchonella reticulata is a flowering plant in the sapodilla family, Sapotaceae. It is a shrub or tree endemic to east-central New Caledonia. The specific epithet refers to the reticulate venation on the leaves.

The Gesnerioideae are a subfamily of plants in the family Gesneriaceae: based on the type genus Gesneria. Although genera typically originate in the New World, some species have become widely distributed as ornamental plants.

















