
The Decapoda or decapods are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 extant species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossils of the group date to the Devonian.

Xanthidae is a family of crabs known as gorilla crabs, mud crabs, pebble crabs or rubble crabs. Xanthid crabs are often brightly coloured and are highly poisonous, containing toxins which are not destroyed by cooking and for which no antidote is known. The toxins are similar to the tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin produced by puffer fish, and may be produced by bacteria in the genus Vibrio living in symbiosis with the crabs, mostly V. alginolyticus and V. parahaemolyticus.

Caridina is a genus of freshwater atyid shrimp. They are widely found in tropical or subtropical water in Asia, Oceania and Africa. They are filter-feeders and omnivorous scavengers. They range from 0.9 to 9.8 mm to 1.2–7.4 mm in carapace length.

Axiidea is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. They are colloquially known as mud shrimp, ghost shrimp, or burrowing shrimp; however, these decapods are only distantly related to true shrimp. Axiidea and Gebiidea are divergent infraoders of the former infraorder Thalassinidea. These infraorders have converged ecologically and morphologically as burrowing forms. Based on molecular evidence as of 2009, it is now widely believed that these two infraorders represent two distinct lineages separate from one another. Since this is a recent change, much of the literature and research surrounding these infraorders still refers to the Axiidea and Gebiidea in combination as "thalassinidean" for the sake of clarity and reference. This division based on molecular evidence is consistent with the groupings proposed by Robert Gurney in 1938 based on larval developmental stages.

Majidae is a family of crabs, comprising around 200 marine species inside 52 genera, with a carapace that is longer than it is broad, and which forms a point at the front. The legs can be very long in some species, leading to the name "spider crab". The exoskeleton is covered with bristles to which the crab attaches algae and other items to act as camouflage.

Macrophthalmus is a genus of crabs which are widespread across the Indo-Pacific. It contains the following species : Species in this genus are often referred to as sentinel crabs.

Upogebia is a genus of mud shrimp, in the family Upogebiidae, containing the following species:

Callianassidae is a family of ghost shrimp crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Axiidea, within the order Decapoda.
Callianassa is a genus of mud shrimps, in the family Callianassidae. Three of the species in this genus have been split off into a new genus, Pestarella, while others such as Callianassa filholi have been moved to Biffarius. The genus is named after the Nereid of the Greco-Roman mythology.

Pagurus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Paguridae. Like other hermit crabs, their abdomen is not calcified and they use snail shells as protection. These marine decapod crustaceans are omnivorous, but mostly prey on small animals and scavenge carrion. Trigonocheirus and Pagurixus used to be considered subgenera of Pagurus, but the former is nowadays included in Orthopagurus, while the latter has been separated as a distinct genus.

Gilvossius is a genus of thalassinidean crustacean erected in 1992 from former members of the genus Callianassa. It is distinguished from Callianassa by the rounded, rather than squarish telson, and by the absence of the first two pleopods in males. The genus contains the following species:

Thalassina is a genus of mud lobsters found in the mangrove swamps of the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean. Its nocturnal burrowing is important for the recycling of nutrients in the mangrove ecosystem, although it is sometimes considered a pest of fish and prawn farms.
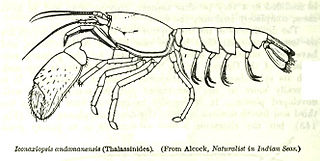
Eiconaxius is a genus of mud lobster that includes the following species:

Paguristes is a genus of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It includes the following species :

Galathea is a genus of squat lobsters in the family Galatheidae. It is one of the largest genera of squat lobsters that in 2008 contained 73 species. Most species of Galathea live in shallow waters.

Neotrypaea californiensis, the Bay ghost shrimp, is a species of ghost shrimp that lives on the Pacific coast of North America. It is a pale animal which grows to a length of 11.5 cm (4.5 in). One claw is bigger than the other, especially in males, and the enlarged claw is thought to have a function in mating. N. californiensis is a deposit feeder that lives in extensive burrow systems, and is responsible for high rates of bioturbation. It adversely affects oyster farms, and its numbers are controlled in some places by the application of pesticides. It carries out an important role in the ecosystem, and is used by fishermen as bait.

Metapenaeopsis, the velvet shrimps, is a prawn genus in the family Penaeidae. It contains these species:

Leucosiidae is a family of crabs containing three subfamilies and a number of genera incertae sedis:

Chaceon is a crab genus in the family Geryonidae, and was first described in 1989 by Raymond Manning and Lipke Holthuis.
Gourretiidae is a family of crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Axiidea, within the order Decapoda.
















