
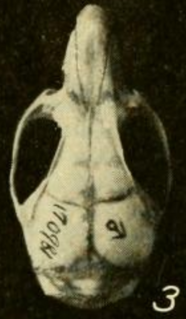
Oryzomys nelsoni is an extinct rodent of María Madre Island, Nayarit, Mexico. Within the genus Oryzomys of the family Cricetidae, it may have been most closely related to the mainland species O. albiventer. Since its first description in 1898, most authors have regarded it as a distinct species, but it has also been classified as a mere subspecies of the marsh rice rat (O. palustris).
Nephelomys albigularis, also known as the white-throated oryzomys or Tomes's rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Described in 1860, it was the first Nephelomys species to be discovered. It was originally described in the defunct genus Hesperomys as Hesperomys albigularis and considered related to the much smaller H. longicaudatus. By 1894, it was placed in Oryzomys, as Oryzomys albigularis, and associated with what is now Nephelomys meridensis. In the early 1960s, the scope of the species was considerably expanded to include most of the species that are now in Nephelomys, as well as a single name, boliviae, that is currently a synonym of Euryoryzomys nitidus. From 1976 on, several of these were reinstated as separate species.

Handleyomys alfaroi, also known as Alfaro's rice rat or Alfaro's oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the genus Handleyomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in Belize, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. It was previously included in Oryzomys as Oryzomys alfaroi. Its natural habitats are subtropical and tropical lowland or montane dry forests at elevations ranging from sea level to 2500 m.
Oreoryzomys balneator, also known as the Peruvian rice rat or Ecuadoran oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It is found in Ecuador and northern Peru in cloud forest at elevations from 1500 to 1800 m. It is the only species in the genus Oreoryzomys, which was included in Oryzomys until 2006. The genus name Oreoryzomys is a combination of ορος the Greek word for "mountain" with the old genus name Oryzomys and refers to the mountainous habitat of O. balneator. Recent research suggests that O. balneator is not closely related to Oryzomys, but instead is probably related to Microryzomys within a clade also including Neacomys and Oligoryzomys.

Nephelomys devius, also known as the Talamancan oryzomys, Boquete rice rat, Chiriqui rice rat, or montane rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in cloud forest in the highlands of Costa Rica and western Panama.

Oryzomys gorgasi, also known as Gorgas's oryzomys or Gorgas's rice rat, is a rodent in the genus Oryzomys of family Cricetidae. First recorded in 1967, it is known from only a few localities, including a freshwater swamp in the lowlands of northwestern Colombia and a mangrove islet in northwestern Venezuela. It reportedly formerly occurred on the island of Curaçao off northwestern Venezuela; this extinct population has been described as a separate species, Oryzomys curasoae, but does not differ morphologically from mainland populations.
Nephelomys keaysi, also known as Keays's oryzomys or Keays's rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found from southeastern Peru to northern Bolivia on the eastern slope of the Andes in Yungas humid forest at altitudes of 1000 to 2600 m. Although its continued existence is not in serious danger and it is listed as "least concern", destruction of its habitat may pose a threat to some populations.
Nephelomys levipes, also known as the nimble-footed oryzomys or light-footed rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found on the eastern slope of the Andes from southeastern Peru into west-central Bolivia in cloud forest at elevations from 1,800 to 3,200 metres. It occurs in the same general area as its congener N. keaysi, but at higher altitudes.
Transandinomys talamancae is a rodent in the family Cricetidae that occurs from Costa Rica to southwestern Ecuador and northern Venezuela. Its habitat consists of lowland forests up to 1,500 m (5,000 ft) above sea level. With a body mass of 38 to 74 g, it is a medium-sized rice rat. The fur is soft and is reddish to brownish on the upperparts and white to buff on the underparts. The tail is dark brown above and lighter below and the ears and feet are long. The vibrissae (whiskers) are very long. In the skull, the rostrum is long and the braincase is low. The number of chromosomes varies from 34 to 54.
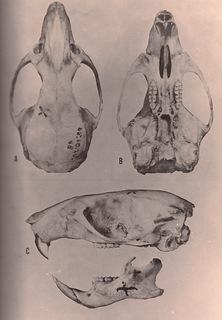
Oryzomys antillarum, also known as the Jamaican rice rat, is an extinct rodent of Jamaica. A member of the genus Oryzomys within the family Cricetidae, it is similar to O. couesi of mainland Central America, from where it may have dispersed to its island during the last glacial period. O. antillarum is common in subfossil cave faunas and is also known from three specimens collected live in the 19th century. Some historical records of Jamaican rats may pertain to it. The species probably became extinct late in the 19th century, perhaps due to the introduction of the small Asian mongoose, competition with introduced rodents such as the brown rat, and habitat destruction.
Nephelomys caracolus, also known as the Costa Central oryzomys or caracol rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in cloud forest in the Cordillera de la Costa Central of Aragua, Miranda, and the Distrito Federal in north-central Venezuela at elevations from 1000 to 2500 m. It is nocturnal and terrestrial, and has a varied diet. In most Nephelomys species, the posterolateral palatal pits, perforations of the palate near the third molar, are conspicuous and receded into a fossa, but in N. caracolus and the Ecuadorian species N. nimbosus, the pits are much smaller.
Nephelomys meridensis, also known as the Mérida oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in cloud forest in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida of western Venezuela at elevations from 1100 to 4000 m. It is solitary, nocturnal and terrestrial, and has a varied diet.

Transandinomys is a genus of rodents in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It includes two species—T. bolivaris and T. talamancae—found in forests from Honduras in Central America south and east to southwestern Ecuador and northwestern Venezuela in northern South America. Until 2006, its members were included in the genus Oryzomys, but phylogenetic analysis showed that they are not closely related to the type species of that genus, and they have therefore been placed in a new genus. They may be most closely related to genera like Hylaeamys and Euryoryzomys, which contain very similar species. Both species of Transandinomys have had eventful taxonomic histories.

Nephelomys is a genus of South American oryzomyine rodents found in the Andes from Bolivia to Venezuela, with a westward extension into the mountains of Costa Rica. Its generic name is derived from the Ancient Greek word nephelê "mist", referring to the cloud forest habitat of the members of the genus.
Nephelomys childi is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. The type locality is at Bogotá, Colombia, and the type locality of its junior synonym, oconnelli, is at a place known as Buenavista, about 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Bogotá. It was named after Mr. George D. Child, who assisted in obtaining the type series.
Nephelomys maculiventer is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. The type locality is in Colombia, at "Sierra El Libano, alt. 6000 ft, Santa Marta District". It was originally described on the basis of 47 specimens, including 34 from Sierra El Libano and 13 from "Valparaiso".
Nephelomys moerex is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. The type locality is at Mindo in western Ecuador, where it has been recorded together with three other rodents of the oryzomyine group, Sigmodontomys aphrastus, Mindomys hammondi, and Handleyomys alfaroi, as well as three opossums, Chironectes minimus and unidentified species of Didelphis and Marmosa. Mindo is a "tiny agricultural community" located at 0°02'S, 78°48'W and 1,264 metres (4,150 ft) above sea level. It was originally described by Oldfield Thomas as a subspecies of Oryzomys albigularis. It remained synonymized under this species until it was recognized as a separate species when the genus Nephelomys was established for Oryzomys albigularis and related species in 2006.
Nephelomys nimbosus is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Its type locality is at San Antonio on the northeastern slope of the Tungurahua in the Andes of Ecuador, at an altitude of about 6,700 feet (2,000 m). The type series included five individuals.

Nephelomys pirrensis, also known as the Mount Pirre rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Its type locality is at Mount Pirri or Pirre in eastern Panama, at an altitude of 4,500 feet (1,400 m), and it has also been recorded on Mount Tacarcuna.
Nephelomys pectoralis is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Its type locality is 40 miles (64 km) west of the city of Popayán, Cauca Department, Colombia, at an altitude of 10,340 feet (3,150 m). American zoologist Joel Asaph Allen first described it in 1912 on the basis of 112 specimens from several locations in the Cordillera Occidental. He classified it as a species of Oryzomys, Oryzomys pectoralis, but later subsumed into the species Oryzomys albigularis. When that species was transferred to the new genus Nephelomys in 2006, N. pectoralis was recognized as a separate species.








