
Euryoryzomys emmonsae, also known as Emmons' rice rat or Emmons' oryzomys, is a rodent from the Amazon rainforest of Brazil in the genus Euryoryzomys of the family Cricetidae. Initially misidentified as E. macconnelli or E. nitidus, it was formally described in 1998. A rainforest species, it may be scansorial, climbing but also spending time on the ground. It lives only in a limited area south of the Amazon River in the state of Pará, a distribution that is apparently unique among the muroid rodents of the region.
Hylaeamys laticeps, also known as the Atlantic Forest oryzomys or the large-headed rice rat, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae.
Cerradomys marinhus, also known as Marinho's rice rat, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Minas Gerais, Brazil. It was formerly known as Oryzomys marinhus, but was transferred to the new genus Cerradomys in 2006.
Cerradomys subflavus, also known as the terraced rice rat or flavescent oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America in the genus Cerradomys. It is found in the states of Goiás, São Paulo, and Minas Gerais, Brazil. Populations in Bolivia, Paraguay, and elsewhere in Brazil that were previously placed in this species are now classified as various other species of Cerradomys.
Hylaeamys yunganus, also known as the Amazonian oryzomys or Yungas rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Hylaeamys of family Cricetidae. It is found in lowland tropical rainforest throughout Amazonia, in northeastern Bolivia, eastern Peru, eastern Ecuador, southeastern Colombia, southern Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and northern Brazil. A closely related species, Hylaeamys tatei, occurs only in a small area in eastern Ecuador. Both were previously placed in Oryzomys.
Handleyomys fuscatus, also known as the dusky-footed Handley's mouse or dusky-footed montane mouse, is a species of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It was previously placed in the genus Aepeomys, but it is closely similar to Handleyomys intectus, and accordingly both species were placed in the new genus Handleyomys in 2002. It is found only in Colombia.
Nephelomys albigularis, also known as the white-throated oryzomys or Tomes's rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Described in 1860, it was the first Nephelomys species to be discovered. It was originally described in the defunct genus Hesperomys as Hesperomys albigularis and considered related to the much smaller H. longicaudatus. By 1894, it was placed in Oryzomys, as Oryzomys albigularis, and associated with what is now Nephelomys meridensis. In the early 1960s, the scope of the species was considerably expanded to include most of the species that are now in Nephelomys, as well as a single name, boliviae, that is currently a synonym of Euryoryzomys nitidus. From 1976 on, several of these were reinstated as separate species.
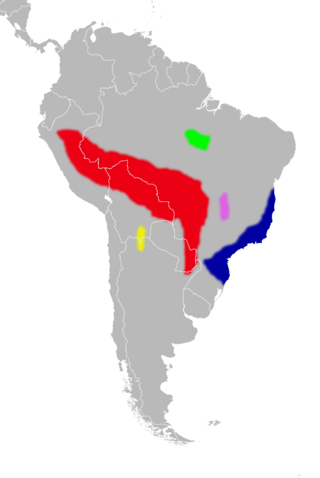
Euryoryzomys lamia, also known as the buffy-sided oryzomys or monster rice rat, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only in central Brazil, where it lives in forest enclaves within the cerrado. The species' known altitudinal range is from 700 to 900 m. The main threats to its survival are the destruction and fragmentation of its forest habitat.
Hylaeamys megacephalus, also known as Azara's broad-headed oryzomys or the large-headed rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Hylaeamys of family Cricetidae, of which it is the type species. It is found mainly in lowland tropical rainforest from its type locality in Paraguay north through central Brazil, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela onto Trinidad and Tobago. To its west and east, other closely related species of Hylaeamys are found: H. perenensis in western Amazonia, H. acritus in Bolivia, and H. laticeps and H. oniscus in the Atlantic Forest of eastern Brazil.

Oryzomyini is a tribe of rodents in the subfamily Sigmodontinae of the family Cricetidae. It includes about 120 species in about thirty genera, distributed from the eastern United States to the southernmost parts of South America, including many offshore islands. It is part of the clade Oryzomyalia, which includes most of the South American Sigmodontinae.

Aegialomys is a genus of oryzomyine rodents from the lowlands and mountains of western Peru and Ecuador, including the Galápagos Islands. The species in this genus have historically been placed in Oryzomys, but according to cladistic research, the genus is more closely related to a group containing, among others, Nectomys and Sigmodontomys, than to Oryzomys. The generic name Aegialomys means "coastal mouse" in Ancient Greek and references the mostly coastal occurrence of the genus.

Euryoryzomys macconnelli, also known as MacConnell's rice rat or MacConnell's oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela, where it lives in lowland tropical rainforest. It was formerly placed in the genus Oryzomys, as Oryzomys macconnelli, but in 2006 it was reclassified as the type species of the new genus Euryoryzomys.
Cerradomys maracajuensis, also known as the Maracaju oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America. It is terrestrial and is found in gallery forests in Bolivia, Paraguay and nearby Brazil and Peru. It was first discovered near the Brazilian city of Maracaju.
Cerradomys scotti, also known as Lindbergh's oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America in the genus Cerradomys. It is terrestrial and is found in the cerrado (savanna) ecozone of south central Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay. The species is common and appears to tolerate a degree of agricultural habitat modification.
Hylaeamys is a genus of South American oryzomyine rodents found principally in humid forested areas east of the Andes. The species in this genus have historically been placed in Oryzomys. They are most closely related to Euryoryzomys, Transandinomys, Nephelomys, Oecomys, and Handleyomys, and most closely resemble species of the former two genera. They are distinguished from members of Euryoryzomys by all-dark or indistinct two-tone tail coloration, from members of Transandinomys by having shorter whiskers above their eyes that do not extend posteriorly behind their ears, and in both cases by differences in carotid circulation. The genus is named after hylaea, the term used by Humboldt for the lowland South American rainforests that are the main habitat of the genus.

Euryoryzomys is a genus of rodents in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It includes seven species, which are distributed in South America. Until 2006, its members were included in the genus Oryzomys, but they are not closely related to the type species of that genus, and therefore they were placed in a new genus. They are most closely related to genera like Hylaeamys and Transandinomys; many members of these genera were previously placed in a single species, known as Oryzomys capito. The genus name, Euryoryzomys, combines the name "Oryzomys" with the Ancient Greek word eurus "broad", referring to the broad range in distribution of the genus.

Handleyomys is a genus of Central and South American rodents in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It was first described in 2002 to include two species from the Colombian Andes which were previously included in distinct and unrelated genera, Aepeomys and Oryzomys, but which turned out to be closely related. Later, in 2006, six other species were provisionally added from Oryzomys; these are expected to be placed in new genera in the future.

Nephelomys is a genus of South American oryzomyine rodents found in the Andes from Bolivia to Venezuela, with a westward extension into the mountains of Costa Rica. Its generic name is derived from the Ancient Greek word nephelê "mist", referring to the cloud forest habitat of the members of the genus.
Nephelomys moerex is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. The type locality is at Mindo in western Ecuador, where it has been recorded together with three other rodents of the oryzomyine group, Sigmodontomys aphrastus, Mindomys hammondi, and Handleyomys alfaroi, as well as three opossums, Chironectes minimus and unidentified species of Didelphis and Marmosa. Mindo is a "tiny agricultural community" located at 0°02'S, 78°48'W and 1,264 metres (4,150 ft) above sea level. It was originally described by Oldfield Thomas as a subspecies of Oryzomys albigularis. It remained synonymized under this species until it was recognized as a separate species when the genus Nephelomys was established for Oryzomys albigularis and related species in 2006.
In anatomy, posterolateral palatal pits are gaps at the sides of the back of the bony palate, near the last molars. Posterolateral palatal pits are present, in various degrees of development, in several members of the rodent family Cricetidae. Many members of the family lack them or have only simple pits, but Arvicolinae and Oryzomyini have more highly developed posterolateral palatal pits. Posterolateral palatal pits are also present in some other rodents, including Glis, Jaculus, Hystrix, Abrocoma, Ctenomys, Chinchilla, and Lagidium.







