
The rodent subfamily Sigmodontinae includes New World rats and mice, with at least 376 species. Many authorities include the Neotominae and Tylomyinae as part of a larger definition of Sigmodontinae. When those genera are included, the species count numbers at least 508. Their distribution includes much of the New World, but the genera are predominantly South American, such as brucies. They invaded South America from Central America as part of the Great American Interchange near the end of the Miocene, about 5 million years ago. Sigmodontines proceeded to diversify explosively in the formerly isolated continent. They inhabit many of the same ecological niches that the Murinae occupy in the Old World.

The New World rats and mice are a group of related rodents found in North and South America. They are extremely diverse in appearance and ecology, ranging from the tiny Baiomys to the large Kunsia. They represent one of the few examples of muroid rodents in North America, and the only example of muroid rodents to have made it into South America.
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the base of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa.

Melanomys caliginosus, also known as the dusky melanomys or dusky rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Melanomys of family Cricetidae. It is found from Central America, in Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama, into South America, where it occurs in Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. Populations currently classified under M. caliginosus may in fact include more than one species.

Melanomys is a genus of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae, which is distributed in northern South America and adjacent Central America. It contains three species, two of which—Melanomys robustulus and Melanomys zunigae—have limited distributions. The third, Melanomys caliginosus, is more widely distributed, but may be a species complex.
Melanomys robustulus, also known as the robust melanomys or robust dark rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Melanomys of family Cricetidae. It is found on the eastern slope of the Andes in Ecuador.
Melanomys zunigae, also known as Zuniga's melanomys or Zuniga's dark rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Melanomys of family Cricetidae. Known only from a small region of coastal Peru, it is listed as "critically endangered" by the IUCN and may even be extinct.

Mindomys hammondi, also known as Hammond's rice rat or Hammond's oryzomys, is an endangered species of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. Formerly considered to be related with Nectomys, Sigmodontomys, Megalomys, or Oryzomys, it is now placed in then genus Mindomys, but its relationships remain obscure; some evidence supports a placement near Oecomys or as a basal member of Oryzomyini.
Sigmodontomys alfari, also known as the short-tailed sigmodontomys, Alfaro's rice water rat, Cana rice rat, or Allen's rice rat, is a species of rodent in the subfamily Sigmodontinae of family Cricetidae. It is found from Honduras through Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama into South America, where it occurs from Venezuela through Colombia to Ecuador.
Sigmodontomys is a genus of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It is related to Nectomys and Melanomys and used to be included in Nectomys. It includes two species, Sigmodontomys alfari and the much rarer Sigmodontomys aphrastus, but whether these are indeed each other's closest relatives is uncertain.
Tanyuromys aphrastus, known as the long-tailed sigmodontomys, Harris's rice water rat, or the long-tailed rice rat, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is known from Costa Rica, Panama, and Ecuador. In 2012, it was reassigned to its current genus from Sigmodontomys.

Oryzomyini is a tribe of rodents in the subfamily Sigmodontinae of the family Cricetidae. It includes about 120 species in about thirty genera, distributed from the eastern United States to the southernmost parts of South America, including many offshore islands. It is part of the clade Oryzomyalia, which includes most of the South American Sigmodontinae.

Megalomys is a genus of rodent in the family Cricetidae, part of the tribe Oryzomyini. The genus contains five large rodents from various Caribbean islands, of which two are known to have survived into modern times, but all of which are now extinct. The last species to survive was M. desmarestii from Martinique, which became extinct after the Mount Pelée eruption in 1902. Ancient DNA analysis places Megalomys forming a clade with Pennatomys, sister to the clade containing Aegialomys, Nesoryzomys, Melanomys and Sigmodontomys, having diverged from the mainland clade around 7 million years ago.

Aegialomys is a genus of oryzomyine rodents from the lowlands and mountains of western Peru and Ecuador, including the Galápagos Islands. The species in this genus have historically been placed in Oryzomys, but according to cladistic research, the genus is more closely related to a group containing, among others, Nectomys and Sigmodontomys, than to Oryzomys. The generic name Aegialomys means "coastal mouse" in Ancient Greek and references the mostly coastal occurrence of the genus.

Cerradomys is a genus of oryzomyine rodents from eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, and central Brazil found in cerrado, Caatinga and Gran Chaco habitats.
In mammals, ungual tufts are tufts of hairs at the base of claws of the forefeet and hindfeet. Their presence has been used as a character in cladistic studies of the Cricetidae, a large family of rodents.

In rodents, incisor procumbency refers to the orientation of the upper incisor, defined by the position of the cutting edge of the incisor relative to the vertical plane of the incisors. Proodont incisors have the cutting edge in front of the vertical plane, orthodont teeth have it perpendicular to the plane, opisthodont incisors have it behind the plane, and hyper-opisthodont teeth have the cutting edge even behind the back of the alveolus of the incisor.
Hoplopleura oryzomydis is a sucking louse that is known from the southern United States, Nicaragua, Panama, and Venezuela. It is known from several oryzomyine rodents: the marsh rice rat, O. couesi, Handleyomys alfaroi, Transandinomys talamancae, Melanomys caliginosus, and Sigmodontomys alfari.
In some rodents, the subsquamosal fenestra is an opening between two parts of the squamosal bone, at the back of the skull. It can be seen in lateral view. Most Oryzomyini have the fenestra, but some species, including those in the genera Nectomys, Sigmodontomys, and Melanomys among others, lack it.
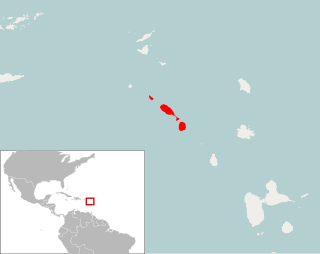
Pennatomys nivalis is an extinct oryzomyine rodent from the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saint Kitts, and Nevis in the Lesser Antilles. The only species in the genus Pennatomys, it is known from skeletal remains found in Amerindian archeological sites on all three islands, with dates ranging from 790–520 BCE to 900–1200 CE. No live specimens are known, but there are several historical records of rodents from Saint Kitts and Nevis that could conceivably refer to Pennatomys. The animal apparently belongs to a group within the tribe Oryzomyini that includes many other island-dwelling species.







