
The Eumuroida are a clade defined in 2004 by Steppan et al. that includes rats, mice and related species, though not all rodents; in other words, a specific group of muroid rodents. The clade is not defined in the standard taxonomic hierarchy, but it is between superfamily and family.

Pouched rats are a group of African rodents in the subfamily Cricetomyinae. They are members of the family Nesomyidae, which contains other African muroids such as climbing mice, Malagasy mice, and the white-tailed rat. All nesomyids are in the superfamily Muroidea, a large and complex clade containing 1⁄4 of all mammal species. Sometimes the pouched rats are placed in the family Muridae along with all other members of the superfamily Muroidea.

Dendromurinae is a subfamily of rodents in the family Nesomyidae and superfamily Muroidea. The dendromurines are currently restricted to Africa, as is the case for all extant members of the family Nesomyidae. The authorship of the subfamily has been attributed to both Alston, 1876, and (incorrectly) to G. M. Allen, 1939.

The Malagasy rodents are the sole members of the subfamily Nesomyinae. These animals are the only native rodents of Madagascar, come in many shapes and sizes, and occupy a wide variety of ecological niches. There are nesomyines that resemble gerbils, rats, mice, voles, and even rabbits. There are arboreal, terrestrial, and semi-fossorial varieties.

Delany's mouse or Delany's swamp mouse is a species of rodent in the family Nesomyidae. It is the only species in the genus Delanymys and the only extant member of subfamily Delanymyinae, which also contains the fossil genus Stenodontomys. It was previously placed in subfamily Petromyscinae, but it is apparently not closely related to Petromyscus. It is found in Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland and swamps. It is threatened by habitat loss.
The tiny fat mouse is a species of rodent in the family Nesomyidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Ethiopia, Kenya, Mozambique, Namibia, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland and subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland.
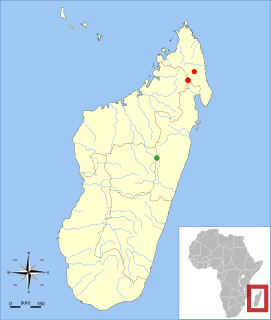
Voalavo is a genus of rodent in the subfamily Nesomyinae, found only in Madagascar. Two species are known, both of which occur in mountain forest above 1250 m (4100 ft) altitude; the northern voalavo lives in northern Madagascar and eastern voalavo is restricted to a small area in the central part of the island. The genus was discovered in 1994 and formally described in 1998. Within Nesomyinae, it is most closely related to the genus Eliurus, and DNA sequence data suggest that the current definitions of these two genera need to be changed.
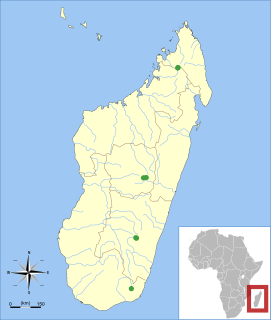
The Malagasy mountain mouse or Koopman's montane voalavo(Monticolomys koopmani) is a rodent within the subfamily Nesomyinae of the family Nesomyidae. It is monotypic within the genus Monticolomys, and is closely related to the big-footed mouse (Macrotarsomys). It is found in the highlands of eastern Madagascar. A small mouse-like rodent, it is dark brown on the upperparts and dark gray below. It has small, rounded, densely haired ears and broad feet with well-developed pads. The long tail lacks a tuft at the tip. The skull is delicate and lacks crests and ridges on its roof.







