| Nephelomys devius | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Cricetidae |
| Subfamily: | Sigmodontinae |
| Genus: | Nephelomys |
| Species: | N. devius |
| Binomial name | |
| Nephelomys devius (Bangs, 1902) | |
| Synonyms | |
Oryzomys devius Bangs, 1902 | |
Nephelomys devius, also known as the Talamancan oryzomys, [3] Boquete rice rat, [4] Chiriqui rice rat, [5] or montane rice rat, [6] is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. [7] It is found in cloud forest in the highlands of Costa Rica and western Panama. [1] [3]
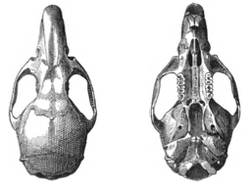
The upperparts are light brown and become lighter towards the sides. The underparts are buffy or dull white, with a whitish area at the throat. The ears are blackish, as is the nose, and the feet are yellow to brown. [5] The tail is dark brown above and somewhat lighter below. In juveniles, the fur of the upperparts is darker. In three specimens, the total length ranges from 335 to 360 millimetres (13.19 to 14.17 in), the combined length of the tail vertebrae from 180 to 195 millimetres (7.09 to 7.68 in), the hindfoot length from 33 to 36 millimetres (1.30 to 1.42 in), and the skull length from 35.8 to 37.5 millimetres (1.409 to 1.476 in). [8]
N. devius is the westernmost representative of its genus, with a related species, N. pirrensis , known from eastern Panama. In contrast to that species, the chest region is marked by a white patch, as in various other Nephelomys species. The skull is more rounded, the auditory bullae are larger, [9] and the fur is somewhat paler. [5] Unlike Transandinomys talamancae , possibly the closest relative of the genus Nephelomys, N. devius apparently lacks preputial glands. [10]
It was originally described, in 1902, as a species of Oryzomys, Oryzomys devius, and considered to be related to O. meridensis . [2] In 1966, it was subsumed into Oryzomys albigularis , as were all other species of this group, but subsequently it was reinstated as a species. [3] In 2006, members of the O. albigularis group were transferred into a new genus, Nephelomys; since then, the species has been known as Nephelomys devius. [7]
