
A moving violation or traffic violation is any violation of the law committed by the driver of a vehicle while it is in motion. The term "moving" distinguishes it from other motor vehicle violations, such as paperwork violations, parking violations, or equipment violations. The United States Department of State makes reference to moving violations in its enforcement guidance.

An ignition interlock device or breath alcohol ignition interlock device is a breathalyzer for an individual's vehicle. It requires the driver to blow into a mouthpiece on the device before starting or continuing to operate the vehicle. If the resultant breath-alcohol concentration analyzed result is greater than the programmed blood alcohol concentration, the device prevents the engine from being started. The interlock device is located inside the vehicle, near the driver’s seat, and is directly connected to the engine’s ignition system. It is a form of electronic monitoring.

A traffic ticket is a notice issued by a law enforcement official to a motorist or other road user, indicating that the user has violated traffic laws. Traffic tickets generally come in two forms, citing a moving violation, such as exceeding the speed limit, or a non-moving violation, such as a parking violation, with the ticket also being referred to as a parking citation, or parking ticket.
License suspension or revocation traditionally follows conviction for alcohol-impaired or drunk driving. However, under administrative license suspension (ALS) laws, sometimes called administrative license revocation or administrative per se, licenses are confiscated and automatically suspended independent of criminal proceedings whenever a driver either (1) refuses to submit to chemical testing, or (2) submits to testing with results indicating a blood alcohol content of 0.08% or higher.
The Driver License Compact is an agreement between states in the United States of America. The compact is used to exchange data between motorist's home state and a state where the motorist incurred a vehicular violation. Not all states are members, and states respond to the data differently.
In the United States, the Driver License Agreement (DLA) is an interstate compact written by the Joint Executive Board of the Driver License Compact (DLC) and the Non-Resident Violator Compact (NRVC) with staff support provided by the American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators (AAMVA). The DLA requires all states to honor licenses issued by other member states, report traffic convictions to the licensing state, prohibit a member state from confiscating an out-of-state driver's license or jailing an out-of-state driver for a minor violation; and maintain a complete driver's history, including withdrawals and traffic convictions including those committed in non-DLA states.
Under traffic violations reciprocity agreements, non-resident drivers are treated like residents when they are stopped for a traffic offense that occurs in another jurisdiction. They also ensure that punishments such as penalty points on one's license and the ensuing increase in insurance premiums follow the driver home. The general principle of such interstate, interprovincial, and/or international compacts is to guarantee the rule "one license, one record."
The American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators (AAMVA) is a non-governmental, voluntary, tax-exempt, nonprofit educational association. AAMVA is a private corporation which strives to develop model programs in motor vehicle administration, police traffic services, and highway safety.
Graduated driver licensing systems (GDLS) are designed to provide new drivers of motor vehicles with driving experience and skills gradually over time in low-risk environments. There are typically three steps or stages through which new drivers pass. They begin by acquiring a learner's permit, progress to a restricted, probationary or provisional license, followed by receipt of a full driver's license. Graduated drivers' licensing generally restricts nighttime, expressway, and unsupervised driving during initial stages, but lifts these restrictions with time and further testing of the individual, eventually concluding with the individual attaining a full driver's license.
The National Driver Register (NDR) is a computerized database of information about United States drivers who have had their driver's licenses revoked or suspended, or who have been convicted of serious traffic violations, such as driving under the influence or drugs or alcohol.. The records are added and maintained and deleted by the motor vehicle agency (MVA) of the state that convicted the driver or withdrew the driver's license.

School bus stop laws are laws dictating what a motorist must do in the vicinity of a bus stop being used by a school bus or other bus, coach or minibus providing school transport.
Many countries have adopted a penalty point or demerit point system under which a person’s driving license is revoked or suspended based on the number of points they’ve accumulated over a specific period of time, points are given for traffic offenses or infringements committed by them in that period. The demerit points schemes of each jurisdiction varies. These demerit schemes are usually in addition to fines or other penalties which may be imposed for a particular offence or infringement, or after a prescribed number of points have been accumulated.

A parking violation is the act of parking a motor vehicle in a restricted place or in an unauthorized manner. It is against the law virtually everywhere to park a vehicle in the middle of a highway or road; parking on one or both sides of a road, however, is commonly permitted. However, restrictions apply to such parking, and may result in an offense being committed. Such offenses are usually cited by a police officer or other government official in the form of a traffic ticket.
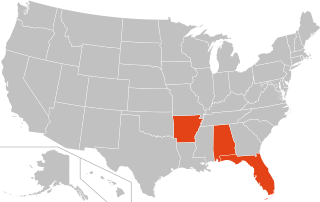
The Solomon–Lautenberg amendment is a U.S. federal law enacted in 1990 that urges states to suspend the driver's license of anyone who commits a drug offense. A number of states passed laws in the early 1990s seeking to comply with the amendment, in order to avoid a penalty of reduced federal highway funds. These laws imposed mandatory driver's license suspensions of at least six months for committing any type of drug offense, regardless of whether any motor vehicle was involved in the offense. As the amendment allows states to "opt out" without penalty, however, only three states continue to have such laws in effect as of 2021.

In the United States, driver licenses are issued by each individual state, territory, and the District of Columbia rather than by the federal government due to federalism. Drivers are normally required to obtain a license from their state of residence. All states of the United States and provinces and territories of Canada recognize each other's licenses for non-resident age requirements. There are also licenses for motorcycle use. Generally, a minimum age of 15 is required to apply for a non-commercial driver license, and 25 for commercial licenses which drivers must have to operate vehicles that are too heavy for a non-commercial licensed driver or vehicles with at least 16 passengers or containing hazardous materials that require placards. A state may also suspend an individual's driving privilege within its borders for traffic violations. Many states share a common system of license classes, with some exceptions, e.g. commercial license classes are standardized by federal regulation at 49 CFR 383. Many driving permits and ID cards display small digits next to each data field. This is required by the American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators' design standard and has been adopted by many US states. According to the United States Department of Transportation, as of 2018, there are approximately 227 million licensed drivers in the United States.
The Liquor Control Commission is an Illinois state government commission, with four divisions.

The Vermont Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) is the governmental agency responsible for registering and inspecting automobiles and other motor vehicles as well as licensing drivers in the U.S. state of Vermont.

Gun laws in Utah regulate the sale, possession, and use of firearms and ammunition in the state of Utah in the United States.

A driver's license or driving permit is a legal authorization, or the official document confirming such an authorization, for a specific individual to operate one or more types of motorized vehicles—such as motorcycles, cars, trucks, or buses—on a public road. Such licenses are often plastic and the size of a credit card.
The Interstate Wildlife Violator Compact (IWVC) is a United States interstate compact to provide reciprocal sharing of information regarding sportsman fishing, hunting, and trapping violations and allows for recognition of suspension or revocation of hunting, fishing, and trapping licenses and permits in other member states resulting from violations concerning hunting, fishing and trapping laws in order to prevent poaching across state lines. All 50 US states are members of the compact.









