
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel, and often a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

Source Mage is a Linux distribution. As a package is being installed, its source code is automatically downloaded, compiled, and installed. Source Mage is descended from Sorcerer.

A Beowulf cluster is a computer cluster of what are normally identical, commodity-grade computers networked into a small local area network with libraries and programs installed which allow processing to be shared among them. The result is a high-performance parallel computing cluster from inexpensive personal computer hardware.

Gentoo Linux is a Linux distribution built using the Portage package management system. Unlike a binary software distribution, the source code is compiled locally according to the user's preferences and is often optimized for the specific type of computer. Precompiled binaries are available for some packages.

KNOPPIX is an operating system based on Debian designed to be run directly from a CD / DVD or a USB flash drive, one of the first live operating system distributions. Knoppix was developed by, and named after, Linux consultant Klaus Knopper. When starting a program, it is loaded from the removable medium and decompressed into a RAM drive. The decompression is transparent and on-the-fly.

Damn Small Linux (DSL) is a discontinued computer operating system for the x86 family of personal computers. It is free and open-source software under the terms of the GNU GPL and other free and open source licenses. It was designed to run graphical user interface applications on older PC hardware, for example, machines with 486 and early Pentium microprocessors and very little random-access memory (RAM). DSL is a Live CD with a size of 50 megabytes (MB). What originally began as an experiment to see how much software could fit in 50 MB eventually became a full Linux distribution. It can be installed on storage media with small capacities, like bootable business cards, USB flash drives, various memory cards, and Zip drives.
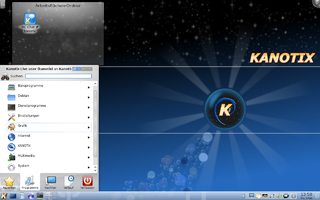
Kanotix, also referred to as KANOTIX, is an operating system based on Debian, with advanced hardware detection. It can run from an optical disc drive or other media i.e. USB-stick without using a hard disk drive.
MOSIX is a proprietary distributed operating system. Although early versions were based on older UNIX systems, since 1999 it focuses on Linux clusters and grids. In a MOSIX cluster/grid there is no need to modify or to link applications with any library, to copy files or login to remote nodes, or even to assign processes to different nodes – it is all done automatically, like in an SMP.
OpenSSI is an open-source single-system image clustering system. It allows a collection of computers to be treated as one large system, allowing applications running on any one machine access to the resources of all the machines in the cluster.
Free and Open source Software Developers' European Meeting (FOSDEM) is a non-commercial, volunteer-organized European event centered on free and open-source software development. It is aimed at developers and anyone interested in the free and open-source software movement. It aims to enable developers to meet and to promote the awareness and use of free and open-source software.
udev is a device manager for the Linux kernel. As the successor of devfsd and hotplug, udev primarily manages device nodes in the /dev directory. At the same time, udev also handles all user space events raised when hardware devices are added into the system or removed from it, including firmware loading as required by certain devices.

CHAOS is a small Linux distribution designed for creating ad hoc computer clusters.

Ututo is a Linux distribution consisting entirely of free software. The distribution is named for a variety of gecko found in northern Argentina.
aufs implements a union mount for Linux file systems. The name originally stood for AnotherUnionFS until version 2.

Calculate Linux is a Linux distribution optimized for fast deployment in an organization environment. It is based on the Gentoo Linux project and includes many preconfigured functions.

Linux-libre is a modified version of the Linux kernel that contains no binary blobs, obfuscated code, or code released under proprietary licenses. In the Linux kernel, they are mostly used for proprietary firmware images. While generally redistributable, binary blobs do not give the user the freedom to audit, modify, or, consequently, redistribute their modified versions. The GNU Project keeps Linux-libre in synchronization with the mainline Linux kernel.
Dracut is a set of tools that provide enhanced functionality for automating the Linux boot process. The tool named dracut is used to create a Linux boot image (initramfs) by copying tools and files from an installed system and combining it with the Dracut framework, which is usually found in /usr/lib/dracut/modules.d.












