
Sphyrna is a genus of hammerhead sharks with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. Members of Sphyrna have a tendency to inhabit coastal waters along the intertidal zone rather than the open ocean, as their prey such as invertebrates, fish, rays, small crustaceans, and other benthic organisms hide in the sands and sediment along these zones. Members of Sphyrna are also known by synonyms such as Zygaena, Cestracion, and Sphyrichthys. The earliest species described of this genus was Sphyrna zygaena by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, while the latest described member, Sphyrna gilberti, was discovered and described in 2013.

Serrasalmus is a genus of piranhas. They are collectively known as pirambebas; the "typical" piranhas like the piraya piranha are nowadays placed in Pygocentrus. Like all piranhas, Serrasalmus are native to South America.

Eleotridae is a family of fish commonly known as sleeper gobies, with about 34 genera and 180 species. Most species are found in the tropical Indo-Pacific region, but there are also species in subtropical and temperate regions, warmer parts of the Americas and near the Atlantic coast in Africa. While many eleotrids pass through a planktonic stage in the sea and some spend their entire lives in the sea; as adults, the majority live in freshwater streams and brackish water. One of its genera, Caecieleotris, is troglobitic. They are especially important as predators in the freshwater stream ecosystems on oceanic islands such as New Zealand and Hawaii that otherwise lack the predatory fish families typical of nearby continents, such as catfish. Anatomically, they are similar to the gobies (Gobiidae), though unlike the majority of gobies, they do not have a pelvic sucker.

Gobio is a genus of typical gudgeons, ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae many of which are endemics of south-eastern Europe. Members of the genus are usually small fish, rarely longer than 10 cm.
Awaous is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae, the gobies. They are native to fresh, marine and brackish waters from Africa to the Americas.

Bathygobius is a circumtropical genus of fish in the family Gobiidae.

Butis is a genus of fishes in the family Butidae found in fresh, brackish, and marine waters from the Indian Ocean coast of Africa through Southeast Asia to the Pacific islands and Australia.

Hypseleotris is a genus of fishes in the family Eleotridae. Most are from fresh water in Australia and New Guinea, but species in fresh and brackish water are found around islands in the western Indian Ocean, southern and eastern Africa, southern and eastern Asia, and Pacific islands. The largest species reaches a length of 12 cm (4.7 in). They are sometimes seen in the aquarium trade; especially H. compressa. In Australia they are known as carp gudgeons.

Amblygobius is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae found in the Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Prochilodus is a genus of freshwater fish from the family Prochilodontidae. This family include two other genera, Ichthyoelephas and Semaprochilodus, which have been included in Prochilodus instead. The greatest species richness of Prochilodus is in river basins in eastern, southeastern and southern Brazil, but there are also species in the river basins of the Amazon, Guianas, Colombia, Venezuela, Paraguay and northeastern Argentina. The largest species in the genus reach about 80 centimetres (2.6 ft) in length, but most species barely reach half that size.

Oplopomus is a genus of gobies found in coral reefs of the Indo-Pacific region. It contains two species.

Gobiomorphus is a genus of fishes in the family Eleotridae native to New Zealand and Australia. They are typically small, benthic fishes with large, rounded fins and two dorsal fins. Many have an amphidromous lifecycle: the eggs are laid in fresh water, but the fry are dispersed to sea soon after hatching, and grow there for several months before returning to fresh water.

Guavina is a genus of fishes in the family Eleotridae native to fresh, marine, and brackish waters of the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of the Americas.

Paranthias is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, groupers from the subfamily Epinephelinae, part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. They are found in the Atlantic Ocean and the eastern Pacific Ocean.
Parapocryptes is a genus of gobies native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Gymnocranius is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Lethrinidae, the emperors and emperor breams. These fishes are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Lethrinus is a genus of emperors found from the eastern Atlantic Ocean through the Indian Ocean to the western Pacific Ocean.

Megaleporinus is a genus of fish in the family Anostomidae native to South America.
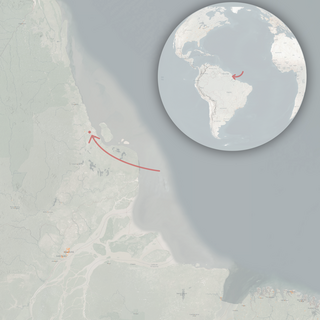
Arapaima mapae is a species of freshwater fish endemic to Brazil, where it is known only from Lago do Amapá in Amapá State.

















