Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:

In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to organic chemistry:
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.

Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.

Oxazolidine is a five-membered heterocycle ringwith the formula (CH2)3(NH)O.The O atom and NH groups are not mutually bonded, in contrast to isoxazolidine. Oxazolidines are derivatives of the parent oxazolidine owing to the presence of substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines.
Isoxazole is an electron-rich azole with an oxygen atom next to the nitrogen. It is also the class of compounds containing this ring. Isoxazolyl is the univalent functional group derived from isoxazole.

Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
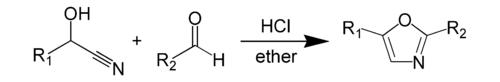
The Fischer oxazole synthesis is a chemical synthesis of an oxazole from a cyanohydrin and an aldehyde in the presence of anhydrous hydrochloric acid. This method was discovered by Emil Fischer in 1896. The cyanohydrin itself is derived from a separate aldehyde. The reactants of the oxazole synthesis itself, the cyanohydrin of an aldehyde and the other aldehyde itself, are usually present in equimolar amounts. Both reactants usually have an aromatic group, which appear at specific positions on the resulting heterocycle.
Azoles are a class of five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing a nitrogen atom and at least one other non-carbon atom as part of the ring. Their names originate from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature. The parent compounds are aromatic and have two double bonds; there are successively reduced analogs with fewer. One, and only one, lone pair of electrons from each heteroatom in the ring is part of the aromatic bonding in an azole. Names of azoles maintain the prefix upon reduction. The numbering of ring atoms in azoles starts with the heteroatom that is not part of a double bond, and then proceeds towards the other heteroatom.

Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine. Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

1-Methylimidazole or N-methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. It is a colourless liquid that is used as a specialty solvent, a base, and as a precursor to some ionic liquids. It is a fundamental nitrogen heterocycle and as such mimics for various nucleoside bases as well as histidine and histamine.

Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C3H5NO. It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines, which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond.
The Kharasch–Sosnovsky reaction is a method that involves using a copper or cobalt salt as a catalyst to oxidize olefins at the allylic position, subsequently condensing a peroxy ester or a peroxide resulting in the formation of allylic benzoates or alcohols via radical oxidation. This method is noteworthy for being the first allylic functionalization to utilize first-row transition metals and has found numerous applications in chemical and total synthesis. Chiral ligands can be used to render the reaction asymmetric, constructing chiral C–O bonds via C–H bond activation. This is notable as asymmetric addition to allylic groups tends to be difficult due to the transition state being highly symmetric. The reaction is named after Morris S. Kharasch and George Sosnovsky who first reported it in 1958. This method is noteworthy for being the first allylic functionalization to utilize first-row transition metals and has found numerous applications in chemical and total synthesis.

tert-Butyl peroxybenzoate (TBPB) an organic compound with the formula C6H5CO3CMe3 (Me = CH3). It is the most widely produced perester; it is an ester of peroxybenzoic acid (C6H5CO3H). It is often used as a radical initiator in polymerization reactions, such as the production of LDPE from ethylene, and for crosslinking, such as for unsaturated polyester resins.






![Where X = H, CH
3 for serine and threonine respectively, B = base.
(1) Enzymatic cyclization. (2) Elimination. (3) [O] = enzymatic oxidation. Biosynthesis of oxazole.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a1/Biosynthesis_of_oxazole.png/450px-Biosynthesis_of_oxazole.png)