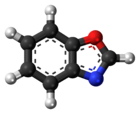
Aromatic compounds are organic compounds also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons". The parent member is benzene. Heteroarenes are closely related, since at least one carbon atom of CH group is replaced by one of the heteroatoms oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples of non-benzene compounds with aromatic properties are furan, a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring that includes a single oxygen atom, and pyridine, a heterocyclic compound with a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom.

A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles.

Optical brighteners, optical brightening agents (OBAs), fluorescent brightening agents (FBAs), or fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs), are chemical compounds that absorb light in the ultraviolet and violet region of the electromagnetic spectrum, and re-emit light in the blue region by fluorescence. These additives are often used to enhance the appearance of color of fabric and paper, causing a "whitening" effect; they make intrinsically yellow/orange materials look less so, by compensating the deficit in blue and purple light reflected by the material, with the blue and purple optical emission of the fluorophore.
Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound similar to pyridine. One of the three diazines, it has the nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine and pyridazine. In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.

Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.

An oxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbon atoms, a nitrogen atom and an oxygen atom. The O atom and NH group are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon atom between the O and N atoms. All of the carbon atoms in oxazolidines are reduced. Some of their derivatives, the oxazolidinediones, are used as anticonvulsants.

Isoquinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It is a structural isomer of quinoline. Isoquinoline and quinoline are benzopyridines, which are composed of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring. In a broader sense, the term isoquinoline is used to make reference to isoquinoline derivatives. 1-Benzylisoquinoline is the structural backbone in naturally occurring alkaloids including papaverine. The isoquinoline ring in these natural compound derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine.
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine. It is a "deliquescent crystal or wax-like solid with a pungent, sweet, corn-like, nutty odour".

Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a pKa of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole.
Simple aromatic rings, also known as simple arenes or simple aromatics, are aromatic organic compounds that consist only of a conjugated planar ring system. Many simple aromatic rings have trivial names. They are usually found as substructures of more complex molecules. Typical simple aromatic compounds are benzene, indole, and pyridine.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen; the term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
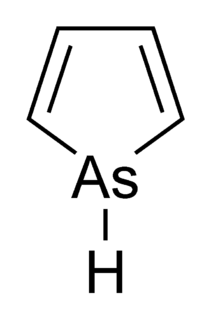
Arsole, also called arsenole or arsacyclopentadiene, is an organoarsenic compound with the formula C4H4AsH. It is classified as a metallole and is isoelectronic to and related to pyrrole except that an arsenic atom is substituted for the nitrogen atom. Whereas the pyrrole molecule is planar, the arsole molecule is not, and the hydrogen atom bonded to arsenic extends out of the molecular plane. Arsole is only moderately aromatic, with about 40% the aromaticity of pyrrole. Arsole itself has not been reported in pure form, but several substituted analogs called arsoles exist. Arsoles and more complex arsole derivatives have similar structure and chemical properties to those of phosphole derivatives. When arsole is fused to a benzene ring, this molecule is called arsindole, or benzarsole.

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.
Azoles are a class of five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing a nitrogen atom and at least one other non-carbon atom as part of the ring. Their names originate from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature. The parent compounds are aromatic and have two double bonds; there are successively reduced analogs with fewer. One, and only one, lone pair of electrons from each heteroatom in the ring is part of the aromatic bonding in an azole. Names of azoles maintain the prefix upon reduction. The numbering of ring atoms in azoles starts with the heteroatom that is not part of a double bond, and then proceeds towards the other heteroatom.
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.
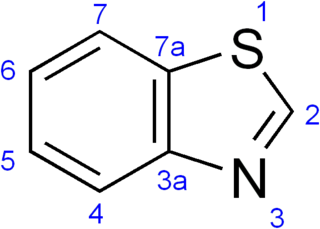
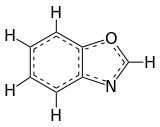
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
5NS. It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole.

Metalloles are derivatives of cyclopentadiene in which the carbon atom at position 5, the saturated carbon, is replaced by a heteroatom. In contrast to its parent compound, the numbering of the metallole starts at the heteroatom. Some of these compounds are described as organometallic compounds, but in the list below quite a number of metalloids are present too. Many metalloles are fluorescent. Polymeric derivatives of pyrrole and thiophene are of interest in molecular electronics. Metalloles, which can also be viewed as structural analogs of pyrrole, include:

Selenopyrylium is an aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and a positively charged selenium atom.